| Spermatic plexus | |
|---|---|
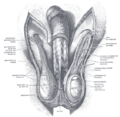
 The celiac ganglia with the sympathetic plexuses of the abdominal viscera radiating from the ganglia. (Spermatic plexus labeled at right, third from the bottom.) | |
| Details | |
| From | renal plexus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | plexus testicularis, plexus spermaticus |
| TA98 | A14.3.03.035M |
| TA2 | 6707 |
| FMA | 6637 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The spermatic plexus (or testicular plexus) is derived from the renal plexus, receiving branches from the aortic plexus. It accompanies the internal spermatic artery to the testis.