Sarnath is a place located 10 kilometres northeast of Varanasi, near the confluence of the Ganges and the Varuna rivers in Uttar Pradesh, India.

Taxila or Takshashila is a city in Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately 25 kilometres (16 mi) northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and is just south of the Haripur District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. In 326 BCE, Alexander the Great gained control of the city without a battle, as it was immediately surrendered to him by Omphis.

Gandhāra was an ancient region located in the present-day north-west Pakistan and parts of south-east Afghanistan. The region centered around the Peshawar valley and Swat valley, though the cultural influence of "Greater Gandhara" extended across the Indus river to the Taxila region in Potohar Plateau and westwards into the Kabul valley in Afghanistan, and northwards up to the Karakoram range.
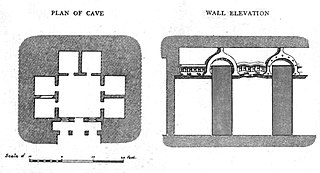
Vihāra generally refers to a Buddhist monastery for Buddhist renunciates, mostly in the Indian subcontinent. The concept is ancient and in early Sanskrit and Pali texts, it meant any arrangement of space or facilities for dwellings. The term evolved into an architectural concept wherein it refers to living quarters for monks with an open shared space or courtyard, particularly in Buddhism. The term is also found in Ajivika, Hindu and Jain monastic literature, usually referring to temporary refuge for wandering monks or nuns during the annual Indian monsoons. In modern Jainism, the monks continue to wander from town to town except during the rainy season (Chaturmas), and the term "vihara" refers to their wanderings.

Sirkap is the name of an archaeological site on the bank opposite to the city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan.
Buddhism, which originated in India, gradually dwindled and was replaced by approximately the 12th century. According to Lars Fogelin, this was "not a singular event, with a singular cause; it was a centuries-long process."

Azes II, may have been the last Indo-Scythian king, speculated to have reigned circa 35–12 BCE, in the northern Indian subcontinent. His existence has been questioned; if he did not exist, artefacts attributed to his reign, such as coins, are likely to be those of Azes I.

Buddhist religious architecture developed in the Indian subcontinent. Three types of structures are associated with the religious architecture of early Buddhism: monasteries (viharas), places to venerate relics (stupas), and shrines or prayer halls, which later came to be called temples in some places.

The Butkara Stupa is an important Buddhist stupa near Mingora, in the area of Swat, Pakistan. It may have been built by the Mauryan emperor Ashoka, but it is generally dated slightly later to the 2nd century BCE.

The Dharmarajika Stupa, also referred to as the Great Stupa of Taxila, is a Buddhist stupa near Taxila, Pakistan. It was built over the relics of the Buddha by Ashoka in the 3rd century BCE. The stupa, along with the large monastic complex that later developed around it, forms part of the Ruins of Taxila - which were inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1980.

Buddhism in Pakistan took root in the third century BCE under the Mauryan king Ashoka.

Indo-Greek art is the art of the Indo-Greeks, who reigned from circa 200 BCE in areas of Bactria and the Indian subcontinent. Initially, between 200 and 145 BCE, they remained in control of Bactria while occupying areas of Indian subcontinent, until Bactria was lost to invading nomads. After 145 BCE, Indo-Greek kings ruled exclusively in parts of ancient India, especially in Gandhara, in what is now present-day the northwestern Pakistan. The Indo-Greeks had a rich Hellenistic heritage and artistic proficiency as seen with the remains of the city of Ai-Khanoum, which was founded as a Greco-Bactrian city. In modern-day Pakistan, several Indo-Greeks cities are known such as Sirkap near Taxila, Barikot, and Sagala where some Indo-Greek artistic remains have been found, such as stone palettes. Some Buddhist cultural objects related to the Indo-Greeks are known, such as the Shinkot casket.By far the most important Indo-Greek remains found are numerous coins of the Indo-Greek kings, considered as some of the most artistically brilliant of Antiquity. Most of the works of art of the Greco-Buddhist art of Gandhara are usually attributed to the direct successors of the Indo-Greeks in Ancient India in the 1st century CE, such as the nomadic Indo-Scythians, the Indo-Parthians and, in an already decadent state, the Kushans. Many Gandharan works of art cannot be dated exactly, leaving the exact chronology open to interpretation. With the realization that the Indo-Greeks ruled in India until at least 10-20 CE with the reign of Strato II in the Punjab, the possibility of a direct connection between the Indo-Greeks and Greco-Buddhist art has been reaffirmed recently.

Jaulian is a ruined Buddhist monastery dating from the 2nd century CE, located in Taxila, in Pakistan.

Bhamala Stupa is a ruined Buddhist stupa and National Heritage Site near Haripur, Pakistan that dates to the 2nd century CE. It is located on the bank of Haro River, a tributary of a Khanpur Dam, and is a tourist destination. Bhamala stupa is part of the larger Bhamala Buddhist Complex. The site is known for its 1,700 year old statue of the Buddha attaining enlightenment - considered the oldest such statue in the world.

Devnimori, or Devni Mori, is a Buddhist archaeological site in northern Gujarat, about 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) from the city of Shamlaji, in the Aravalli District of northern Gujarat, India. The site is variously dated to the 3rd century or 4th century CE, or circa 400 CE. Its location was associated with trade routes and caravans in the area of Gujarat. Site excavations have yielded Buddhist artifacts dated prior to 8th-century in the lowest layer, mixed Buddhist and Hindu artwork from the Gurjara-Pratihara period in the middle, topped by Muslim glazed ware attributed to the 14th century. The site was excavated between 1960 and 1963. The site became flooded by the Meswo reservoir, a project started in 1959 and completed over 1971–1972 over the nearby Meshwo River.

Gandhāran Buddhism refers to the Buddhist culture of ancient Gandhāra which was a major center of Buddhism in the northwestern Indian subcontinent from the 3rd century BCE to approximately 1200 CE. Ancient Gandhāra corresponds to modern day north Pakistan, mainly the Peshawar valley and Potohar plateau as well as Afghanistan's Jalalabad. The region has yielded the Gandhāran Buddhist texts written in Gāndhārī Prakrit the oldest Buddhist manuscripts yet discovered. Gandhāra was also home to a unique Buddhist artistic and architectural culture which blended elements from Indian, Hellenistic, Roman and Parthian art. Buddhist Gandhāra was also influential as the gateway through which Buddhism spread to Central Asia and China.

The Sikri stupa is a work of Buddhist art dated to 3rd-4th century from the Kushan period in Gandahara, consisting of 13 narrative panels with events from the life of Buddha. Modern restoration accounts for their order in the Lahore Museum. The restoration began while Harold Arthur Deane was still assigned to the North-West Frontier Province in what was then British India. Three photos taken around 1890 show the order of the panels in the earliest restoration.

Ancient Indian architecture ranges from the Indian Bronze Age to around 800 CE. By this endpoint Buddhism in India had greatly declined, and Hinduism was predominant, and religious and secular building styles had taken on forms, with great regional variation, which they largely retain even after some forceful changes brought about by the arrival of first Islam, and then Europeans.
Kumāralāta was an Indian founder of the Sautrāntika school of Buddhism. He was a native of Taxila, in modern day Pakistan.
The Indian subcontinent has a long history of education and learning from the era of Indus Valley civilization. Important ancient institutions of learning in ancient India are Takshashila, Kashmir Smast, Nalanda, Valabhi University, Sharada Peeth, Pushpagiri Vihara, Odantapuri University, Vikramashila, Somapura Mahavihara, Bikrampur Vihara, Jagaddala Mahavihara.