
Hydrodynastes gigas is a New World species of large, rear-fanged, Dipsadin snake endemic to South America. It is commonly and alternatively known as the false water cobra and the Brazilian smooth snake. The false water cobra is so named because when the snake is threatened it "hoods" as a true cobra does. Unlike a true cobra, though, it does not rear up, but remains in a horizontal position. No subspecies are currently recognized as being valid.

Pseudoboa neuwiedii, commonly known as the dark-headed red false boa or Neuwied's false boa, is a species of snake in the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to northern South America.

The brown-banded water snake is a species of aquatic snake found in tropical South America and Trinidad and Tobago. It is also known as the water mapepire.

Bothrops alternatus is a highly venomous pit viper species found in South America. Within its range, it is an important cause of snakebite. The specific name, alternatus, which is Latin for "alternating", is apparently a reference to the staggered markings along the body. No subspecies are currently recognized.
The striped crayfish snake is a species of semiaquatic North American snake in the family Colubridae. The species derives its common name from its principal prey, crayfish. This snake is also called Allen's snake, the striped swamp snake, the striped swampsnake, or simply the swamp snake. It is endemic to peninsular Florida. Although rarely seen due to its secretive behavior, it can be found in large numbers in wet areas, with densities approaching 1,300 snakes per hectare.
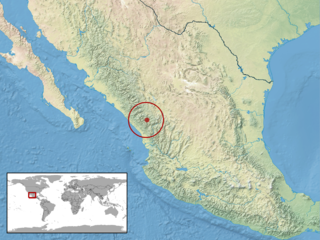
Fox's mountain meadow snake, also known commonly as culebra-de vega de Fox and pradera de Fox in Mexican Spanish, is a species of ovoviviparous snake in the family Colubridae. The species, which was described by Douglas A. Rossman and Richard M. Blaney in 1968, is native to northwestern Mexico.

Bothrops neuwiedi is a highly venomous pit viper species endemic to South America. This relatively small snake has a wide range and is a major source of snakebite in Argentina. It was named after German naturalist Prince Maximilian of Wied-Neuwied (1782-1867), who made important collections in Brazil (1815-1817). Seven subspecies are currently recognized, including the nominate subspecies described here.

Thamnophis proximus, commonly known as the western ribbon snake or western ribbonsnake, is a species of garter snake in the subfamily Natricinae of the family Colubridae. The species is found in the central and southern United States, Mexico, and Central America south to central Costa Rica. The species has six recognized subspecies.

Dipsadinae is a large subfamily of colubroid snakes, sometimes referred to as a family (Dipsadidae). Species of the subfamily Dipsadinae are found in most of the Americas, including the West Indies, and are most diverse in South America. There are more than 700 member species.

Helicops is a genus of snakes of the family Colubridae. The genus is endemic to South America.

Helicops infrataeniatus is a species of snake in the family Colubridae. It is endemic to South America, and can be found in Uruguay, Argentina, Paraguay, and southern Brazil.

Helicops leopardinus, the leopard keelback, is a species of snake in the family Colubridae. It is endemic to South America, and can be found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, and Suriname.

Helicops carinicaudus is a species of snake in the family Colubridae. It is endemic to eastern Brazil. Specimens from Colombia are likely mislabeled, probably representing Helicops danieli.

Clelia clelia, commonly known as the mussurana, black mussurana or windward cribo, is a species of snake in the subfamily Dipsadinae of the family Colubridae. The species is native to the New World.
Ihering's snake is a species of snake in the subfamily Dipsadinae of the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to Brazil. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Lioheterophis.

Phimophis guerini, also known commonly as the Argentine pampas snake, is a species of snake in the subfamily Dipsadinae of the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to South America.
Atractus guentheri, also known commonly as Günther's ground snake and coral-falsa in Brazilian Portuguese, is a species of snake in the subfamily Dipsadinae of the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to Brazil.
Helicops apiaka is a species of snake in the family Colubridae. It is endemic to Brazil, in the state of Mato Grosso.
Helicops gomesi, also known commonly as the São Paulo keelback and cobra d'água in Brazilian Portuguese, is a species of snake in the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to Brazil.
Helicops trivittatus, the equatorial keelback, is a species of snake in the family Colubridae. It is found in Brazil.














