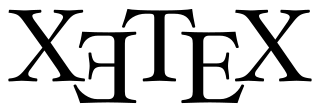OpenType is a format for scalable computer fonts. Derived from TrueType, it retains TrueType's basic structure but adds many intricate data structures for describing typographic behavior. OpenType is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.

The Tibetan script is a segmental writing system (abugida) of Indic origin used to write certain Tibetic languages, including Tibetan, Dzongkha, Sikkimese, Ladakhi, Jirel and Balti. It has also been used for some non-Tibetic languages in close cultural contact with Tibet, such as Thakali. The printed form is called uchen script while the hand-written cursive form used in everyday writing is called umê script. This writing system is used across the Himalayas, and Tibet.

Dzongkha is a Sino-Tibetan language that is the official and national language of Bhutan. It is written using the Tibetan script.
The National Library at Kolkata romanisation is a widely used transliteration scheme in dictionaries and grammars of Indic languages. This transliteration scheme is also known as (American) Library of Congress and is nearly identical to one of the possible ISO 15919 variants. The scheme is an extension of the IAST scheme that is used for transliteration of Sanskrit.
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that emerged during the 19th century from suggestions by Charles Trevelyan, William Jones, Monier Monier-Williams and other scholars, and formalised by the Transliteration Committee of the Geneva Oriental Congress, in September 1894. IAST makes it possible for the reader to read the Indic text unambiguously, exactly as if it were in the original Indic script. It is this faithfulness to the original scripts that accounts for its continuing popularity amongst scholars.
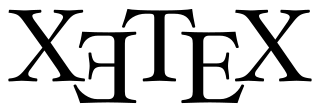
XeTeX is a TeX typesetting engine using Unicode and supporting modern font technologies such as OpenType, Graphite and Apple Advanced Typography (AAT). It was originally written by Jonathan Kew and is distributed under the X11 free software license.
Technical variations of Linux distributions include support for different hardware devices and systems or software package configurations. Organizational differences may be motivated by historical reasons. Other criteria include security, including how quickly security upgrades are available; ease of package management; and number of packages available.

There are Unicode typefaces which are open-source and designed to contain glyphs of all Unicode characters, or at least a broad selection of Unicode scripts. There are also numerous projects aimed at providing only a certain script, such as the Arabeyes Arabic font. The advantage of targeting only some scripts with a font was that certain Unicode characters should be rendered differently depending on which language they are used in, and that a font that only includes the characters a certain user needs will be much smaller in file size compared to one with many glyphs. Unicode fonts in modern formats such as OpenType can in theory cover multiple languages by including multiple glyphs per character, though very few actually cover more than one language's forms of the unified Han characters.
Graphite is a programmable Unicode-compliant smart font technology and rendering system developed by SIL International as free software, distributed under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License and the Common Public License.

The DejaVu fonts are a superfamily of fonts designed for broad coverage of the Unicode Universal Character Set. The fonts are derived from Bitstream Vera (sans-serif) and Bitstream Charter (serif), two fonts released by Bitstream under a free license that allowed derivative works based upon them; the Vera and Charter families were limited mainly to the characters in the Basic Latin and Latin-1 Supplement portions of Unicode, roughly equivalent to ISO/IEC 8859-15, and Bitstream's licensing terms allowed the fonts to be expanded upon without explicit authorization. The DejaVu fonts project was started with the aim to "provide a wider range of characters ... while maintaining the original look and feel through the process of collaborative development". The development of the fonts is done by many contributors and is organized through a wiki and a mailing list.
A Unicode font is a computer font that maps glyphs to code points defined in the Unicode Standard. The vast majority of modern computer fonts use Unicode mappings, even those fonts which only include glyphs for a single writing system, or even only support the basic Latin alphabet. Fonts which support a wide range of Unicode scripts and Unicode symbols are sometimes referred to as "pan-Unicode fonts", although as the maximum number of glyphs that can be defined in a TrueType font is restricted to 65,535, it is not possible for a single font to provide individual glyphs for all defined Unicode characters. This article lists some widely used Unicode fonts that support a comparatively large number and broad range of Unicode characters.

GNU FreeFont is a family of free OpenType, TrueType and WOFF vector fonts, implementing as much of the Universal Character Set (UCS) as possible, aside from the very large CJK Asian character set. The project was initiated in 2002 by Primož Peterlin and is now maintained by Steve White.

Liberation is the collective name of four TrueType font families: Liberation Sans, Liberation Sans Narrow, Liberation Serif, and Liberation Mono. These fonts are metrically compatible with the most popular fonts on the Microsoft Windows operating system and the Microsoft Office software package, for which Liberation is intended as a free substitute. The fonts are default in LibreOffice.
The Tibetan and Himalayan Library (THL), formerly the Tibetan and Himalayan Digital Library (THDL), is a multimedia guide and digital library hosted by the University of Virginia focused on the languages, history and geography of Tibet and the Himalayas. The THL has also designed a scholarly transcription for Standard Tibetan known as the THL Simplified Phonetic Transcription.

WeeChat is a free and open-source Internet Relay Chat client that is designed to be light and fast. It is released under the terms of the GNU GPL-3.0-or-later and has been developed since 2003.

Linux-libre is a modified version of the Linux kernel that contains no binary blobs, obfuscated code, or code released under proprietary licenses. In the Linux kernel, they are mostly used for proprietary firmware images. While generally redistributable, binary blobs do not give the user the freedom to audit, modify, or, consequently, redistribute their modified versions. The GNU Project keeps Linux-libre in synchronization with the mainline Linux kernel.

Ubuntu is an OpenType-based font family, designed to be a modern, humanist-style typeface by London-based type foundry Dalton Maag, with funding by Canonical Ltd. The font was under development for nearly nine months, with only a limited initial release through a beta program, until September 2010. It was then that it became the new default font of the Ubuntu operating system in Ubuntu 10.10. Its designers include Vincent Connare, creator of the Comic Sans and Trebuchet MS fonts.
KVIrc is a graphical IRC client for Linux, Unix, Mac OS and Windows. The name is an acronym of K Visual IRC in which the K stands for a dependency to KDE, which became optional from version 2.0.0. The software is based on the Qt framework and its code is released under a modified GNU General Public License.

Noto is a font family comprising over 100 individual fonts, which are together designed to cover all the scripts encoded in the Unicode standard. As of October 2016, Noto fonts cover all 93 scripts defined in Unicode version 6.1, although fewer than 30,000 of the nearly 75,000 CJK unified ideographs in version 6.0 are covered. In total, Noto fonts cover nearly 64,000 characters, which is under half of the 149,186 characters defined in Unicode 15.0.