The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that carries sensory fibers that create a pathway that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract.
Articles related to anatomy include:

In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax. On the left side of the body, the subclavian comes directly off the aortic arch, while on the right side it arises from the relatively short brachiocephalic artery when it bifurcates into the subclavian and the right common carotid artery.

The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior and middle cerebral circulation.

The vertebral arteries are major arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline basilar artery. As the supplying component of the vertebrobasilar vascular system, the vertebral arteries supply blood to the upper spinal cord, brainstem, cerebellum, and posterior part of brain.

The otic ganglion is a small parasympathetic ganglion located immediately below the foramen ovale in the infratemporal fossa and on the medial surface of the mandibular nerve. It is functionally associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve and innervates the parotid gland for salivation.

The inferior thyroid artery is an artery in the neck. It arises from the thyrocervical trunk and passes upward, in front of the vertebral artery and longus colli muscle. It then turns medially behind the carotid sheath and its contents, and also behind the sympathetic trunk, the middle cervical ganglion resting upon the vessel.

The superior laryngeal nerve is a branch of the vagus nerve. It arises from the middle of the inferior ganglion of the vagus nerve and additionally receives a sympathetic branch from the superior cervical ganglion.

The cardiac plexus is a plexus of nerves situated at the base of the heart that innervates the heart.

The costocervical trunk arises from the upper and back part of the second part of subclavian artery, behind the scalenus anterior on the right side, and medial to that muscle on the left side.

The intercostal arteries are a group of arteries passing within an intercostal space. There are 9 anterior and 11 posterior intercostal arteries on each side of the body. The anterior intercostal arteries are branches of the internal thoracic artery and its terminal branch – the musculophrenic artery. The posterior intercostal arteries are branches of the supreme intercostal artery and thoracic aorta.

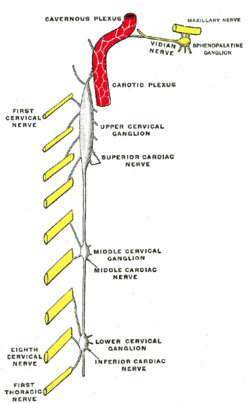
The middle cervical ganglion is the smallest of the three cervical sympathetic ganglia. It presumably represents the merging of the sympathetic ganglia of cervical segments C5–C6. It is usually situated at the level of the sixth cervical vertebra.

The inferior cervical ganglion is one of the three cervical sympathetic ganglia. It is situated between the base of the transverse process of the last cervical vertebra and the neck of the first rib, on the medial side of the costocervical artery.

The cervical ganglia are paravertebral ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system. Preganglionic nerves from the thoracic spinal cord enter into the cervical ganglions and synapse with its postganglionic fibers or nerves. The cervical ganglion has three paravertebral ganglia:

The middle cervical cardiac nerve is the largest of the three cardiac nerves. It arises from the middle cervical ganglion, or directly from the sympathetic trunk. It joins the deep cardiac plexus. It may occasionally be absent.

The superior cardiac nerve arises by two or more branches from the superior cervical ganglion, and occasionally receives a filament from the trunk between the first and second cervical ganglia. It runs down the neck behind the common carotid artery, and in front of the Longus colli muscle; and crosses in front of the inferior thyroid artery, and recurrent nerve. The course of the nerves on the two sides then differs.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The ciliary ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion located just behind the eye in the posterior orbit. Three types of axons enter the ciliary ganglion but only the preganglionic parasympathetic axons synapse there. The entering axons are arranged into three roots of the ciliary ganglion, which join enter the posterior surface of the ganglion.