King Joseph's reply
- THE LETTER OF JOSEPH THE KING, SON OF AARON THE KING, THE TURK-MAY HIS CREATOR PRESERVE HIM TO THE HEAD OF THE ASSEMBLY, HASDAI, THE SON OF ISAAC, SON OF EZRA
....I wish to inform you that your beautifully phrased letter was given us by Isaac, son of Eliezer, a Jew of the land of Germany [Isaac carried it through Germany, Hungary, and Kievan Rus to Khazaria.] You made us happy and we are delighted with your understanding and wisdom.... Let us, therefore, renew the diplomatic relations that once obtained between our fathers, and let us transmit this heritage to our children. [Joseph believed the Khazars had once had diplomatic relations with the Spanish Arabs.]
You ask us also in your epistle: "Of what people, of what family, and of what tribe are you?" Know that we are descended from Japheth, through his son Togarmah. [In Jewish literature Togarmah is the father of all the Turks.] I have found in the genealogical books of my ancestors that Togarmah had ten sons. These are their names: the eldest was Ujur, the second Tauris, the third Avar, the fourth Uauz, the fifth Bizal, the sixth Tarna, the seventh Kozar, the eighth Janur, the ninth Bulgar, the tenth Sawir. [These are the mythical founders of tribes that once lived in the neighborhood of the Black and Caspian Seas.] I am a descendant of Khazar, the seventh son.
I have a record that although our fathers were few in number, the Holy One blessed be He [this is a common name for God], gave them strength, power, and might so that they were able to carry on war after war with many nations who were more powerful and numerous than they. By the help of God they drove them out and took possession of their country. Upon some of them they have imposed forced labor even to this very day. The land [along the Volga] in which I now live was formerly occupied by the Bulgars. Our ancestors, the Khazars, came and fought with them, and, although these Bulgars were as numerous as the sand on the shores of the sea [a reference to the Book of Joshua], they could not withstand the Khazars. So they left their country and fled while the Khazars pursued them as far as the Danube River. Up to this very day the Bulgars camp along the Danube and are close to Constantinople. The Khazars have occupied their land up till now.
After this, several generations passed until a certain King arose whose name was Bulan. He was a wise and God-fearing man, trusting in his Creator with all his heart. He expelled the wizards and idolaters from the land and took refuge in the shadow of his wings ... After this his fame was spread broadcast. The king of the Byzantines and the Arabs who had heard of him sent their envoys and ambassadors with great riches and many great presents to the King as well as some of their wise men with the object of converting him to their own religion. [The Byzantines and Arabs hoped to stop the raids of the Khazars by converting them and later make them allies through shared faith.]
But the King-may his soul be bound up in the bundle of life [a standard burial phrase for Jews] With the Lord his God-being wise, sent for a learned Israelite. the King searched, inquired, and investigated carefully and brought the sages together that they might argue about their respective religions. Each of them refuted, however, the arguments of his opponent so that they could not agree. When the King saw this he said to them: "Go home, but return to me on the third day…"
On the third day he called all the sages together and said to them. "Speak and argue with one another and make clear to me which is the best religion." They began to dispute with one another without arriving at any results until the King said to the Christian priest "What do you think? Of the religion of the Jews and the Muslims, which is to be preferred?" The priest answered: "The religion of the Israelites is better than that of the Muslims."
The King then asked the qadi: "What do you say? Is the religion of the Israelites, or that of the Christians preferable?" The qadi answered: "The religion of the Israelites is preferable."
Upon this the King said: "If this is so, you both have admitted with your own mouths that the religion of the Israelites is better Wherefore, trusting in the mercies of God and the power of the Almighty, I choose the religion of Israel, that is, the religion of Abraham. If that God in whom I trust, and in the shadow of whose wings I find refuge, will aid me, He can give me without labor the money, the gold, and the silver which you have promised me. As for you all, go now in peace to your land."
From that time on the Almighty helped Bulan, fortified him, and strengthened him. He circumcised himself, his servants, attendants, and all his people. [Arabic sources say the royal family and nobility became Jews, but most of the commoners did not.][?] Then Bulan sent for and brought from all places wise men of Israel who interpreted the Torah for him and arranged the precepts in order, and up to this very day we have been subject to this religion. May God's name be blessed and may His remembrance be exalted for ever!
Since that day, when my fathers entered into this religion, the God of Israel has humbled all of their enemies, subjecting every folk and tongue round about them, whether Christian, Muslim, or pagan. No one has been able to stand before them to this day [about 960]. All of them are tributary. [But only about ten years later Joseph was defeated by Sviatoslav I of Kiev, 969.]
After the days of Bulan there arose one of his descendants, a king Obadiah by name [the name means "God's servant"], who reorganized the kingdom and established the Jewish religion properly and correctly. He built synagogues and yeshivot, brought in Jewish scholars, and rewarded them with gold and silver. [The Jewish scholars could have come from Baghdad and Constantinople.] They explained to him the Bible, Mishnah, Talmud and the order of divine services. The King was a man who revered and loved the Torah. He was one of the true servants of God. May the Divine Spirit give him rest!
He was succeeded by Hezekiah, his son; next to him was Manasseh, his son; next to him was Hanukkah, the brother of Obadiah; next Isaac, his son; afterwards, his son Zebulun; then his son Moses; then his son Nissi; then his son Aaron; then his son Menahem; then his son Benjamin; then his son Aaron II; and I, Joseph, the son of Aaron the King, am King, the son of a King, and the descendant of kings. No stranger can occupy the throne of my ancestors: the son succeeds the father. This has been our custom and the custom of our forefathers since they have come into existence. May it be the gracious will of Him who appoints all kings that the throne of my kingdom shall endure to all eternity.
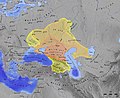
You have also asked me about the affairs of my country and the extent of my empire. I wish to inform you that I dwell by the banks of the river known as the Itil [Volga]. At the mouth of the river lies the Caspian Sea. The headwaters of the river turn eastward, a journey of four months distance.
Alongside the river dwell many tribes in cities and towns, in open as well as fortified places.... Bear in mind that I dwell at the delta of the Itil and, by God's help, I guard the mouth of the river and do not permit the Rus who come in ships to enter into the Caspian so as to get at the Muslims. Nor do I allow any of their [the Muslims'] enemies who come by land to penetrate as far as Derbend [Derbend, an Arab city, was the gate through which the nomads of eastern and southern Europe hoped to rush through and raid the rich towns of Asia Minor.] I have to wage war with them, for if I would give them any chance at all they would lay waste the whole land of the Muslims as far as Baghdad...
You have also asked me about the place where I live. I wish to inform you that, by the grace of God, I dwell alongside this river on which there are situated three capital cities. The queen dwells in one of them; it is my birthplace. It is quite large, built round like a circle, the diameter of which is fifty parasangs. [The King lived in an island in the Volga; there were also towns on both banks.]
Jews, Christians, and Moslems live in the second city. Besides these there are many slaves of all nations in it. It is of medium size, eight square parasangs in length and breadth.
In the third I reside with my princes, officers, servants, cupbearers and those who are close to me. It is round in shape and its diameter is three parasangs. The river flows within its walls. This is my residence during the winter. From the month of Nisan [March–April] on we leave the city and each one goes forth to his vineyards, fields and to his work...
You mention in your letter that you yearn to see my face. I also would very much like to see your pleasant countenance and the rare beauty of your wisdom and greatness. Would that it were according to your word. If it were granted me to be associated with you and to behold your honored, charming, and pleasant countenance then you would be as my father and I as your son. According to your command would all my people be ruled, and according to your order and discreet counsel would I conduct all my affairs. Farewell.