| La Mesa Ecopark | |
|---|---|
| La Mesa Resort Zone | |
  The ecopark pond in November 2011 | |
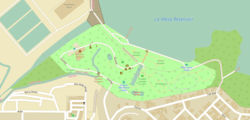 Approximate boundaries of La Mesa Ecopark are shown in light green. | |
| Location | East Fairview, Greater Lagro, Quezon City, Metro Manila, the Philippines |
| Coordinates | 14°42′43″N121°04′27.5″E / 14.71194°N 121.074306°E |
| Area | 33 hectares (82 acres) |
| Opened | 1950s |
| Founder | Metropolitan Waterworks and Sewerage System |
| Etymology | La Mesa Watershed Reservation |
| Owned by | Quezon City Parks Development and Administration Department |
| Operated by | La Mesa Ecopark Administration Manila Water Foundation ABS-CBN Foundation (former operator) |
| Visitors | 280,000(in 2011) [1] |
| Website | former Facebook page |
The La Mesa Ecopark is a public park located in Greater Lagro, Quezon City, Metro Manila, Philippines. It is in the La Mesa Watershed Reservation and near the La Mesa Dam.
Contents
The park closed temporarily on February 12, 2024 after the ABS-CBN Foundation returned management of the park to the Metropolitan Waterworks and Sewerage System. [2] It is partially reopened on June 29, 2024 under the management of the Manila Water Foundation. [3] [4]



