
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dog teeth, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or vampire fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. In the context of the upper jaw, they are also known as fangs. They can appear more flattened however, causing them to resemble incisors and leading them to be called incisiform. They developed and are used primarily for firmly holding food in order to tear it apart, and occasionally as weapons. They are often the largest teeth in a mammal's mouth. Individuals of most species that develop them normally have four, two in the upper jaw and two in the lower, separated within each jaw by incisors; humans and dogs are examples. In most species, canines are the anterior-most teeth in the maxillary bone. The four canines in humans are the two upper maxillary canines and the two lower mandibular canines. They are specially prominent in dogs (Canidae), hence the name.

Lesothosaurus is a monospecific genus of ornithischian dinosaur that lived during the Early Jurassic in what is now South Africa and Lesotho. It was named by paleontologist Peter Galton in 1978, the name meaning "lizard from Lesotho". The genus has only one valid species, Lesothosaurus diagnosticus. Lesothosaurus is one of the most completely-known early ornithischians, based on numerous skull and postcranial fossils from the Upper Elliot Formation. It had a simpler tooth and jaw anatomy than later ornithischians, and may have been omnivorous in some parts of the year.

Cow sharks are a shark family, the Hexanchidae, characterized by an additional pair or pairs of gill slits. Its 37 species are placed within the 10 genera: Gladioserratus, Heptranchias, Hexanchus, Notidanodon, Notorynchus, Pachyhexanchus, Paraheptranchias, Pseudonotidanus, Welcommia, and Weltonia.

Cretoxyrhina is an extinct genus of large mackerel shark that lived about 107 to 73 million years ago during the late Albian to late Campanian of the Late Cretaceous. The type species, C. mantelli, is more commonly referred to as the Ginsu shark, first popularized in reference to the Ginsu knife, as its theoretical feeding mechanism is often compared with the "slicing and dicing" when one uses the knife. Cretoxyrhina is traditionally classified as the likely sole member of the family Cretoxyrhinidae but other taxonomic placements have been proposed, such as within the Alopiidae and Lamnidae.

Dorudon ("spear-tooth") is a genus of extinct basilosaurid ancient whales that lived alongside Basilosaurus 40.4 to 33.9 million years ago in the Eocene. It was a small whale, with D. atrox measuring 5 metres (16 ft) long and weighing 1–2.2 metric tons. Dorudon lived in warm seas around the world and fed on small fish and mollusks. Fossils have been found along the former shorelines of the Tethys Sea in present-day Egypt and Pakistan, as well as in the United States, New Zealand and Western Sahara.

The maxillary central incisor is a human tooth in the front upper jaw, or maxilla, and is usually the most visible of all teeth in the mouth. It is located mesial to the maxillary lateral incisor. As with all incisors, their function is for shearing or cutting food during mastication (chewing). There is typically a single cusp on each tooth, called an incisal ridge or incisal edge. Formation of these teeth begins at 14 weeks in utero for the deciduous (baby) set and 3–4 months of age for the permanent set.

The maxillary lateral incisors are a pair of upper (maxillary) teeth that are located laterally from both maxillary central incisors of the mouth and medially from both maxillary canines. As with all incisors, their function is for shearing or cutting food during mastication, commonly known as chewing. There are generally no cusps on the teeth, but the rare condition known as talon cusps are most prevalent on the maxillary lateral incisors. The surface area of the tooth used in eating is called an incisal ridge or incisal edge. Though relatively the same, there are some minor differences between the deciduous (baby) maxillary lateral incisor and that of the permanent maxillary lateral incisor. The maxillary lateral incisors occlude in opposition to the mandibular lateral incisors.

The sharpnose sevengill shark, also known as one-finned shark, perlon shark, sevengill cow shark, sharpsnouted sevengill or slender sevengill, is a species of shark in the family Hexanchidae, and the only living species in the genus Heptranchias. Found almost circumglobally in deep water, it is one of the few species of sharks with seven pairs of gill slits as opposed to the usual five. The other shark species with seven gill slits is the broadnose sevengill shark. Though small, this shark is an active, voracious predator of invertebrates and fish. When caught, this species is notably defensive and will attempt to bite. It is of minor commercial importance.
Dental anatomy is a field of anatomy dedicated to the study of human tooth structures. The development, appearance, and classification of teeth fall within its purview. Tooth formation begins before birth, and the teeth's eventual morphology is dictated during this time. Dental anatomy is also a taxonomical science: it is concerned with the naming of teeth and the structures of which they are made, this information serving a practical purpose in dental treatment.
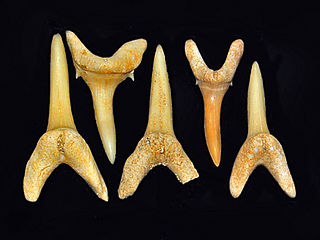
Striatolamia is an extinct genus of sharks belonging to the family Odontaspididae. These extinct sharks lived from the Early Paleocene to Late Miocene.
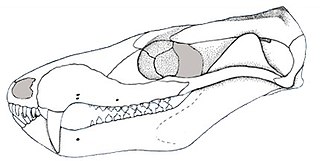
Brasilodon is an extinct genus of small, mammal-like cynodonts that lived in what is now Brazil during the Norian age of the Late Triassic epoch, about 225.42 million years ago. While no complete skeletons have been found, the length of Brasilodon has been estimated at 12 centimetres (4.7 in). Its dentition shows that it was most likely an insectivore. The genus is monotypic, containing only the species B. quadrangularis. Brasilodon belongs to the family Brasilodontidae, whose members were some of the closest relatives of mammals, the only cynodonts alive today. Two other brasilodontid genera, Brasilitherium and Minicynodon, are now considered to be junior synonyms of Brasilodon.
The flagtail swellshark is a little-known species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae, found at a depth of 480–700 m (1,570–2,300 ft) off northeastern Queensland, and possibly also nearby islands. This stout-bodied shark has a short, broad, and flattened head with a capacious mouth. Adults have a variegated brown coloration with 9–10 darker dorsal saddles and V-shaped blotch at the tip of the upper caudal fin lobe. Juveniles are yellow with narrow brown bars instead of saddles, and a distinctive marking between the spiracles shaped like two loops connected by a line. Like other swellsharks, this species can inflate its body when threatened.
Many different terms have been proposed for features of the tooth crown in mammals.

Cardabiodon is an extinct genus of large mackerel shark that lived about 95 to 91 million years ago (Ma) during the Cenomanian to Turonian of the Late Cretaceous. It is a member of the Cardabiodontidae, a family unique among mackerel sharks due to differing dental structures, and contains the two species C. ricki and C. venator. Cardabiodon fossils have been found in Australia, North America, England, and Kazakhstan. It was likely an antitropical shark that inhabited temperate neritic and offshore oceans between 40° and 60° paleolatitude, similar to the modern porbeagle shark.

Otodus auriculatus is an extinct species of large sharks in the genus Otodus of the family Otodontidae, closely related to the sharks of the genus Otodus, and also closely related to the later species megalodon. The largest individuals were about 9.5 metres (31 ft) long. Its teeth were large, having coarse serrations on the cutting edge, and also with two large cusplets. The teeth can reach up to 130 millimetres (5.1 in), and belonged to a large "megatoothed" shark.

Cretalamna is a genus of extinct otodontid shark that lived from the latest Early Cretaceous to Eocene epoch. It is considered by many to be the ancestor of the largest sharks to have ever lived, such as Otodus angustidens, Otodus chubutensis, and Otodus megalodon.

Galeocerdo alabamensis is an extinct relative of the modern tiger shark. Nomenclature of this shark has been debated, and recent literature identified it more closely with the Physogaleus genus of prehistoric shark, rather than Galeocerdo. The classification of Physogaleus is known as tiger-like sharks while Galeocerdo refers to tiger sharks. In 2003, P. alabamensis was classified as Galeocerdo. However, in 2019, they were proclaimed to be more morphologically similar to the genus Physogaleus. This definition was based primarily on tooth shape, as the majority of information on P. alabamensis is a result of studying tooth fossils. Distinctions between Physogaleus and Galeocerdo are difficult with extinct sharks from the Oilgocene/Miocene as there is little paleobiological information allowing for hard conclusions.

Cretacladoides is a genus of chondrichthyan, possibly a falcatid, found in France and Austria. Known solely from teeth, mainly found in the Klausrieglerbach locality of Austria, it consists of two species, C. ogiveformis and C. noricum. Assuming a falcatid identity, it is the most recent member of the family, which otherwise became extinct at the end of the Carboniferous.
Namafelis is an extinct genus of felids that lived in what is now Namibia during the Early Miocene. It contains a single species, Namafelis minor. Closely related to Diamantofelis, it is of “Pseudaelurus-grade”, and therefore a rather basal member of the cat family.

Xampylodon is an extinct genus of cow shark. Fossils assigned to this genus are known from the Late Cretaceous and early Paleocene. Xampylodon was recently erected after a revision on the taxonomy of hexanchid fossil teeth, and includes four species, most of them previously included in Notidanodon.















