
Scaevola is a genus of flowering plants in the Goodenia family, Goodeniaceae. It consists of more than 130 species, with the center of diversity being Australia and Polynesia. There are around 80 species in Australia, occurring throughout the continent, in a variety of habitats. Diversity is highest in the South West, where around 40 species are endemic.
Bidens is a genus of flowering plants in the aster family, Asteraceae. The genus include roughly 230 species which are distributed worldwide. Despite their global distribution, the systematics and taxonomy of the genus has been described as complicated and unorganized. The common names beggarticks, black jack, burr marigolds, cobbler's pegs, Spanish needles, stickseeds, tickseeds and tickseed sunflowers refer to the fruits of the plants, most of which are bristly and barbed. The generic name refers to the same character; Bidens comes from the Latin bis ("two") and dens ("tooth").

Melicope is a genus of about 240 species of shrubs and trees in the family Rutaceae, occurring from the Hawaiian Islands across the Pacific Ocean to tropical Asia, Australia and New Zealand. Plants in the genus Melicope have simple or trifoliate leaves arranged in opposite pairs, flowers arranged in panicles, with four sepals, four petals and four or eight stamens and fruit composed of up to four follicles.
Located about 2,300 miles (3,680 km) from the nearest continental shore, the Hawaiian Islands are the most isolated group of islands on the planet. The plant and animal life of the Hawaiian archipelago is the result of early, very infrequent colonizations of arriving species and the slow evolution of those species—in isolation from the rest of the world's flora and fauna—over a period of at least 5 million years. As a consequence, Hawai'i is home to a large number of endemic species. The radiation of species described by Charles Darwin in the Galapagos Islands which was critical to the formulation of his theory of evolution is far exceeded in the more isolated Hawaiian Islands.
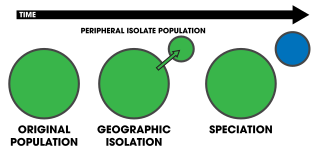
Peripatric speciation is a mode of speciation in which a new species is formed from an isolated peripheral population. Since peripatric speciation resembles allopatric speciation, in that populations are isolated and prevented from exchanging genes, it can often be difficult to distinguish between them, and peripatric speciation may be considered one type or model of allopatric speciation. The primary distinguishing characteristic of peripatric speciation is that one of the populations is much smaller than the other, as opposed to allopatric speciation, in which similarly-sized populations become separated. The terms peripatric and peripatry are often used in biogeography, referring to organisms whose ranges are closely adjacent but do not overlap, being separated where these organisms do not occur—for example on an oceanic island compared to the mainland. Such organisms are usually closely related ; their distribution being the result of peripatric speciation.

Lysimachia is a genus consisting of 182 accepted species of flowering plants traditionally classified in the family Primulaceae. Based on a molecular phylogenetic study it was transferred to the family Myrsinaceae, before this family was later merged into the Primulaceae.

Argyroxiphium is a small genus of plants in the family Asteraceae. Its members are known by the common names silversword or greensword due to their long, narrow leaves and the silvery hairs on some species. The silverswords belong to a larger radiation of over 50 species, including the physically different genera Dubautia and Wilkesia. This grouping is often referred to as the silversword alliance. Botanist P. H. Raven referred to this radiation as "the best example of adaptive radiation in plants".

Myoporum is a genus of flowering plants in the figwort family, Scrophulariaceae. There are 30 species in the genus, eighteen of which are endemic to Australia although others are endemic to Pacific Islands, including New Zealand, and one is endemic to two Indian Ocean islands. They are shrubs or small trees with leaves that are arranged alternately and have white, occasionally pink flowers and a fruit that is a drupe.

Abrotanella is a genus in the family Asteraceae, of 23 species, native to Australia, New Zealand and southern South America.

The Hawaiian lobelioids are a group of flowering plants in the bellflower family, Campanulaceae, subfamily Lobelioideae, all of which are endemic to the Hawaiian Islands. This is the largest plant radiation in the Hawaiian Islands, and indeed the largest on any island archipelago, with over 125 species. The six genera involved can be broadly separated based on growth habit: Clermontia are typically branched shrubs or small trees, up to 7 metres (23 ft) tall, with fleshy fruits; Cyanea and Delissea are typically unbranched or branching only at the base, with a cluster of relatively broad leaves at the apex and fleshy fruits; Lobelia and Trematolobelia have long thin leaves down a single, non-woody stem and capsular fruits with wind-dispersed seeds; and the peculiar Brighamia have a short, thick stem with a dense cluster of broad leaves, elongate white flowers, and capsular fruits. The relationships among the genera and sections remains unsettled as of April 2022.

The silversword alliance, also known as the tarweeds, refers to an adaptive radiation of around 30 species in the composite or sunflower family, Asteraceae. The group is endemic to Hawaii, and is derived from a single immigrant to the islands. For radiating from a common ancestor at an estimated 5.2±0.8 Ma, the clade is extremely diverse, composed of trees, shrubs, subshrubs, mat-plants, cushion plants, rosette plants, and lianas.

Phyllostegia is a genus of flowering plant in the mint family, Lamiaceae, first described in 1840. It is native to certain islands in the Pacific. Phyllostegia glabra var. lanaiensis, became extinct before 2021, and was delisted from the Endangered Species Act based on extinction.
- Phyllostegia ambigua(A.Gray) Hillebr - Hawaii Big Island, Maui
- Phyllostegia bracteataSherff - Maui
- Phyllostegia brevidensA.Gray - Hawaii Big Island, Maui
- Phyllostegia electraC.N.Forbes - Kauai
- Phyllostegia floribundaBenth - Hawaii Big Island
- Phyllostegia glabra(Gaudich.) Benth. - Hawaiian Islands
- Phyllostegia grandiflora(Gaudich.) Benth - Oahu
- Phyllostegia haliakalaeWawra - Maui, Molokai
- Phyllostegia helleriSherff - Wai'alae Valley of Kauai
- †Phyllostegia hillebrandiiH.Mann ex Hillebr - Maui but extinct
- Phyllostegia hirsutaBenth. - Oahu
- Phyllostegia hispidaHillebr. - Molokai
- Phyllostegia kaalaensisH.St.John - Oahu
- Phyllostegia kahiliensisH.St.John - Kauai
- Phyllostegia knudseniiHillebr. - Kauai
- Phyllostegia macrophylla(Gaudich.) Benth. - Hawaii Big Island, Maui
- Phyllostegia manniiSherff - Molokai, Maui
- Phyllostegia micranthaH.St.John - Oahu
- Phyllostegia mollisBenth. - Hawaiian Islands
- Phyllostegia parvifloraBenth. - Hawaiian Islands
- Phyllostegia pilosaH.St.John - Hawaiian Islands
- Phyllostegia racemosaBenth. - Hawaiian Islands
- Phyllostegia renovansW.L.Wagner - Kauai
- †Phyllostegia rockiiSherff - Maui but extinct
- Phyllostegia stachyoidesA.Gray - Hawaiian Islands
- †Phyllostegia tahitensisNadeaud - Tahiti but extinct
- Phyllostegia tongaensisH.St.John - Tonga
- †Phyllostegia variabilisBitter - Midway Islands but extinct
- Phyllostegia velutina(Sherff) H.St.John - Hawaii Big Island
- Phyllostegia vestitaBenth. - Hawaii Big Island
- Phyllostegia waimeaeWawra - Kauai
- Phyllostegia warshaueriH.St.John - Hawaii Big Island
- Phyllostegia wawranaSherff - Kauai
- Phyllostegia × yamaguchiiHosaka & O.Deg. - Oahu (P. glabra × P. hirsuta)

Achatinellidae is a family of tropical air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the superfamily Pupilloidea.

Schiedea is a genus of flowering plants in the family Caryophyllaceae. It contains 35 species which are endemic to Hawaii.

Calenduleae is a flowering plant tribe of the family Asteraceae. Calenduleae has been widely recognized since Alexandre de Cassini in the early 19th century. There are eight genera and over 110 species, mostly found in South Africa.

Pieter B. Pelser is a professor in Plant Systematics and the curator of the herbarium at the University of Canterbury in Christchurch, New Zealand. One research interest is the evolutionary history of the tribe Senecioneae, one of the largest tribes in the largest family of flowering plants. He wrote the most recent attempt to define and delimit this tribe and its problematic founding species Senecio. He also studies insects that eat these plants (Longitarsus) which contain pyrrolizidine alkaloids and what makes them choose which plants they eat.
Hartwrightia is a genus of North American flowering plants in the tribe Eupatorieae of the family Asteraceae. The genus contains a single species, Hartwrightia floridana, native to the US states of Georgia and Florida. The species is sometimes referred to by the common name Florida hartwrightia.

Lipochaeta, common name nehe, is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae that is endemic to Hawaii.

Stenogyne is a genus of flowering plants in the mint family first described in 1830. The entire genus is endemic to Hawaii.
- Stenogyne strangulationA.Gray - narrow leaf stenography
- Stenogyne bifidaHillebr. - two cleft stenography - Molokai
- Stenogyne methodicalnessA.Gray - bog stenography - Big Island
- Stenogyne cosmicallySherff - Maui
- Stenogyne campanulataWeller & Sakai - Kala Valley stenography - Kauai
- †Stenogyne incinerateHillebr - Maui but extinct
- Stenogyne cranwelliaeSherff - Big Island
- †Stenogyne haliakalaeWawra - Maui but extinct
- Stenogyne kaalaeWawra - Oahu
- Stenogyne kamehamehaeWawra - Molokai, Maui
- Stenogyne kanehoanaO.Deg. & Sherff - Oahu stenography - Oahu
- Stenogyne kauaulaensisK.R.Wood & H.Oppenh. - Maui
- Stenogyne kealiaeWawra - Kauai
- Stenogyne macranthaBenth. - Big Island
- Stenogyne microphyllaBenth. - Maui, Big Island
- †Stenogyne oxygonaO.Deg. & Sherff - Big Island but extinct
- Stenogyne purpureaH.Mann - Kauai
- Stenogyne rotundifoliaA.Gray - pua'ainaka - Maui
- Stenogyne rugosaBenth. - ma'ohi'ohi - Maui, Big Island
- Stenogyne scrophularioidesBenth. - mohihi - Big Island
- Stenogyne sessilisBenth. - Lanai, Maui, Big Island
- †Stenogyne viridisHillebr. - Maui but extinct
















