Galactokinase is an enzyme (phosphotransferase) that facilitates the phosphorylation of α-D-galactose to galactose 1-phosphate at the expense of one molecule of ATP. Galactokinase catalyzes the second step of the Leloir pathway, a metabolic pathway found in most organisms for the catabolism of α-D-galactose to glucose 1-phosphate. First isolated from mammalian liver, galactokinase has been studied extensively in yeast, archaea, plants, and humans.
In molecular biology, biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism.

The enzyme Trehalase is a glycoside hydrolase, produced by cells in the brush border of the small intestine, which catalyzes the conversion of trehalose to glucose. It is found in most animals.

Inositol oxygenase, also commonly referred to as myo-inositol oxygenase (MIOX), is a non-heme di-iron enzyme that oxidizes myo-inositol to glucuronic acid. The enzyme employs a unique four-electron transfer at its Fe(II)/Fe(III) coordination sites and the reaction proceeds through the direct binding of myo-inositol followed by attack of the iron center by diatomic oxygen. This enzyme is part of the only known pathway for the catabolism of inositol in humans and is expressed primarily in the kidneys. Recent medical research regarding MIOX has focused on understanding its role in metabolic and kidney diseases such as diabetes, obesity and acute kidney injury. Industrially-focused engineering efforts are centered on improving MIOX activity in order to produce glucaric acid in heterologous hosts.

Guanosine monophosphate synthetase, also known as GMPS is an enzyme that converts xanthosine monophosphate to guanosine monophosphate.
In enzymology, a mycothiol-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.306) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a mycothione reductase (EC 1.8.1.15) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme methionine γ-lyase (EC 4.4.1.11, MGL) is in the γ-family of PLP-dependent enzymes. It degrades sulfur-containing amino acids to α-keto acids, ammonia, and thiols:
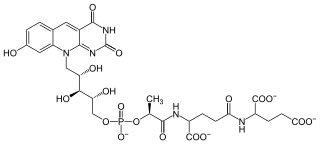
Coenzyme F420 or 8-hydroxy-5-deazaflavin is a coenzyme (sometimes called a cofactor) involved in redox reactions in methanogens, in many Actinomycetota, and sporadically in other bacterial lineages. It is a flavin derivative with an absorption maximum at 420 nm—hence its name. The coenzyme is a substrate for coenzyme F420 hydrogenase, 5,10-methylenetetrahydromethanopterin reductase and methylenetetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenase.
In enzymology, a 2-isopropylmalate synthase (EC 2.3.3.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1D-1-guanidino-3-amino-1,3-dideoxy-scyllo-inositol transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a galactinol-raffinose galactosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a galactinol-sucrose galactosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Mycothiol is an unusual thiol compound found in the Actinomycetota. It is composed of a cysteine residue with an acetylated amino group linked to glucosamine, which is then linked to inositol. The oxidized, disulfide form of mycothiol (MSSM) is called mycothione, and is reduced to mycothiol by the flavoprotein mycothione reductase. Mycothiol biosynthesis and mycothiol-dependent enzymes such as mycothiol-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase and mycothione reductase have been proposed to be good drug targets for the development of treatments for tuberculosis.
Mycothiol synthase is an enzyme with systematic name acetyl-CoA:desacetylmycothiol O-acetyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
D-inositol-3-phosphate glycosyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:1D-myo-inositol 3-phosphate alpha-D-glycosyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Lipid IVA 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinosyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name 4-amino-4-deoxy-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl ditrans, octacis-undecaprenyl phosphate:lipid IVA 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinopyranosyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
N-acetyl-1-D-myo-inositol-2-amino-2-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranoside deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.103, MshB) is an enzyme with systematic name 1-(2-acetamido-2-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl)-1D-myo-inositol acetylhydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction







