
The Buggery Act 1533, formally An Acte for the punishment of the vice of Buggerie, was an Act of the Parliament of England that was passed during the reign of Henry VIII.
Gross indecency is a crime in some parts of the English-speaking world, originally used to criminalize sexual activity between men that fell short of sodomy, which required penetration. The term was first used in British law in a statute of the British Parliament in 1885 and was carried forward in other statutes throughout the British Empire. The offence was never actually defined in any of the statutes which used it, which left the scope of the offence to be defined by court decisions.
The Bolton 7 were a group of gay and bisexual men who were convicted on 12 January 1998 in the United Kingdom before Judge Michael Lever at Bolton Crown Court of the offences of gross indecency under the Sexual Offences Act 1956. Although gay sex was partially decriminalised by the Sexual Offences Act 1967, they were all convicted under section 13 of the 1956 Act because more than two men had sex together, which was still illegal. One of the participants was also six months under the statutory age of consent for male gay sex: at the time, such an age was set at 18, while the heterosexual and lesbian age of consent was instead set at 16.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Nigeria face severe challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. LGBT rights are generally infringed upon; both male and female expressions of homosexuality are illegal in Nigeria and punishable by up to 14 years of prison in the conventional court system. There is no legal protection for LGBT rights in Nigeria—a largely conservative country of more than 230 million people, split between a mainly Muslim north and a mainly Christian south. Very few LGBT persons are open about their sexual orientation, as violence against them is frequent. According to PinkNews, Nigerian authorities generally target the LGBT community. Many LGBT Nigerians are fleeing to countries with progressive law to seek protection.
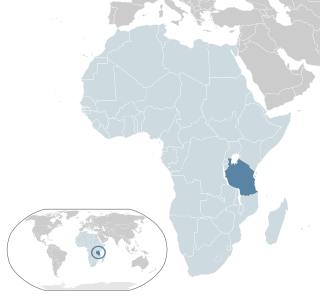
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Tanzania face severe challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Homosexuality in Tanzania is a socially taboo topic, and same-sex sexual acts are criminal offences, punishable with life imprisonment. The law also criminalises heterosexuals who engage in oral sex and anal intercourse.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Trinidad and Tobago face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same rights and benefits as that of opposite-sex couples.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Sri Lanka face significant challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Zambia face significant challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Same-sex sexual activity is illegal for both men and women in Zambia. Formerly a colony of the British Empire, Zambia inherited the laws and legal system of its colonial occupiers upon independence in 1964. Laws concerning homosexuality have largely remained unchanged since then, and homosexuality is covered by sodomy laws that also proscribe bestiality. Social attitudes toward LGBT people are mostly negative and coloured by perceptions that homosexuality is immoral and a form of insanity. However, in recent years, younger generations are beginning to show positive and open minded attitudes towards their LGBT peers.

This is a list of important events relating to the LGBT community from 1801 to 1900. The earliest published studies of lesbian activity were written in the early 19th century.

A sodomy law is a law that defines certain sexual acts as crimes. The precise sexual acts meant by the term sodomy are rarely spelled out in the law, but are typically understood and defined by many courts and jurisdictions to include any or all forms of sexual acts that are illegal, illicit, unlawful, unnatural and immoral. Sodomy typically includes anal sex, oral sex, manual sex, and bestiality. In practice, sodomy laws have rarely been enforced to target against sexual activities between individuals of the opposite sex, and have mostly been used to target against sexual activities between individuals of the same sex.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Antigua and Barbuda may face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ citizens.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Barbados do not possess the same legal rights as non-LGBT people. In December 2022, the courts ruled Barbados' laws against buggery and "gross indecency" were unconstitutional and struck them from the Sexual Offences Act. However, there is no recognition of same-sex relationships and only limited legal protections against discrimination.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Niue face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Male same-sex sexual activity is illegal in Niue, although there is no recent instance of it being actively prosecuted. Same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex married couples.
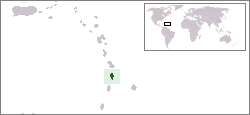
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people living in Saint Lucia face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ members of the population. Same-sex sexual activity is illegal for males, though the law is not enforced.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Grenada may face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. The penal code makes same-sex acts on Grenada proper illegal with a punishment up to 10 years in prison, it also does not address discrimination or harassment on the account of sexual orientation or gender identity, nor does it recognize same sex unions in any form, whether it be marriage or partnerships. Household headed by same-sex couples are also not eligible for any of the same rights given to opposite-sex married couples.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. The Penal Code makes same-sex sexual acts illegal with a punishment up to 10 years in prison, although the law is not enforced. In addition, it outlaws the practice of "buggery", whether homosexual or heterosexual and irrespective of whether the act was consensual. The country's laws also do not address discrimination or harassment on account of sexual orientation or gender identity, nor recognize same-sex unions in any form, whether it be marriage or partnerships. Households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for any of the same rights given to opposite-sex married couples. In 2024, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines upheld its constitutional ban on same-sex sexual activity within its High Court.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Tuvalu face legal difficulties not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Sections 153, 154 and 155 of the Penal Code outlaw male homosexual intercourse with a penalty of up to 14 years in prison, but the law is not enforced. Employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation has been banned since 2017. Since 2023, the Constitution of Tuvalu has banned same-sex marriage.
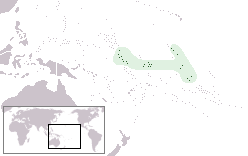
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Kiribati face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Male homosexuality is illegal in Kiribati with a penalty of up to 14 years in prison, but the law is not enforced. Female homosexuality is legal, but lesbians may face violence and discrimination. Despite this, employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation has been prohibited since 2015.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Northern Nigeria face unique legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Federal law prohibits all forms of homosexual activities and prescribes up to 14 years imprisonment for those found culpable. While the Maliki form of Shari'a law applied in 12 states have lesser penalty for unmarried persons, it prescribes the death penalty for married individuals.
Article 365 of the Sri Lankan Penal Code criminalizes "carnal intercourse against the order of nature" and provides for a penalty of up to ten years in prison.

![Recognition of same-sex unions in the Lesser Antilles and Puerto Rico
.mw-parser-output .legend{page-break-inside:avoid;break-inside:avoid-column}.mw-parser-output .legend-color{display:inline-block;min-width:1.25em;height:1.25em;line-height:1.25;margin:1px 0;text-align:center;border:1px solid black;background-color:transparent;color:black}.mw-parser-output .legend-text{}
Same-sex marriage
Unregistered cohabitation
Island subject to IACHR ruling
No recognition of same-sex couples
Constitutional ban on same-sex marriage
Same-sex sexual activity illegal but penalties not enforced
.mw-parser-output .hlist dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist ul{margin:0;padding:0}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt,.mw-parser-output .hlist li{margin:0;display:inline}.mw-parser-output .hlist.inline,.mw-parser-output .hlist.inline dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist.inline ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist.inline ul,.mw-parser-output .hlist dl dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist dl ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist dl ul,.mw-parser-output .hlist ol dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist ol ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist ol ul,.mw-parser-output .hlist ul dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist ul ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist ul ul{display:inline}.mw-parser-output .hlist .mw-empty-li{display:none}.mw-parser-output .hlist dt::after{content:": "}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li::after{content:" * ";font-weight:bold}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li:last-child::after{content:none}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd dd:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dd dt:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dd li:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt dd:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt dt:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt li:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist li dd:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist li dt:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist li li:first-child::before{content:" (";font-weight:normal}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd dd:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dd dt:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dd li:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt dd:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt dt:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt li:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li dd:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li dt:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li li:last-child::after{content:")";font-weight:normal}.mw-parser-output .hlist ol{counter-reset:listitem}.mw-parser-output .hlist ol>li{counter-increment:listitem}.mw-parser-output .hlist ol>li::before{content:" "counter(listitem)"\a0 "}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd ol>li:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt ol>li:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist li ol>li:first-child::before{content:" ("counter(listitem)"\a0 "}
.mw-parser-output .navbar{display:inline;font-size:88%;font-weight:normal}.mw-parser-output .navbar-collapse{float:left;text-align:left}.mw-parser-output .navbar-boxtext{word-spacing:0}.mw-parser-output .navbar ul{display:inline-block;white-space:nowrap;line-height:inherit}.mw-parser-output .navbar-brackets::before{margin-right:-0.125em;content:"[ "}.mw-parser-output .navbar-brackets::after{margin-left:-0.125em;content:" ]"}.mw-parser-output .navbar li{word-spacing:-0.125em}.mw-parser-output .navbar a>span,.mw-parser-output .navbar a>abbr{text-decoration:inherit}.mw-parser-output .navbar-mini abbr{font-variant:small-caps;border-bottom:none;text-decoration:none;cursor:inherit}.mw-parser-output .navbar-ct-full{font-size:114%;margin:0 7em}.mw-parser-output .navbar-ct-mini{font-size:114%;margin:0 4em}html.skin-theme-clientpref-night .mw-parser-output .navbar li a abbr{color:var(--color-base)!important}@media(prefers-color-scheme:dark){html.skin-theme-clientpref-os .mw-parser-output .navbar li a abbr{color:var(--color-base)!important}}@media print{.mw-parser-output .navbar{display:none!important}}
v
t
e Same-sex legislation Lesser Antilles (named).svg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/dd/Same-sex_legislation_Lesser_Antilles_%28named%29.svg/280px-Same-sex_legislation_Lesser_Antilles_%28named%29.svg.png)
















