| Baenids Temporal range: (Valanginian to Eocene, | |
|---|---|
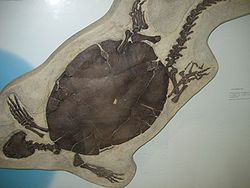 | |
| Chisternon , AMNH | |
 | |
| Shellof Baena arenosa (AMNH 1112) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Pantestudines |
| Clade: | Testudinata |
| Clade: | † Paracryptodira |
| Superfamily: | † Baenoidea |
| Family: | † Baenidae Cope, 1882 |
Baenidae is an extinct family of paracryptodiran turtles known from the Early Cretaceous to Eocene of North America. [1] [2] While during the Early Cretaceous they are found across North America, during the Late Cretaceous they are only found in Laramidia, having disappeared from Appalachia. Most lineages survived the K-Pg Extinction, but the family was extinct by the latest Eocene. The name of the type genus, Baena, appears to be of Native American origin, likely from the Arapaho be’enoo. They are primarily found in freshwater deposits, and are considered to be aquatic, with a largely generalist habit. [3]


