| Chinese hare | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Lagomorpha |
| Family: | Leporidae |
| Genus: | Lepus |
| Species: | L. sinensis |
| Binomial name | |
| Lepus sinensis J. E. Gray, 1832 | |
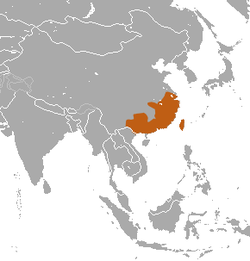 | |
| Chinese hare range | |
The Chinese hare (Lepus sinensis) is a species of mammal in the family Leporidae. [2] It is found in China, Taiwan and Vietnam. [1]
