
The Amu Darya ,(Persian: آمو دریا) also shortened to Amu and historically known as the Oxus, is a major river in Central Asia, which flows through Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan and Afghanistan. Rising in the Pamir Mountains, north of the Hindu Kush, the Amu Darya is formed by the confluence of the Vakhsh and Panj rivers, in the Tigrovaya Balka Nature Reserve on the border between Afghanistan and Tajikistan, and flows from there north-westwards into the southern remnants of the Aral Sea. In its upper course, the river forms part of Afghanistan's northern border with Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan. In ancient history, the river was regarded as the boundary of Greater Iran with Turan, which roughly corresponded to present-day Central Asia. The Amu Darya has a flow of about 70 cubic kilometres per year on average.
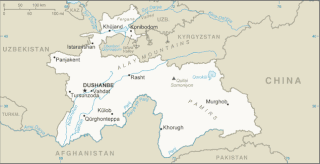
Tajikistan is nestled between Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan to the north and west, China to the east, and Afghanistan to the south. Mountains cover 93 percent of Tajikistan's surface area. The two principal ranges, the Pamir Mountains and the Alay Mountains, give rise to many glacier-fed streams and rivers, which have been used to irrigate farmlands since ancient times. Central Asia's other major mountain range, the Tian Shan, skirts northern Tajikistan. Mountainous terrain separates Tajikistan's two population centers, which are in the lowlands of the southern and northern sections of the country. Especially in areas of intensive agricultural and industrial activity, the Soviet Union's natural resource utilization policies left independent Tajikistan with a legacy of environmental problems.

Bactria, or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area within the north of modern Afghanistan. Bactria was strategically located south of Sogdia and the western part of the Pamir Mountains. The extensive mountain ranges acted as protective "walls" on three sides, with the Pamir on the north and the Hindu Kush on south forming a junction with the Karakoram range towards the east.

The Syr DaryaSEER-DAR-yə, historically known as the Jaxartes, is a river in Central Asia. The name, which is Persian, literally means Syr Sea or Syr River. It originates in the Tian Shan Mountains in Kyrgyzstan and eastern Uzbekistan and flows for 2,256.25 kilometres (1,401.97 mi) west and north-west through Uzbekistan, Sughd province of Tajikistan, and southern Kazakhstan to the northern remnants of the Aral Sea. It is the northern and eastern of the two main rivers in the endorheic basin of the Aral Sea, the other being the Amu Darya.

The Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex (BMAC) is the modern archaeological designation for a particular Middle Bronze Age civilisation of southern Central Asia, also known as the Oxus Civilization. The civilisation's urban phase or Integration Era, was dated in 2010 by Sandro Salvatori to c. 2400–1950 BC, but a different view is held by Nadezhda A. Dubova and Bertille Lyonnet, c. 2250–1700 BC.

Osh is the second-largest city in Kyrgyzstan, located in the Fergana Valley in the south of the country. It is often referred to as the "capital of the south". It is the oldest city in the country and has served as the administrative center of Osh Region since 1939. The city has an ethnically mixed population of 322,164 in 2021, comprising Kyrgyz, Uzbeks, Ukrainians, Koreans, and other smaller ethnic groups.

Termez is the capital of Surxondaryo Region in southern Uzbekistan. Administratively, it is a district-level city. Its population is 182,800 (2021). It is notable as the site of Alexander the Great's city Alexandria on the Oxus, as a center of early Buddhism, as a site of Muslim pilgrimage, and as a base of Soviet Union military operations in Afghanistan, accessible via the nearby Hairatan border crossing.

Zorkul is a lake in the Pamir Mountains that runs along the border between the Wakhan District in Badakhshan Province of Afghanistan and the Gorno-Badakhshan autonomous region of Tajikistan. It is part of both the Wakhan National Park of Afghanistan and the Tajik National Park.
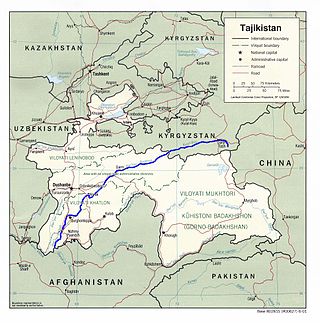
The Vakhsh, also known as the Surkhob in north-central Tajikistan and as the Kyzyl-Suu in Kyrgyzstan, is a Central Asian river and one of the main rivers of Tajikistan. It is a tributary of the Amu Darya river.

The National Museum of Tajikistan is a museum in Dushanbe, the capital city of Tajikistan.

The Oxus treasure is a collection of about 180 surviving pieces of metalwork in gold and silver, most relatively small, and around 200 coins, from the Achaemenid Persian period which were found by the Oxus river about 1877–1880. The exact place and date of the find remain unclear, but is often proposed as being near Kobadiyan. It is likely that many other pieces from the hoard were melted down for bullion; early reports suggest there were originally some 1500 coins, and mention types of metalwork that are not among the surviving pieces. The metalwork is believed to date from the sixth to fourth centuries BC, but the coins show a greater range, with some of those believed to belong to the treasure coming from around 200 BC. The most likely origin for the treasure is that it belonged to a temple, where votive offerings were deposited over a long period. How it came to be deposited is unknown.

The Amu Darya sturgeon or false shovelnose sturgeon is a critically endangered species of fish in the family Acipenseridae. It is found in Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan and perhaps Afghanistan. It inhabits quite shallow flowing waters that are turbid and muddy.

The Uzboy was a distributary of the Amu Darya which flowed through the northwestern part of the Karakum Desert of Turkmenistan until the 17th century, when it abruptly dried up, eliminating the agricultural population that had thrived along its banks..

Takht-i Sangin is an archaeological site located near the confluence of the Vakhsh and Panj rivers, the source of the Amu Darya, in southern Tajikistan. During the Hellenistic period it was a city in the Greco-Bactrian kingdom with a large temple dedicated to the Oxus, which remained in use in the following Kushan period, until the third century AD. The site may have been the source of the Oxus Treasure.

Saksanokhur (Саксанохур) is the modern name of a Hellenistic settlement of the Greco-Bactrian and Kushan kingdoms, located at the village of Shaftolubogh near Farkhor on a plateau of arable land near the meeting of the Kyzylsu and Panj rivers, in the south of present-day Tajikistan.

The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom was a Greek state of the Hellenistic period located in Central Asia. The kingdom was founded c. 256 BC by the Seleucid satrap Diodotus I Soter and lasted until its fall c. 120 BC. At its peak the kingdom consisted of present-day Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan, and small parts of Kazakhstan, Pakistan and Iran. An extension further east, with military campaigns and settlements, may have reached the borders of the Qin State in China by about 230 BC.
Sangtuda is a village and jamoat in Tajikistan. It is located in Danghara District in Khatlon Region. The jamoat has a total population of 12,686 (2015).
Torbulok is an archaeological site located in a foothill zone 50 km northwest of the Kyzylsu river valley and 20 km southeast of Danghara in the south of present-day Tajikistan. The site lies at the foot of the Čaltau mountain range. It was the site of a small sanctuary during the Hellenistic period, when the area was part of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom.

Oxus was an ancient Eastern Iranian god regarded as the divine representation of the Amu Darya. In Bactria he was also considered the king of the gods. Multiple different depictions of him are known from ancient Central Asian art. On an altar from his temple discovered in Takht-i Sangin he is depicted in the form of the Greek river god Marsyas presumably introduced by soldiers and settlers who arrived in this area during the reigns of Alexander the Great and the Seleucids. In Kushan art he was instead depicted as a Poseidon-like figure holding a staff and a fish. In Sogdian art he might have been depicted either as a horse or as a figure seated on a throne with horse protomes, though this proposal remains a matter of debate.




















