Related Research Articles

Boston Harbor Islands National and State Park is a combination national recreation area and state park situated among the islands of Boston Harbor. The park is made up of 34 islands and peninsulas and is managed by the Boston Harbor Islands Partnership. Twenty-one of the islands are also included in the Boston Harbor Islands Archeological District.

Boston Harbor is a natural harbor and estuary of Massachusetts Bay, located adjacent to Boston Massachusetts. It is home to the Port of Boston, a major shipping facility in the Northeastern United States.
The Graves is an aggregation of rock outcroppings in Massachusetts Bay, Massachusetts, United States. Situated some 11 miles (18 km) offshore of downtown Boston, it is the outermost island in the Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area.

Houghs Neck is a one-square-mile (2.6 km2) peninsula in Quincy, Massachusetts. It is surrounded by Quincy Bay, Hingham Bay and Rock Island Cove. It is lined by Perry Beach, which runs along Manet Avenue; Nut Island, which is just beyond Great Hill at the very end of the peninsula; and Edgewater Drive.

Lovells Island, or Lovell's Island, is a 62-acre (250,000 m2) island in the Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area, in Massachusetts. The island is across The Narrows from Georges Island and some 7 miles (11 km) offshore of downtown Boston. It is named after Captain William Lovell, who was an early settler of nearby Dorchester. The island is known as the site of several shipwrecks, including the 74-gun French warship Magnifique in 1782.

Little Brewster Island is a rocky outer island in the Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area. It is best known as the location of Boston Light, one of only five remaining Coast Guard-staffed lighthouses in the United States, and an important navigation aid for traffic to and from the Port of Boston. The island is situated some 9 miles (14 km) offshore of downtown Boston and has a permanent size of 3 acres (12,000 m2), plus an intertidal zone of a further 4 acres (16,000 m2).

Rainsford Island, formerly known Hospital Island, Pest House Island, and Quarantine Island, is a 11-acre (45,000 m2) island in the Boston Harbor, situated between Long Island and Peddocks Island. The island is composed of two drumlins, reaching an elevation of 49 feet (15 m) above sea level. The shoreline is predominantly rocky with a sandy cove in the south side, and a variety of wildflowers abound. Access is by private boat only. Since 1996 it has been part of the Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area.

Moon Island is an island in Quincy Bay, in the middle of Boston Harbor, Massachusetts. It is the location of the Boston Fire Department Training Academy, and Boston Police Department shooting range. All of the land on the island is owned by the City of Boston but the island is under the jurisdiction of Quincy, Massachusetts. It is also part of the Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area.

Bumpkin Island, also known as Round Island, Bomkin Island, Bumkin Island, or Ward's Island, is an island in the Hingham Bay area of the Boston Harbor. Bumpkin Island is part of Boston Harbor Islands National and State Park. The island has an area of 30 acres (120,000 m2), plus an intertidal zone of a further 31 acres (130,000 m2). It is composed of a central drumlin with an elevation of 70 feet (21 m) above sea level, surrounded by a rock-strewn shoreline. A sand spit, exposed at low tide, connects the eastern end of the island to Sunset Point in Hull.

Great Brewster Island is one of the outer islands in the Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area, situated some 9 miles (14 km) offshore of downtown Boston. The island has a permanent size of 18 acres (73,000 m2), plus an intertidal zone of a further 49 acres (200,000 m2). Unlike the other outer islands, which are low-lying outcroppings of bedrock, Great Brewster is a drumlin which reaches a height of over 100 feet (30 m) above sea level. It has vegetation cover consisting of Apple Trees, Pear Trees, Sumac, Beach Roses, Grasses and Common Reeds, together with a large Gull colony. The birds are aggressive during nesting season and access by humans, which is by private boat only, is discouraged during that time.
Middle Brewster Island is a rugged outer island in the Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area, located 9 miles (14 km) offshore from downtown Boston. The island has a permanent size of 13 acres (53,000 m2), reaches a height of 52 feet (16 m) above sea level, and is bounded by sharp cliffs and sunken crags. It has only sparse vegetation and serves primarily as a nesting site for gulls and cormorants. The birds are aggressive during their nesting season and access by humans is discouraged during this period. Access is difficult due to the lack of beaches and inlets, and is only accessible by private boat.

Deer Island is a peninsula in Boston, Massachusetts. Since 1996, it has been part of the Boston Harbor Islands National and State Park. Although still an island by name, Deer Island has been connected to the mainland since the former Shirley Gut channel, which once separated the island from the town of Winthrop, was filled in by the 1938 New England hurricane. Today, Deer Island is the location of the Deer Island Wastewater Treatment Plant, whose 150-foot-tall (46 m) egg-like sludge digesters are major harbor landmarks.

Long Wharf is a historic American pier in Boston, Massachusetts, built between 1710 and 1721. It once extended from State Street nearly a half-mile into Boston Harbor; today, the much-shortened wharf functions as a dock for passenger ferries and sightseeing boats.

Grape Island is an island in the Hingham Bay area of the Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area. The island is part of the territory of the town of Weymouth, Massachusetts. The island has a permanent size of 54 acres (220,000 m2), plus an intertidal zone of a further 46 acres (190,000 m2), and is composed of two drumlins, reaching an elevation of 70 feet (21 m) above sea level, and connected by a marshy lowland. Tidal sand spits extend from the west end towards Weymouth Neck in Webb Memorial State Park and from the east end towards Slate Island.

Langlee Island or Langley Island is an island in the Hingham Bay area of the Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area. The island has a permanent size of 4 acres (16,000 m2), plus an intertidal zone of a further 3 acres (12,000 m2), and is composed of a massing of Roxbury puddingstone which rises to a height of 40 feet (12 m) above sea level. This results in steep cliffs on the northern shore, while there are several small sandy beaches and a tidal mudflat on the east side. The center of the island contains glacial till that supports tree and shrub cover. As a result of previous planting, the island hosts large examples of oak, maple, juniper, and birch trees, while self-seeded huckleberry and viburnum mix with common greenbriar, dewberry, sumac, and poison ivy.

Raccoon Island is an island in the Hingham Bay area of the Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area, situated just offshore of Hough's Neck in the city of Quincy. The island has a permanent size of just under 4 acres (16,000 m2), and is composed of bedrock outcroppings which reach an elevation of 30 feet (9.1 m) above sea level. The island is characterized by gravel beaches and rocky slopes. While it is possible to walk to the island at low tide, public access is discouraged.

Germantown is a primarily residential neighborhood in the city of Quincy, Massachusetts. The neighborhood is located on a peninsula surrounded by Town River bay on the west and Rock Island Cove on the east. This peninsula was known since the 1640s as “Shed's Neck”.

Squantum is a neighborhood of Quincy, Massachusetts, connected to the mainland by a causeway that crosses over a wetland area of the bay. Often thought of as a peninsula, Squantum proper is technically a barrier island as it is surrounded on all four sides by water and is only connected to the mainland and Moon Island via causeways. Located in the northernmost portion of the city, Squantum is bordered on the north by Dorchester Bay and Boston Harbor, on the east by Moon Island and Quincy Bay, on the south by Quincy Bay and North Quincy, and on the west by the Marina Bay development. The population of the neighborhood in 2010 according to the United States Census Bureau was 2,365. Squantum has scenic, waterfront views of Boston Harbor and the Boston skyline and has many of Quincy’s most expensive homes. Squantum residents are the wealthiest of any neighborhood in Quincy, according to the 2010 United States Census Bureau, and the home ownership rate is approximately 92%. The neighborhood is further characterized by its tree-lined streets, its "island getaway" feel, close-knit community, and its annual Squantum Fourth of July Parade. As described in a 2020 book, "One road leads in and out of a square mile of land that is a playground for children and a haven for adults." Squantum also has one of the largest Irish populations, on a per capita basis, of any neighborhood in the United States.

Fort Andrews was created in 1897 as part of the Coast Defenses of Boston, Massachusetts. Construction began in 1898 and the fort was substantially complete by 1904. The fort was named after Major General George Leonard Andrews, an engineer and Civil War commander, who assisted in the construction of nearby Fort Warren in Boston Harbor. It occupies the entire northeast end of Peddocks Island in Boston Harbor, and was originally called the Peddocks Island Military Reservation. Once an active Coast Artillery post, it was manned by hundreds of soldiers and bristled with mortars and guns that controlled the southern approaches to Boston and Quincy Bay. The fort also served as a prisoner-of-war camp for Italian prisoners during World War II, who were employed as laborers following the Italian surrender to the Allies in 1943. Today, the fort is abandoned, and is managed by the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation, as part of the Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area.
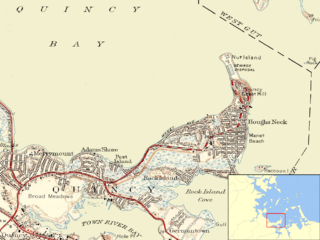
Nut Island is a former island in Boston Harbor, part of the Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area. The island has been connected through a short causeway to the end of Houghs Neck, becoming part of the mainland of Quincy, Massachusetts.
References
- ↑ "Hangman Island Factsheet". Boston Harbor Islands Partnership. Archived from the original on August 26, 2006. Retrieved August 30, 2006.
- ↑ "Hangman Island Google Map Closeup". Google Maps. Archived from the original on October 21, 2012. Retrieved July 26, 2007.
- ↑ Quincy Patriot 1861 July-Sept. Thomas Crane Public Library. John A. Green. 1861.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ↑ "Boston Harbor Islands Comprehensive Plan" (PDF). NPS History Electronic Library. Retrieved January 21, 2022.
42°17′24.25″N70°58′14.28″W / 42.2900694°N 70.9706333°W