
Podocnemididae is a family of pleurodire (side-necked) turtles, once widely distributed. Most of its 41 genera and 57 species are now extinct. Seven of its eight surviving species are native to South America: the genus Peltocephalus, with two species, only one of which is extant ; and the genus Podocnemis, with six living species of South American side-necked river turtles and four extinct. There is also one genus native to Madagascar: Erymnochelys, the Madagascan big-headed turtle, whose single species E. madagascariensis.

Archelon is an extinct marine turtle from the Late Cretaceous, and is the largest turtle ever to have been documented, with the biggest specimen measuring 4.6 m (15 ft) from head to tail and 2.2–3.2 t in body mass. It is known only from the Pierre Shale and has one species, A. ischyros. In the past, the genus also contained A. marshii and A. copei, though these have been reassigned to Protostega and Kansastega, respectively. The genus was named in 1895 by American paleontologist George Reber Wieland based on a skeleton from South Dakota, who placed it into the extinct family Protostegidae. The leatherback sea turtle was once thought to be its closest living relative, but now, Protostegidae is thought to be a completely separate lineage from any living sea turtle.

Zuniceratops is a genus of ceratopsian dinosaurs that lived during the Turonian stage of the Late Cretaceous in what is now New Mexico, United States. Only a single species is known, Zuniceratops christopheri.
The Lakota Formation is a sequence of rocks of early Cretaceous age from Western North America. Located in South Dakota, the name of the formation is derived from the Lakota Native American tribe.

The Fort Union Formation is a geologic unit containing sandstones, shales, and coal beds in Wyoming, Montana, and parts of adjacent states. In the Powder River Basin, it contains important economic deposits of coal, uranium, and coalbed methane.
Tyler R. Lyson is an American paleontologist. He is the discoverer of the dinosaur fossil Dakota, a fossilized mummified hadrosaur. He has done significant research on the evolution of turtles and on the rise of mammals after the extinction of the dinosaurs.

The Pierre Shale is a geologic formation or series in the Upper Cretaceous which occurs east of the Rocky Mountains in the Great Plains, from Pembina Valley in Canada to New Mexico.

Toxochelys is an extinct genus of marine turtle from the Late Cretaceous period. It is the most commonly found fossilized turtle species in the Smoky Hill Chalk, in western Kansas.
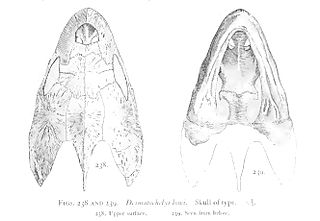
Desmatochelys is an extinct genus of sea turtles belonging to the family Protostegidae. This genus contains two known species, D. lowii and D. padillai. D. lowii was first discovered in 1895, followed by D. padillai in 2015. Having been estimated at over 120 million years old, D. padillai is currently the oldest known species of sea turtle.

Brachychampsa is an extinct genus of alligatorid, possibly a basal caiman. Specimens have been reported from New Mexico, Colorado, Wyoming, Montana, North and South Dakota, New Jersey, and Saskatchewan, though only those from Montana, Utah, and New Mexico are based on material sufficient to justify the referral. Some specimens have been reported from the Campanian-aged deposits of Central Asia, although the species status is indeterminate for these fossils. The genus first appeared during the late Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous and became extinct during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Cretaceous. Brachychampsa is distinguished by an enlarged fifth maxillary tooth in the upper jaw.
Peckemys is an extinct genus of baenid turtle which existed in the Hell Creek Formation, United States during the late Cretaceous period. It was first named by Tyler R. Lyson and Walter G. Joyce in 2009 and the type species is Peckemys brinkman.
Gamerabaena is an extinct genus of baenid turtle which existed in North Dakota during the late Cretaceous Period. It is known from a single fragmentary skull that was found in the Maastrichtian-age Hell Creek Formation. It contains the species Gamerabaena sonsalla. Gamerabaena is similar to the genus Palatobaena, but it differs in its lack of a posterior expansion of the triturating surface, a somewhat rectangular skull, and a wide angle between the maxillae. Gamerabaena also has a lingual ridge on the inner side of the jaw that is not seen in Palatobaena.
Palatobaena is an extinct genus of baenid turtle. It was first named by Gaffney in 1972 and the type species is Palatobaena bairdi. It based on a fragmentary skull from the Fort Union Formation of the Bighorn Basin of Wyoming. The two other species are P. gaffneyi and P. cohen which existed in Hell Creek Formation, North Dakota during the late Cretaceous period.

Baenidae is an extinct family of paracryptodiran turtles known from the Early Cretaceous to Eocene of North America. While during the Early Cretaceous they are found across North America, during the Late Cretaceous they are only found in Laramidia, having disappeared from Appalachia. The majority of lineages survived the K-Pg Extinction, but the family was extinct by the latest Eocene. The name of the type genus, Baena, appears to be of Native American origin. They are primarily found in freshwater deposits, and are considered to be aquatic, with a largely generalist habit.
Denazinemys was a genus of baenid turtle that lived in the Late Cretaceous of New Mexico. The holotype specimen, which D. nodosa was based on, USNM 8345, consists of a partial carapace and plastron. It came from the De-na-zin Member of the Kirtland Formation, and therefore, Denazinemys lived in the Kirtlandian land-vertebrate age. Many specimens other than the holotype have been assigned to Denazinemys.

Suskityrannus is a genus of small tyrannosauroid theropod from the Late Cretaceous in southern Laramidia. It contains a single species, Suskityrannus hazelae, and the type specimen was found in the Turonian-age Moreno Hill Formation of the Zuni Basin in western New Mexico.

Adelolophus is a genus of lambeosaurine dinosaur from Upper Cretaceous rocks in the U.S. state of Utah. The type and only known species is A. hutchisoni; the type specimen consists only of a broken maxilla. It constitutes the oldest known lambeosaur remains from North America, as well as the only known lambeosaur species from the Wahweap Formation, of which it pertains to the Upper Member. Among its relatives, it seems to be particularly similar to Parasaurolophus, rather than animals like Lambeosaurus; phylogenetic analysis confirms this, finding it in Parasaurolophini. It would have lived in a wet environment, bordering on the sea but with a more arid season during some times of the year. This environment would have been shared with a diverse variety of fish and turtles, as well as other dinosaurs like ceratopsids and tyrannosaurids.

Neurankylus is an extinct genus of turtles in the family Baenidae that lived between 112 and 61 million years ago in Canada and the United States. It was originally placed within the monotypic family Neurankylidae, but it has since been placed in the Neurankylinae, alongside Trinitichelys. The type species, Neurankylus eximius, was described by Lawrence Lambe in 1902. The species N. lithographicus was discovered in the Milk River Formation (Canada), alongside the holotype of the pachycephalosaurid dinosaur Acrotholus audeti.
Arvinachelys goldeni is an extinct baenid turtle from the Late Cretaceous of Utah. A. goldeni is notable among turtles for the presence of two nasal openings instead of one, giving it a vaguely pig-nosed appearance in life.

Compsemydidae is an extinct family of turtles, likely belonging to the clade Paracryptodira. The earliest undisputed member is Tongemys from the Berriasian age of the Early Cretaceous; two Late Jurassic genera have also sometimes been included in the group, but may alternatively be members of the family Pleurosternidae. The genus Compsemys survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event and lasted until the Thanetian age of the Paleocene.












