
Leporidae is the family of rabbits and hares, containing over 70 species of extant mammals in all. The Latin word Leporidae means "those that resemble lepus" (hare). Together with the pikas, the Leporidae constitute the mammalian order Lagomorpha. Leporidae differ from pikas in that they have short, furry tails and elongated ears and hind legs.

The snowshoe hare, also called the varying hare or snowshoe rabbit, is a species of hare found in North America. It has the name "snowshoe" because of the large size of its hind feet. The animal's feet prevent it from sinking into the snow when it hops and walks. Its feet also have fur on the soles to protect it from freezing temperatures.

The Amami rabbit, also known as the Ryukyu rabbit is a dark-furred species of rabbit which is only found on Amami Ōshima and Tokunoshima, two small islands between southern Kyūshū and Okinawa in Japan. Often called a living fossil, the Amami rabbit is a living remnant of ancient rabbits that once lived on the Asian mainland, where they died out, remaining only on the two small Japanese islands where they live today.

The brush rabbit, or western brush rabbit, or Californian brush rabbit, is a species of cottontail rabbit found in western coastal regions of North America, from the Columbia River in Oregon to the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula. Its range extends as far east as the eastern sides of the Sierra Nevada and Cascade mountain ranges.

The riverine rabbit, also known as the bushman rabbit or bushman hare, is a rabbit with an extremely limited distribution area, found only in the central and southern regions of the Karoo Desert of South Africa's Northern Cape Province. It is the only member of the genus Bunolagus because of unique traits that separate it from the other leporids. It is one of the most endangered mammals in the world, with only around 500 living adults, and 1500 overall.

The white-tailed jackrabbit, also known as the prairie hare and the white jack, is a species of hare found in western North America. Like all hares and rabbits, it is a member of the family Leporidae of order Lagomorpha. It is a solitary individual except where several males court a female in the breeding season. Litters of four to five young are born in a form, a shallow depression in the ground, hidden among vegetation. This jackrabbit has two described subspecies: L. townsendii townsendii occurring west of the Rocky Mountains and L. townsendii campanius occurring east of the Rocky Mountains.

The Japanese hare is a species of hare endemic to Japan. In Japanese, it is called the Nousagi, meaning "field rabbit".

The black-flanked rock-wallaby, also known as the black-footed rock-wallaby or warru, is a species of wallaby, one of several rock-wallabies in the genus Petrogale. A shy, nocturnal herbivore, its two main subspecies are found in mostly isolated populations across western and southern Western Australia (WA), the Northern Territory and parts of South Australia (SA). With some subspecies showing a decline in populations in recent years, the whole species is classed as an endangered species under the Commonwealth EPBC Act.

The Zacatecan deer mouse or southern rock mouse is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found only in Mexico, and is not considered endangered.

The Ethiopian highland hare or Starck's hare is a medium-sized species of mammal in the rabbit and hare family, Leporidae. Its dorsal pelage is grizzled, buff white and spotted and streaked with black, while its belly fur is pure white and fluffy. It is endemic to the Ethiopian Highlands, ranging over the Afroalpine regions of the Shoa, Bale, and Arsi Provinces of Ethiopia. A herbivore, it mostly feeds on moorland grasses. The IUCN rates it as a species of least concern.

The Yarkand hare is a species of mammal in the family Leporidae. It has soft, straight, sandy brown dorsal pelage which has grayish-black stripes, and completely white ventral pelage. Endemic to China, the Yarkand hare is restricted to the Tarim Basin in Southern Xinjiang, China. It is mainly nocturnal, and forages on grass and crops. The female produces two or three litters annually, each consisting of two to five young. It is rated as near threatened on the International Union for Conservation of Nature Red List of Endangered Species and by the Red List of China's Vertebrates. However, Chinese geneticists have stated the species is "endangered" due to limited habitat and its fragmentation, and over-hunting and poaching.

Hoffmann's pika is a species of mammal in the pika family, Ochotonidae, that is endemic to Mongolia. It is currently listed as endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).

The Afghan pika is a species of small mammal in the pika family, Ochotonidae. It is found in Iranian Plateau or Afghanistan, Iran, Pakistan and Turkmenistan and the IUCN lists it as being of "least concern".
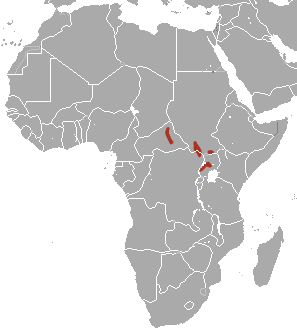
The Bunyoro rabbit or Central African rabbit is a species of mammal in the family Leporidae. It is monotypic within the genus Poelagus. It is found in central Africa and its typical habitat is damp savannah, often with rocky outcrops.

The Natal red rock hare or greater red rock hare is a species of mammal in the family Leporidae. It has a slightly grizzled, grayish brown head and reddish brown upperparts. The dense fur is thick and rougher than other rock hares. It is endemic to Africa, and found in southeastern provinces of South Africa, eastern Lesotho, Eswatini, and southern Mozambique. It is a herbivore, primarily feeding on grass. It breeds throughout the year, and one or two pups are usually born in the summer. It is rated as a species of least concern on the IUCN Red List of Endangered Species.
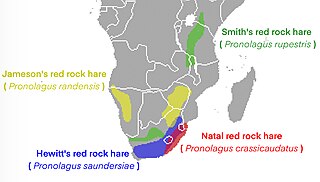
The red rock hares are the four species in the genus Pronolagus. They are African lagomorphs of the family Leporidae.

Smith's red rockhare, Smith's red rock hare or Smith's red rock rabbit is a species of mammal in the family Leporidae, and is the smallest member of the genus Pronolagus. The upperparts and gular collar are reddish brown in colour. It has warm, brown, grizzled, thicker hairs at the back of the body, and white to tawny, thinner underfur. It is native to Africa, found in parts of Kenya, Lesotho, Malawi, Namibia, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia and Zimbabwe. It is a folivore, and usually forages on grasses, shrubs and herbs. It breeds from September to February, and the female litters one or two offspring. The young leave the nest at three years of age. In 1996, it was rated as a species of least concern on the IUCN Red List of Endangered Species.

The fauna of South Africa is diverse and largely typical of the ecosystems in Africa. South Africa is ranked sixth out of the world's 17 megadiverse countries. Many endemic species are unique to South Africa. The country is among the world leaders in conservation, but at the time wildlife is threatened by poaching and canned hunting.

The Hewitt's red rock hare is a species of mammal in the family Leporidae. It had previously been classified as a subspecies of Pronolagus rupestris, but is now regarded as its own species due to differences in morphology and genetic differences in cytochrome b, and 12S rRNA.





















