
Commuter rail, or suburban rail, is a passenger rail transport service that primarily operates within a metropolitan area, connecting commuters to a central city from adjacent suburbs or commuter towns. Commuter rail systems are considered heavy rail, using electrified or diesel trains. Distance charges or zone pricing may be used.

The 7 Flushing Local and <7> Flushing Express are two rapid transit services in the A Division of the New York City Subway, providing local and express services along the full length of the IRT Flushing Line. Their route emblems, or "bullets", are colored purple, since they serve the Flushing Line.

The Porto Metro, part of the public transport system of Porto, Portugal, is a light rail network that runs underground in central Porto and above ground into the city's suburbs. Metro do Porto S.A. was founded in 1993, and the first line of the system opened in 2002.

Edale railway station serves the rural village of Edale in the Derbyshire Peak District, in England. It is located 20 miles (32 km) west of Sheffield and 22 miles (35 km) east of Manchester Piccadilly. The station was opened in 1894 on the Midland Railway's Dore and Chinley line, now known as the Hope Valley Line.

Stamford station, officially known as the Stewart B. McKinney Transportation Center or the Stamford Transportation Center, is a major railroad station in the city of Stamford, Connecticut, serving passengers traveling on Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line, Amtrak's Northeast Corridor, and CTrail's Shore Line East. In addition, it is also a major bus terminal for Greyhound, Peter Pan, and CTtransit buses. Annual ridership on Metro-North exceeded 8.4 million in 2016, making it the second busiest station in the entire system, after Grand Central Terminal.

7th Street/Metro Center station is an underground light rail and rapid transit station on the A, B, D, and E lines of the Los Angeles Metro Rail system. The station also has street level stops for the J Line of the Los Angeles Metro Busway system. The station is located under 7th Street, after which the station is named, at its intersections with Figueroa, Flower and Hope Streets.

The Rio de Janeiro Metro, commonly referred to as just the Metrô is a rapid transit network that serves the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The Metrô was inaugurated on 5 March 1979, and consisted of five stations operating on a single line. The system currently covers a total of 58 kilometres (36 mi), serving 41 stations, divided into three lines: Line 1 ; Line 2, which together travel over a shared stretch of line that covers 10 stations of an approximate distance of 5 kilometres (3.1 mi); and Line 4. Metrô Rio has the second highest passenger volume of the metro systems in Brazil, after the São Paulo Metro.

The Cathcart Circle Lines form a mostly suburban railway route linking Glasgow (Central) to Cathcart via a circular line, with branches to Newton and Neilston, on the south bank of the River Clyde. They are part of the Strathclyde Partnership for Transport network.

There once were four direct railway routes between Liverpool and Manchester in the North West of England; only two remain, the two centre routes of the four. The most northerly and the most southerly of the four routes are no longer direct lines. Of the remaining two direct routes, the northern route of the two is fully electric, while the now southern route is a diesel-only line. The most northerly of the four has been split into two routes: the western section operated by Merseyrail electric trains and the eastern section by diesel trains, requiring passengers to change trains between the two cities. The fourth route, the most southerly of the four, has been largely abandoned east of Warrington; the remaining section caters mainly for freight trains.

The South Wales Main Line, originally known as the London, Bristol and South Wales Direct Railway or simply as the Bristol and South Wales Direct Railway, is a branch of the Great Western Main Line in Great Britain. It diverges from the core London-Bristol line at Royal Wootton Bassett beyond Swindon, first calling at Bristol Parkway, after which the line continues through the Severn Tunnel into South Wales.

The Estrada de Ferro Central do Brasil was one of the principal railways of Brazil, uniting the states of Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo and Minas Gerais.

Utrecht Centraal, officially Station Utrecht Centraal, is the transit hub that integrates three bicycle parkings, two bus stations, two tram stops and the central railway station for the city of Utrecht in the province of Utrecht, Netherlands. It is the biggest train station in The Netherlands.

SuperVia Trens Urbanos is a rapid transit and commuter rail company operator, founded in Rio de Janeiro (Brazil) in November 1998. It carries around 750,000 passengers a day on a railroad network comprising 104 stations in 12 cities: Rio de Janeiro, Duque de Caxias, Guapimirim, Nova Iguaçu, Nilópolis, Mesquita, Queimados, São João de Meriti, Belford Roxo, Japeri, Paracambi and Magé.

Transport in São Paulo plays a key role in the daily lives of the people of São Paulo and offers various methods of public transport that are offered in the city, including a complex bus system run by SPTrans, and various subway and railway lines. A contactless smartcard is used to pay fares for the buses, subway, and railway systems. São Paulo also has three airports.

Méier is a middle class and upper middle class neighborhood in the North Zone of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The neighborhood is the historic center of the "Área dos Engenhos", or "Mill Area", which today is known as Grande Méier and has been a sub-prefecture since 2013. As a result, it has a wide range of shops and a variety of services and transport, although it is not one of the largest neighborhoods of the municipality. In the neighborhood is located one of the first shopping centers in Brazil, Shopping do Méier, opened in 1963. It has two distinct urban appearances, one more bustling, commercial, in the areas close to the train station, and a quieter one, on more residential streets.
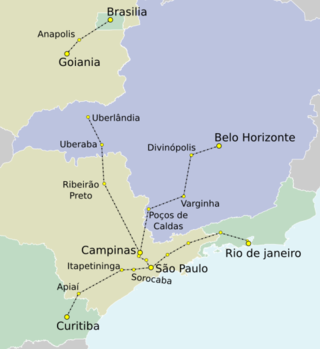
The TAV is Brazil's first planned high-speed rail service. The first line is proposed to run between Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo. Travel over the 403 kilometres (250 mi) between Barão de Mauá station and Campo de Marte Airport will take 85 minutes, reaching a maximum speed of 350 kilometres per hour (220 mph).

Avenida Brasil is an expressway-like thoroughfare in Rio de Janeiro. Its emergence is associated with the expansion of the city to residential areas further away from its central region during the first half of the 20th century. It started to serve as a gateway by road, hitherto hitched by sea or by the path taken by trains. The avenue that was linked to Petrópolis in 1941 became the first federal highway (BR-01) in 1948.
The Deodoro Line was a commuter rail line operated by SuperVia before being interconnected to the Santa Cruz Line in June 2020.
Santa Cruz Line is a commuter rail line operated by SuperVia. It is a shortening of the old Mangaratiba Branch of Central do Brasil Railway, as this line continued towards the extinct Mangaratiba station, in the homonymous city, located in the coastal region of Costa Verde.

VR commuter rail is a Finnish commuter rail system operated by VR – the national railway operator of Finland – under a public service obligation agreement with the Ministry of Transport and Communications of Finland. The operations are planned in trilateral co-operation between the ministry, the operator and various regional transport authorities.



















