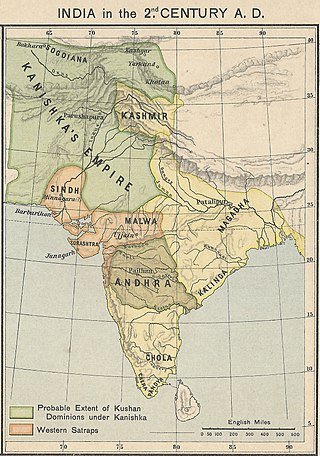
The Kushan Empire was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of modern-day territory of Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan and Northern India, at least as far as Saketa and Sarnath near Varanasi (Benares), where inscriptions have been found dating to the era of the Kushan Emperor Kanishka the Great.

Haḍḍa is a Greco-Buddhist archeological site located ten kilometers south of the city of Jalalabad, in the Nangarhar Province of eastern Afghanistan.

Mes Aynak, also called Mis Ainak or Mis-e-Ainak, was a major Buddhist settlement 40 km (25 mi) southeast of Kabul, Afghanistan, located in a barren region of Logar Province. The site is also the location of Afghanistan's largest copper deposit.

The Bimaran casket or Bimaran reliquary is a small gold reliquary for Buddhist relics that was found inside the stupa no.2 at Bimaran, near Jalalabad in eastern Afghanistan.
The Kidarites, or Kidara Huns, were a dynasty that ruled Bactria and adjoining parts of Central Asia and South Asia in the 4th and 5th centuries. The Kidarites belonged to a complex of peoples known collectively in India as the Huna, and in Europe as the Chionites, and may even be considered as identical to the Chionites. The 5th century Byzantine historian Priscus called them Kidarite Huns, or "Huns who are Kidarites". The Huna/Xionite tribes are often linked, albeit controversially, to the Huns who invaded Eastern Europe during a similar period. They are entirely different from the Hephthalites, who replaced them about a century later.
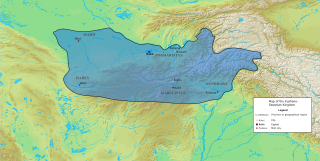
Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom is a historiographic term used by modern scholars to refer to a branch of the Sasanian Persians who established their rule in Bactria during the 3rd and 4th centuries CE at the expense of the declining Kushans. They captured the provinces of Sogdiana, Bactria and Gandhara from the Kushans in 225 CE. The Sasanians established governors for the Sasanian Empire, who minted their own coinage and took the title of Kushanshas, i.e. "Kings of the Kushans". They are sometimes considered as forming a "sub-kingdom" inside the Sasanian Empire. This administration continued until 360-370 CE, when the Kushano-Sasanians lost much of its domains to the invading Kidarite Huns, whilst the rest was incorporated into the imperial Sasanian Empire. Later, the Kidarites were in turn displaced by the Hephthalites. The Sasanians were able to re-establish some authority after they destroyed the Hephthalites with the help of the Turks in 565, but their rule collapsed under Arab attacks in the mid 7th century.

Tillya tepe, Tillia tepe or Tillā tapa is an archaeological site in the northern Afghanistan province of Jowzjan near Sheberghan, excavated in 1978 by a Soviet-Afghan team led by the Soviet archaeologist Viktor Sarianidi. The hoard found there is often known as the Bactrian gold.
Zunbil, also written as Zhunbil, or Rutbils of Zabulistan, was a royal dynasty south of the Hindu Kush in present southern Afghanistan region. They ruled from circa 680 AD until the Saffarid conquest in 870 AD. The Zunbil dynasty was founded by Rutbil, the elder brother of the Turk Shahi ruler, who ruled over Hephthalite kingdom from his capital in Kabul. The Zunbils are described as having Turkish troops in their service by Arabic sources like Tarikh al-Tabari and Tarikh-i Sistan.

Dilberjin Tepe, also Dilberjin or Delbarjin, is the modern name for the remains of an ancient town in modern (northern) Afghanistan. The town was perhaps founded in the time of the Achaemenid Empire. Under the Kushan Empire it became a major local centre. After the Kushano-Sassanids the town was abandoned.

Tepe Narenj, also Tappe-e Narenj, is the archaeological site for the remains of a 5th or 6th century Buddhist monastery near Kabul, Afghanistan. The site has been excavated under the direction of Zafar Paiman.

The Tillya Tepe Buddhist coin is a gold coin that was discovered at the archaeological site of Tillya Tepe in modern Afghanistan.

The Alchon Huns, also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. They were first mentioned as being located in Paropamisus, and later expanded south-east, into the Punjab and central India, as far as Eran and Kausambi. The Alchon invasion of the Indian subcontinent eradicated the Kidarite Huns who had preceded them by about a century, and contributed to the fall of the Gupta Empire, in a sense bringing an end to Classical India.

Kidara I fl. 350-390 CE) was the first major ruler of the Kidarite Kingdom, which replaced the Indo-Sasanians in northwestern India, in the areas of Kushanshahr, Gandhara, Kashmir and Punjab.

The Turk Shahis or Kabul Shahis were a dynasty of Western Turk, or mixed Turko-Hephthalite, origin, that ruled from Kabul and Kapisa to Gandhara in the 7th to 9th centuries AD. They may have been of Khalaj ethnicity. The Gandhara territory may have been bordering the Kashmir kingdom and the Kanauj kingdom to the east. From the 560s, the Western Turks had gradually expanded southeasterward from Transoxonia, and occupied Bactria and the Hindu-Kush region, forming largely independent polities. The Turk Shahis may have been a political extension of the neighbouring Western Turk Yabghus of Tokharistan. In the Hindu-Kush region, they replaced the Nezak Huns – the last dynasty of Bactrian rulers with origins among the Xwn (Xionite) and/or Huna peoples.

Gandhāran Buddhism refers to the Buddhist culture of ancient Gandhāra which was a major center of Buddhism in the northwestern Indian subcontinent from the 3rd century BCE to approximately 1200 CE. Ancient Gandhāra corresponds to modern day north Pakistan, mainly the Peshawar valley and Potohar plateau as well as Afghanistan's Jalalabad. The region has yielded the Gandhāran Buddhist texts written in Gāndhārī Prakrit the oldest Buddhist manuscripts yet discovered. Gandhāra was also home to a unique Buddhist artistic and architectural culture which blended elements from Indian, Hellenistic, Roman and Parthian art. Buddhist Gandhāra was also influential as the gateway through which Buddhism spread to Central Asia and China.

Balalyk tepe, in former Bactria, modern Uzbekistan, is a Central Asian archaeological site with many mural paintings. It was the site of a small fortified manor belonging to a princely Hephthalite clan. It is generally dated a bit later than the painting at Dilberjin, from the late 5th century to the early 7th century CE, or from the end of the 6th century to the early 7th century CE. The paintings of Balalyk Tepe are part of a "Tokharistan school", which also includes Adzhina-tepe and Kafyr-kala. They are succeeded chronologically by the Sogdian art of Penjikent.

The Fondukistan monastery was a Buddhist monastery located at the very top of a conical hill next to the Ghorband Valley, Parwan Province, about 117 kilometers northeast of Kabul. The monastery dates to the early 8th century CE, with a terminus post quem in 689 CE obtained through numismatic evidence, so that the Buddhist art of the site has been estimated to around 700 CE. This is the only secure date for this artistic period in the Hindu Kush, and it serves as an important chronological reference point.

Khair Khaneh is an archaeological site located near Kabul, Afghanistan. A Brahmanical Temple was excavated there in the 1930s by Joseph Hackin. The construction of the Khair Khaneh temple itself is dated to 608-630 CE, at the beginning of the Turk Shahis period. Most of the remains, including marble statuettes, date to the 7th–8th century, during the time of the Turk Shahi.

Tepe Sardar, also Tapa Sardar or Tepe-e-Sardar, is an ancient Buddhist monastery in Afghanistan. It is located near Ghazni, and it dominates the Dasht-i Manara plain. The site displays two major artistic phases, an Hellenistic phase during the 3rd to 6th century CE, followed by a Sinicized-Indian phase during the 7th to 9th century.

Tapa Shotor, also Tape Shotor or Tapa-e-shotor, was a large Sarvastivadin monastery near Hadda, Afghanistan, and is now an archaeological site. According to archaeologist Raymond Allchin, the site of Tapa Shotor suggests that the Greco-Buddhist art of Gandhara descended directly from the art of Hellenistic Bactria, as seen in Ai-Khanoum.



























