Same-sex marriage, also known as gay marriage, is the marriage of two people of the same legal sex. As of 2024, marriage between same-sex couples is legally performed and recognized in 36 countries, with a total population of 1.5 billion people. The most recent jurisdictions to legalize same-sex marriage are Greece and Aruba and Curaçao in the Netherlands. Two more countries, Liechtenstein and Thailand, are set to begin performing same-sex marriages in early 2025.
Same-sex marriage has been legal in the Netherlands since 1 April 2001. A bill for the legalisation of same-sex marriage was passed in the House of Representatives by 109 votes to 33 on 12 September 2000 and by the Senate by 49 votes to 26 on 19 December 2000. The law received royal assent by Queen Beatrix of the Netherlands on 21 December 2000 and took effect on 1 April 2001. The Netherlands was the first country in the world to legalize same-sex marriage. Polling suggests that a significant majority of Dutch people support the legal recognition of same-sex marriage.
This is a list of notable events in the history of LGBT rights that took place in the year 2002.

Rights affecting lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people vary greatly by country or jurisdiction—encompassing everything from the legal recognition of same-sex marriage to the death penalty for homosexuality.
Same-sex marriage is legal in Aruba and Curaçao, which are constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The islands are obliged to conduct same-sex marriages following a ruling from the Supreme Court of the Netherlands on 12 July 2024. In September 2021, a lower court in Curaçao ruled that preventing same-sex couples from marrying violates the equality provisions of the Constitution of Curaçao, but left the decision of whether to legalise same-sex marriage up to the Parliament of Curaçao. In December 2022, the Joint Court of Justice of Aruba, Curaçao, Sint Maarten, and of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba ruled on appeal that Aruba's and Curaçao's same-sex marriage bans were unconstitutional. The court order was set to go into effect on 7 March 2023 if not appealed to the Supreme Court; however, the governments of both Curaçao and Aruba subsequently appealed. On 12 July 2024, the Supreme Court upheld the lower court ruling, effectively legalizing same-sex marriage in Aruba and Curaçao with immediate effect.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Suriname may face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Both male and female expressions of same-sex sexual activity are legal in Suriname. Since 2015, hate speech and discrimination in employment and the provision of goods and services on the basis of sexual orientation has been banned in the country. Same-sex marriage and civil unions are not recognised by law. Nevertheless, Suriname is legally bound to the January 2018 Inter-American Court of Human Rights ruling, which held that same-sex marriage is a human right protected by the American Convention on Human Rights.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) rights in the Netherlands are among the most advanced in the world. Same-sex sexual activity was legalized in 1811 after France invaded the country and installed the Napoleonic Code, erasing any remaining sodomy laws. No more sodomy laws were enacted after the country received independence. An age of consent equal with that of heterosexual activity was put in place in 1971. During the late 20th century, awareness surrounding homosexuality grew and society became more tolerant of gay and bisexual people. The changes eventually led to homosexuality's declassification as a mental illness in 1973 and a ban on discrimination based on sexual orientation in the military. The Equal Treatment Act 1994 bans discrimination on account of sexual orientation in employment, housing, public accommodations, and other areas. This was extended in 2019 to include discrimination based on gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics. After the country began granting same-sex couples registered partnerships benefits in 1998, the Netherlands became the first country in the world to legalize same-sex marriage in 2001. Same-sex joint and stepchild adoption are also permitted, and lesbian couples can access IVF as well.

The Netherlands Antilles was an autonomous Caribbean country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It was dissolved on 10 October 2010.
Many countries in the Americas grant legal recognition to same-sex unions, with almost 85 percent of people in both North America and South America living in jurisdictions providing marriage rights to same-sex couples.
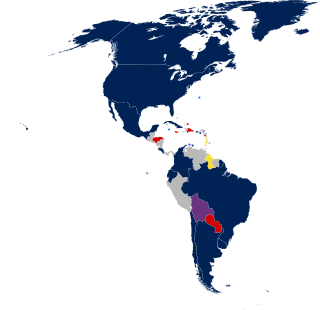
Laws governing lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights are complex and diverse in the Americas, and acceptance of LGBTQ persons varies widely.
The Joint Court of Justice of Aruba, Curaçao, Sint Maarten, and of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba serves the three Caribbean countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands and the three Caribbean special municipalities of the Netherlands. The court primarily hears disputes in first instance and on appeal of these six islands, and is on the same level as similar courts in the Netherlands. Since 2012, the court has also been authorized to hear inquiry procedures originated on Curaçao, of a type that would be heard in the Netherlands by the Enterprise Chamber in Amsterdam.

The history of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender people in the Netherlands has reflected the shades of tolerance or rigidity which were utilized by the rulers of the country at various periods in its history. Since World War II, the movement for LGBT rights has been galvanized by both events abroad and increasing liberalization domestically.
Same-sex marriage is legal in the following countries: Andorra, Argentina, Australia, Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Denmark, Ecuador, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Luxembourg, Malta, Mexico, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Portugal, Slovenia, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, the United Kingdom, the United States, and Uruguay. Same-sex marriage is recognized, but not performed in Israel.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people in Curaçao have similar rights to non-LGBT people. Both male and female same-sex sexual activity are legal in Curaçao. Discrimination on the basis of "heterosexual or homosexual orientation" is outlawed by the Curaçao Criminal Code.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Sint Maarten may face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Both male and female same-sex sexual activity are legal in Sint Maarten, a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, but same-sex marriage is not legal. Same-sex couples with Dutch nationality must travel to the Netherlands to get married, and that will not provide the rights of marriage in Sint Maarten.
Same-sex marriage has been legal in Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba since 10 October 2012, the effective date of legislation passed by the States General of the Netherlands enabling same-sex couples to marry. The Caribbean Netherlands was the first jurisdiction in the Caribbean to legalise same-sex marriage, and was followed a few months later by French Caribbean territories, including Guadeloupe and Martinique, in May 2013.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Bonaire are very progressive by Caribbean standards. Bonaire forms part of the Caribbean Netherlands and is a special municipality of the Netherlands. Both male and female same-sex sexual activity are legal in Bonaire, with same-sex marriage and adoption being legal since 2012. In addition, discrimination on the basis of "heterosexual and homosexual orientation" is outlawed.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Sint Eustatius are quite progressive by Caribbean standards. Sint Eustatius forms part of the Caribbean Netherlands and is a special municipality of the Netherlands. Both male and female same-sex sexual activity are legal in Sint Eustatius, with same-sex marriage, registered partnership, and adoption being legal since 2012. In addition, discrimination on the basis of "heterosexual and homosexual orientation" is outlawed.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Saba are very progressive by Caribbean standards. Saba forms part of the Caribbean Netherlands and is a special municipality of the Netherlands. Both male and female same-sex sexual activity are legal in Saba, with same-sex marriage and adoption being legal since 2012. In addition, discrimination on the basis of "heterosexual and homosexual orientation" is outlawed.

LGBT rights differ between the various states in the Caribbean. They are influenced by previous colonization from Europe as well as each state's own interpretation of laws. For many of the states, perceptions of LGBT individuals are unfavorable, and laws lack protections and rights for the community.













