
The territory of Chile has been populated since at least 3000 BC. By the 16th century, Spanish invaders began to raid the region of present-day Chile, and the territory was a colony from 1540 to 1818, when it gained independence from Spain. The country's economic development was successively marked by the export of first agricultural produce, then saltpeter and later copper. The wealth of raw materials led to an economic upturn, but also led to dependency, and even wars with neighboring states. Chile was governed during most of its first 150 years of independence by different forms of restricted government, where the electorate was carefully vetted and controlled by an elite.

The history of Peru spans 15 millennia, extending back through several stages of cultural development along the country's desert coastline and in the Andes mountains. Peru's coast was home to the Norte Chico civilization, the oldest civilization in the Americas and one of the six cradles of civilization in the world. When the Spanish arrived in the sixteenth century, Peru was the homeland of the highland Inca Empire, the largest and most advanced state in pre-Columbian America. After the conquest of the Incas, the Spanish Empire established a Viceroyalty with jurisdiction over most of its South American domains. Peru declared independence from Spain in 1821, but achieved independence only after the Battle of Ayacucho three years later.

Pedro Gutiérrez de Valdivia or Valdiva was a Spanish conquistador and the first royal governor of Chile. After serving with the Spanish army in Italy and Flanders, he was sent to South America in 1534, where he served as lieutenant under Francisco Pizarro in Peru, acting as his second in command.

Ceviche, cebiche, sebiche, or seviche is a dish consisting of fish or shellfish marinated in citrus and seasonings, and is recognized by UNESCO as an expression of Peruvian traditional cuisine and Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity. Different versions of ceviche are part of the culinary culture of various Spanish-American countries along the Pacific Ocean where each one is native: Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama and Peru. In Peru it is also considered a flagship dish and cultural heritage.

Jorge Mario Pedro Vargas Llosa, 1st Marquess of Vargas Llosa, more commonly known as Mario Vargas Llosa, is a Peruvian novelist, journalist, essayist and former politician. Vargas Llosa is one of Latin America's most significant novelists and essayists and one of the leading writers of his generation. Some critics consider him to have had a larger international impact and worldwide audience than any other writer of the Latin American Boom. In 2010, he won the Nobel Prize in Literature, "for his cartography of structures of power and his trenchant images of the individual's resistance, revolt, and defeat." He also won the 1967 Rómulo Gallegos Prize, the 1986 Prince of Asturias Award, the 1994 Miguel de Cervantes Prize, the 1995 Jerusalem Prize, the 2012 Carlos Fuentes International Prize, and the 2018 Pablo Neruda Order of Artistic and Cultural Merit. In 2021, he was elected to the Académie française.
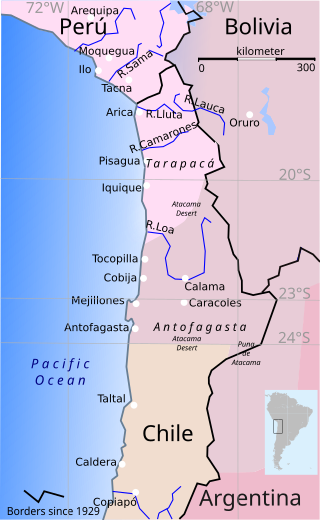
The War of the Pacific, also known by multiple other names, was a war between Chile and a Bolivian–Peruvian alliance from 1879 to 1884. Fought over Chilean claims on coastal Bolivian territory in the Atacama Desert, the war ended with victory for Chile, which gained a significant amount of resource-rich territory from Peru and Bolivia.

Manuel González de Candamo e Iriarte served as the 33rd President of Peru from 1903 until his death in 1904. He also served as Interim President of Peru, officially as the President of the Government Junta, from September 8, 1903, until his death the following year.

José María Arguedas Altamirano was a Peruvian novelist, poet, and anthropologist. Arguedas was an author of mestizo descent who was fluent in the Quechua language. That fluency was gained by Arguedas’s living in two Quechua households from the age of 7 to 11. First, he lived in the Indigenous servant quarters of his stepmother's home, then, escaping her "perverse and cruel" son, with an Indigenous family approved by his father. Arguedas wrote novels, short stories, and poems in both Spanish and Quechua.

A pisco sour is an alcoholic cocktail of Peruvian origin that is traditional to both Peruvian and Chilean cuisine. The drink's name comes from pisco, a brandy which is its base liquor, and the cocktail term sour, implying sour citrus juice and sweetener components. The Peruvian pisco sour uses Peruvian pisco and adds freshly squeezed lime juice, simple syrup, ice, egg white, and Angostura bitters. The Chilean version is similar, but uses Chilean pisco and Pica lime, and excludes the bitters and egg white. Other variants of the cocktail include those created with fruits like pineapple or plants such as coca leaves.

Francisco de Villagra Velázquez was a Spanish conquistador, and three times governor of Chile.

Rodrigo de Quiroga López de Ulloa was a Spanish conquistador of Galician origin. He was twice the Royal Governor of Chile.

Hilarión Daza was a Bolivian military officer who served as the 19th president of Bolivia from 1876 to 1879. During his presidency, the infamous War of the Pacific started, a conflict which proved to be devastating for Bolivia.

The Crossing of the Andes was one of the most important feats in the Argentine and Chilean wars of independence. A combined army of Argentine soldiers and Chilean exiles crossed the Andes mountains, which separate Argentina from Chile, to invade Chile, leading to its liberation from Spanish rule.

Jorge Alfredo Basadre Grohmann was a Peruvian historian known for his extensive publications about the independent history of his country. He served during two different administrations as Minister of Education and was also director of the Peruvian National Library.

Francisco de Aguirre was a Spanish conquistador who participated in the conquest of Peru, Bolivia, Chile and Argentina.

The Conquest of Chile is a period in Chilean historiography that starts with the arrival of Pedro de Valdivia to Chile in 1541 and ends with the death of Martín García Óñez de Loyola in the Battle of Curalaba in 1598, and the subsequent destruction of the Seven Cities in 1598–1604 in the Araucanía region.

Alfonso Ugarte de Chiclín is a Peruvian football club, playing in the city of Trujillo, Peru. The club is the biggest of Trujillo city, and one of the biggest in La Libertad Province.

Germán Alejandro Garmendia Aranis is a Chilean YouTuber, singer-songwriter, comedian and writer. He became famous for his YouTube channel HolaSoyGerman, which uploaded humorous videos about everyday situations. In 2013, he created his gameplay channel, JuegaGerman which, over time, would surpass his previous channel in subscribers. It also is the second-most subscribed channel in the Spanish language, behind Argentine channel El Reino Infantil. He is the most-subscribed YouTuber in Chile.

Serapio Reyes Ortiz was a Bolivian lawyer, professor, and politician who served as acting President of Bolivia in 1879, after the death of Pedro José de Guerra and the continued absence of Hilarión Daza, and as the ninth Vice president of Bolivia from 1888 to 1892. A member of the Conservative Party, he served as second vice president alongside first vice president José Manuel del Carpio during the administration of Aniceto Arce.

Joaquín Marcó Figueroa was a Chilean author, civil engineer and public servant. He was superintendent of the Casa de Moneda de Chile mint from 1930 to his death in 1956. In 1946, he published a book, Chile Marca un Camino, with the intention to highlight the political and social evolution of Chile.



















