
The Río de la Plata, also called the River Plate or La Plata River in English, is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Paraná River at Punta Gorda. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean and forms a funnel-shaped indentation on the southeastern coastline of South America. Depending on the geographer, the Río de la Plata may be considered a river, an estuary, a gulf, or a marginal sea. If considered a river, it is the widest in the world, with a maximum width of 220 kilometres (140 mi).
Nothoscordum is a genus of New World plants in the onion tribe within the Amaryllis family. It is probably paraphyletic. The genus is native to North and South America, though a few species have become naturalized in various parts of the Old World.

Psidium is a genus of trees and shrubs in the family Myrtaceae. It is native to warmer parts of the Western Hemisphere.
The Paraná River is a river in south-central South America, running through Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina for some 4,880 kilometres (3,030 mi). Among South American rivers, it is second in length only to the Amazon River. It merges with the Paraguay River and then farther downstream with the Uruguay River to form the Río de la Plata and empties into the Atlantic Ocean.

Schinus is a genus of flowering trees and tall shrubs in the sumac family, Anacardiaceae. Members of the genus are commonly known as pepper trees. The Peruvian pepper tree is the source of the spice known as pink peppercorn.

The Treaty of the Triple Alliance was a treaty that allied the Empire of Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay against Paraguay. Signed in 1865, after the outbreak of the Paraguayan War, its articles prescribed the allies' actions both during and after the war. The war led to the near-annihilation of Paraguay.
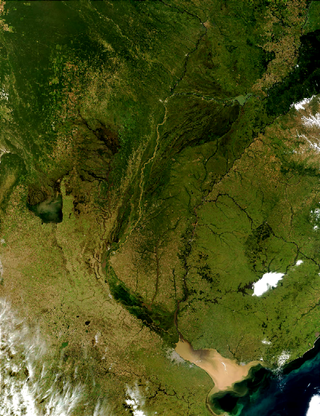
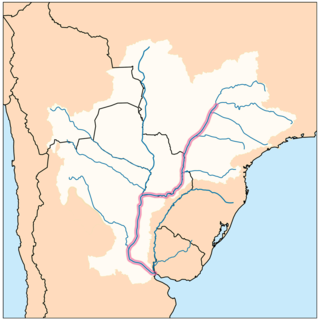
The Río de la Plata basin, more often called the River Plate basin in scholarly writings, sometimes called the Platine basin or Platine region, is the 3,170,000-square-kilometre (1,220,000 sq mi) hydrographical area in South America that drains to the Río de la Plata. It includes areas of southeastern Bolivia, southern and central Brazil, the entire country of Paraguay, most of Uruguay, and northern Argentina. Making up about one fourth of the continent's surface, it is the second largest drainage basin in South America and one of the largest in the world.

Trixis is a genus of shrubs in the family Asteraceae, native to North and South America including the West Indies.

Campomanesia is a genus in the family Myrtaceae described as a genus in 1794. It is native to South America and Trinidad.

Oxypetalum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described with this name in 1810. The genus is native to South America.
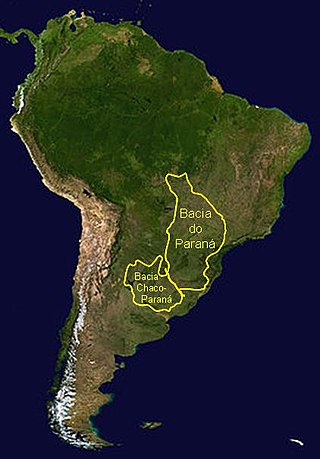
The Paraná Basin is a large cratonic sedimentary basin situated in the central-eastern part of South America. About 75% of its areal distribution occurs in Brazil, from Mato Grosso to Rio Grande do Sul states. The remainder area is distributed in eastern Paraguay, northeastern Argentina and northern Uruguay. The shape of the depression is roughly elliptical and covers an area of about 1,500,000 km2 (580,000 sq mi).

Austroeupatorium is a genus of plants native primarily to South America, including herbaceous perennials and shrubs. The native range is focused on eastern South America and extends as far north as Panama and Trinidad and as far west as Bolivia.

The South American Division (SAD) of Seventh-day Adventists is a sub-entity of the General Conference of Seventh-day Adventists, which oversees the Church's work in most of South America, which includes the nations of Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Ecuador, Peru, Paraguay, and Uruguay. Its headquarters is in Brasilia, Brazil. The Division membership as of June 30, 2021 is 2,545,366

Eustachys is a genus of tropical and subtropical plants in the grass family. It is native primarily to warmer parts of the Americas, with a few species in Africa and Asia.

Podocoma is a genus of South American plants in the tribe Astereae within the family Asteraceae.

Trichocline is a genus of Australian and South American plants in the tribe Mutisieae within the family Asteraceae. It consists of one species from Australia (T. spathulata) and twenty-three from South America.
Pamphalea is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. The genus was first described by Lagasca in 1811, who spelled it Panphalea. de Candolle emended the spelling to Pamphalea in 1812, and that spelling has been generally accepted.
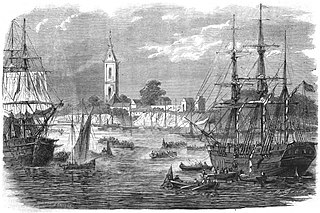
The Battle of Corrientes was an episode occurred at the beginning of the Paraguayan War, in the second stage of the Paraguayan offensive, after the invasion of Mato Grosso, at the beginning of 1865.

The Corrientes campaign or the Paraguayan invasion of Corrientes was the second campaign of the Paraguayan War. During the campaign, Paraguayan forces occupied the Argentinian city of Corrientes and other towns in the province of the same name. The campaign occurred simultaneously with the Siege of Uruguaiana.
















