This is a list of notable events in the history of LGBT rights that took place in the year 1998.
This is a list of notable events in the history of LGBT rights that took place in the year 1997.
This is a list of notable events in the history of LGBT rights that took place in the year 1995.
Section 377 is a British colonial penal code that criminalized all sexual acts "against the order of nature". The law was used to prosecute people engaging in oral and anal sex along with homosexual activity. As per a Supreme Court Judgement since 2018, the Indian Penal Code Section 377 is used to convict non-consensual sexual activities among homosexuals with a minimum of ten years’ imprisonment extended to life imprisonment. It has been used to criminalize third gender people, such as the apwint in Myanmar. In 2018, then British Prime Minister Theresa May acknowledged how the legacies of such British colonial anti-sodomy laws continue to persist today in the form of discrimination, violence, and even death.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people in Jamaica face legal and social issues not experienced by heterosexual and gender-conforming people. Consensual sexual intercourse between same-sex partners is legally punishable by up to 10 years of imprisonment in the country.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Kenya face significant challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Sodomy is a felony per Section 162 of the Kenyan Penal Code, punishable by 21 years' imprisonment, and any sexual practices are a felony under section 165 of the same statute, punishable by five years' imprisonment. On 24 May 2019, the High Court of Kenya refused an order to declare sections 162 and 165 unconstitutional. The state does not recognise any relationships between persons of the same sex; same-sex marriage is banned under the Kenyan Constitution since 2010. There are no explicit protections against discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity. Adoption is restricted to heterosexual couples only.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Botswana face legal issues not experienced by non-LGBTQ citizens. Both female and male same-sex sexual acts have been legal in Botswana since 11 June 2019 after a unanimous ruling by the High Court of Botswana. Despite an appeal by the government, the ruling was upheld by the Botswana Court of Appeal on 29 November 2021.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Trinidad and Tobago face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same rights and benefits as that of opposite-sex couples.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Dominica face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Homosexuality has been legal since 2024, when the High Court struck down the country's colonial-era sodomy law. Dominica provides no recognition to same-sex unions, whether in the form of marriage or civil unions, and no law prohibits discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation or gender identity.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Guyana face legal and societal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Guyana is the only country in South America, and the only mainland country in the Americas, where homosexual acts, including anal sex and oral sex, are illegal. Cross-dressing was illegal until November 2018, when the statute was struck down by the Caribbean Court of Justice, the court of last resort of Guyana.
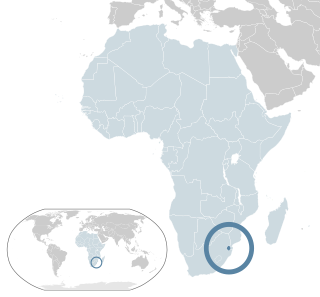
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Eswatini have limited legal rights. According to Rock of Hope, a Swati LGBT advocacy group, "there is no legislation recognising LGBTIs or protecting the right to a non-heterosexual orientation and gender identity and as a result [LGBT people] cannot be open about their orientation or gender identity for fear of rejection and discrimination." Homosexuality is illegal in Eswatini, though this law is in practice unenforced. According to the 2021 Human Rights Practices Report from the US Department of State, "there has never been an arrest or prosecution for consensual same-sex conduct."
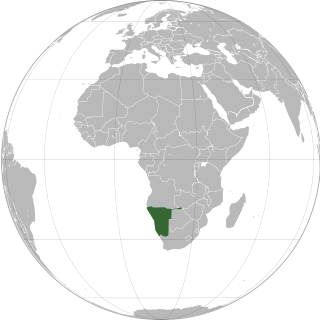
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Namibia have expanded in the 21st century, although LGBT people still have limited legal protections. Namibia's colonial-era laws criminalising male homosexuality were historically unenforced, and were overturned by the country's High Court in 2024.

National Coalition for Gay and Lesbian Equality and Another v Minister of Justice and Others is a decision of the Constitutional Court of South Africa which struck down the laws prohibiting consensual sexual activities between men. Basing its decision on the Bill of Rights in the Constitution – and in particular its explicit prohibition of discrimination based on sexual orientation – the court unanimously ruled that the crime of sodomy, as well as various other related provisions of the criminal law, were unconstitutional and therefore invalid.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Antigua and Barbuda may face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ citizens.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Mauritius have expanded in the 21st century, although LGBT Mauritians may still face legal difficulties not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Prior to 2023, sodomy was criminalized by Section 250 of the Criminal Code. However, Mauritius fully decriminalized homosexuality in October 2023. Although same-sex marriage is not recognized in Mauritius, LGBT people are broadly protected from discrimination in areas such as employment and the provision of goods and services, making it one of the few African countries to have such protections for LGBT people. The Constitution of Mauritius guarantees the right of individuals to a private life.
This article gives a broad overview of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) history in Canada. LGBT activity was considered a crime from the colonial period in Canada until 1969, when Bill C-150 was passed into law. However, there is still discrimination despite anti-discrimination law. For a more detailed listing of individual incidents in Canadian LGBT history, see also Timeline of LGBT history in Canada.

Maurice Tomlinson is a Jamaican lawyer, law professor, and gay rights activist currently living in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. He has been a leading gay rights and HIV activist in the Caribbean for over 20 years and is one of the only Jamaican advocates to challenge the country's 1864 British colonially-imposed anti gay Sodomy Law. This law predominantly affects men who have sex with men (MSM) and carries a possible jail sentence of up to ten years imprisonment with hard labour.

Caleb Orozco is an LGBT activist in Belize. He was the chief litigant in a case successfully challenging the anti-sodomy laws of Belize and the co-founder of the only LGBT advocacy group in the country.

Orozco v Attorney General (2016) 90 WIR 161, also known as Orozco v AG, the Orozco case, or the UNIBAM case, was a landmark case heard by the Supreme Court of Belize, which held that a long-standing buggery statute breached constitutional rights to dignity, equality before the law, freedom of expression, privacy, and non-discrimination on grounds of sex, and which declared the statute null and void to the applicable extent. The decision decriminalised consensual same-sex intercourse for the first time in 127 years, and established that the constitutional right to non-discrimination on grounds of sex extended to sexual orientation.
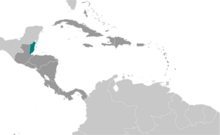

![Homosexuality laws in Central America and the Caribbean Islands.
.mw-parser-output .legend{page-break-inside:avoid;break-inside:avoid-column}.mw-parser-output .legend-color{display:inline-block;min-width:1.25em;height:1.25em;line-height:1.25;margin:1px 0;text-align:center;border:1px solid black;background-color:transparent;color:black}.mw-parser-output .legend-text{}
Same-sex marriage
Other type of partnership
Unregistered cohabitation
Country subject to IACHR ruling
No recognition of same-sex couples
Constitution limits marriage to opposite-sex couples
Same-sex sexual activity illegal but law not enforced
.mw-parser-output .hlist dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist ul{margin:0;padding:0}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt,.mw-parser-output .hlist li{margin:0;display:inline}.mw-parser-output .hlist.inline,.mw-parser-output .hlist.inline dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist.inline ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist.inline ul,.mw-parser-output .hlist dl dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist dl ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist dl ul,.mw-parser-output .hlist ol dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist ol ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist ol ul,.mw-parser-output .hlist ul dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist ul ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist ul ul{display:inline}.mw-parser-output .hlist .mw-empty-li{display:none}.mw-parser-output .hlist dt::after{content:": "}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li::after{content:" * ";font-weight:bold}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li:last-child::after{content:none}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd dd:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dd dt:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dd li:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt dd:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt dt:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt li:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist li dd:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist li dt:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist li li:first-child::before{content:" (";font-weight:normal}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd dd:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dd dt:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dd li:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt dd:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt dt:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt li:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li dd:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li dt:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li li:last-child::after{content:")";font-weight:normal}.mw-parser-output .hlist ol{counter-reset:listitem}.mw-parser-output .hlist ol>li{counter-increment:listitem}.mw-parser-output .hlist ol>li::before{content:" "counter(listitem)"\a0 "}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd ol>li:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt ol>li:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist li ol>li:first-child::before{content:" ("counter(listitem)"\a0 "}
.mw-parser-output .navbar{display:inline;font-size:88%;font-weight:normal}.mw-parser-output .navbar-collapse{float:left;text-align:left}.mw-parser-output .navbar-boxtext{word-spacing:0}.mw-parser-output .navbar ul{display:inline-block;white-space:nowrap;line-height:inherit}.mw-parser-output .navbar-brackets::before{margin-right:-0.125em;content:"[ "}.mw-parser-output .navbar-brackets::after{margin-left:-0.125em;content:" ]"}.mw-parser-output .navbar li{word-spacing:-0.125em}.mw-parser-output .navbar a>span,.mw-parser-output .navbar a>abbr{text-decoration:inherit}.mw-parser-output .navbar-mini abbr{font-variant:small-caps;border-bottom:none;text-decoration:none;cursor:inherit}.mw-parser-output .navbar-ct-full{font-size:114%;margin:0 7em}.mw-parser-output .navbar-ct-mini{font-size:114%;margin:0 4em}html.skin-theme-clientpref-night .mw-parser-output .navbar li a abbr{color:var(--color-base)!important}@media(prefers-color-scheme:dark){html.skin-theme-clientpref-os .mw-parser-output .navbar li a abbr{color:var(--color-base)!important}}@media print{.mw-parser-output .navbar{display:none!important}}
v
t
e Homosexuality laws in Central America and the Caribbean Islands.svg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b4/Homosexuality_laws_in_Central_America_and_the_Caribbean_Islands.svg/280px-Homosexuality_laws_in_Central_America_and_the_Caribbean_Islands.svg.png)













