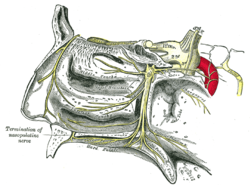
The buccal nerve is a sensory nerve of the face arising from the mandibular nerve. It conveys sensory information from the skin of the cheek, and parts of the oral mucosa, periodontium, and gingiva.

The greater petrosal nerve is a nerve of the head mainly containing pre-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres which ultimately synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion. It branches from the facial nerve and is derived from the parasympathetic part of the nervus intermedius component of CN VII, with its cell bodies located in the superior salivary nucleus. In the connective tissue substance of the foramen lacerum, the greater petrosal nerve unites with the (sympathetic) deep petrosal nerve to form the nerve of the pterygoid canal which proceeds to the pterygopalatine ganglion.

In neuroanatomy, the maxillary nerve (V2) is one of the three branches or divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth (CN V) cranial nerve. It comprises the principal functions of sensation from the maxilla, nasal cavity, sinuses, the palate and subsequently that of the mid-face, and is intermediate, both in position and size, between the ophthalmic nerve and the mandibular nerve.

The nasociliary nerve is a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) (which is in turn a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)). It is intermediate in size between the other two branches of the ophthalmic nerve, the frontal nerve and lacrimal nerve.

The supratrochlear nerve is a branch of the frontal nerve, itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) from the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It provides sensory innervation to the skin of the forehead and the upper eyelid.
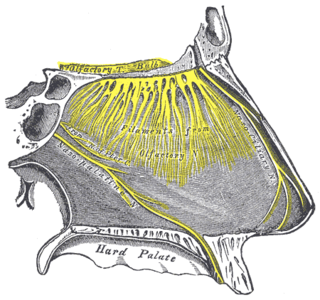
The nasopalatine nerve (also long sphenopalatine nerve) is a nerve of the head. It is a sensory branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2) that passes through the pterygopalatine ganglion (without synapsing) and then through the sphenopalatine foramen to enter the nasal cavity, and finally out of the nasal cavity through the incisive canal and then the incisive fossa to enter the hard palate. It provides sensory innervation to the posteroinferior part of the nasal septum, and gingiva just posterior to the upper incisor teeth.

The meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve that enters the middle cranial fossa through either the foramen spinosum or foramen ovale to innervate the meninges of this fossa as well as the mastoid air cells.

The descending palatine artery is a branch of the third part of the maxillary artery supplying the hard and soft palate.
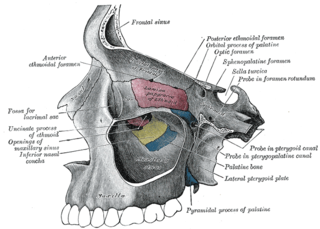
The sphenopalatine foramen is a fissure of the skull that connects the nasal cavity and the pterygopalatine fossa. It gives passage to the sphenopalatine artery, nasopalatine nerve, and the superior nasal nerve.
The greater palatine artery is a branch of the descending palatine artery and contributes to the blood supply of the hard palate and nasal septum.

The lesser petrosal nerve is the general visceral efferent (GVE) nerve conveying pre-ganglionic parasympathetic secretomotor fibers for the parotid gland from the tympanic plexus to the otic ganglion. It passes out of the tympanic cavity through the petrous part of the temporal bone into the middle cranial fossa of the cranial cavity, then exits the cranial cavity through its own canaliculus to reach the infratemporal fossa.

The anterior superior alveolar nerve (or anterior superior dental nerve) is a branch of the infraorbital nerve (itself a branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2)). It passes through the canalis sinuosus to reach and innervate upper front teeth. Through its nasal branch, it also innervates parts of the nasal cavity.

The posterior superior alveolar nerves (also posterior superior dental nerves or posterior superior alveolar branches) are sensory branches of the maxillary nerve (CN V2). They arise within the pterygopalatine fossa as a single trunk. They run on or in the maxilla. They provide sensory innervation to the upper molar teeth and adjacent gum, and the maxillary sinus.

The palatine nerves are distributed to the roof of the mouth, soft palate, tonsil, and lining membrane of the nasal cavity.

The posterior auricular nerve is a nerve of the head. It is a branch of the facial nerve. It communicates with branches from the vagus nerve, the great auricular nerve, and the lesser occipital nerve. Its auricular branch supplies the posterior auricular muscle, the intrinsic muscles of the auricle, and gives sensation to the auricle. Its occipital branch supplies the occipitalis muscle.

The cervical branch of the facial nerve is a nerve in the neck. It is a branch of the facial nerve (VII). It supplies the platysma muscle, among other functions.
The nerve to the stapedius is a branch of the facial nerve which innervates the stapedius muscle. It arises from the CN VII within the facial canal, opposite the pyramidal eminence. It passes through a small canal in this eminence to reach the stapedius muscle.

The digastric branch of facial nerve provides motor innervation to the posterior belly of the digastric muscle. It branches from the facial nerve near to the stylomastoid foramen as the CN VII exits the facial canal. It commonly arises in common with the stylohyoid branch of facial nerve.

The greater palatine nerve is a branch of the pterygopalatine ganglion. This nerve is also referred to as the anterior palatine nerve, due to its location anterior to the lesser palatine nerve. It carries both general sensory fibres from the maxillary nerve, and parasympathetic fibers from the nerve of the pterygoid canal. It may be anaesthetised for procedures of the mouth and maxillary (upper) teeth.

The tympanic plexus is a nerve plexus within the tympanic cavity formed upon the promontory of tympanic cavity by the tympanic nerve, and the superior and inferior caroticotympanic nerves.