
The Chelydridae is a family of turtles that has seven extinct and two extant genera. The extant genera are the snapping turtles, Chelydra and Macrochelys. Both are endemic to the Western Hemisphere. The extinct genera are Acherontemys, Chelydrops, Chelydropsis, Emarginachelys, Macrocephalochelys, Planiplastron, and Protochelydra.

Janenschia is a large herbivorous sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Tendaguru Formation of Tanzania, Africa, 155 million years ago.

Tornieria is a genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaur from Late Jurassic of Tanzania. It has a convoluted taxonomic history.

"Ischyrosaurus" was a genus of sauropod dinosaur from the Kimmeridgian-age Upper Jurassic Kimmeridge Clay of Dorset, England. It was once synonymized with the Early Cretaceous-age Pelorosaurus.

Machimosaurus is an extinct genus of machimosaurid crocodyliform from the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. The type species, Machimosaurus hugii, was found in Switzerland. Other fossils have been found in England, France, Germany, Portugal, Switzerland and Tunisia. Machimosaurus rex is the largest named teleosauroid and thalattosuchian, with an estimated length of approximately 7.2 metres. Machimosaurus is the largest known crocodyliform of the Jurassic.

Placochelys is an extinct genus of placodont reptiles erected by Otto Jaekel in 1902.

Elseya is a genus of large side-necked turtles, commonly known as Australian snapping turtles, in the family Chelidae. Species in the genus Elseya are found in river systems in northern and northeastern Australia and throughout the river systems of New Guinea. They are identified by the presence of alveolar ridges on the triturating surfaces of the mouth and the presence of a complex bridge strut.

Manouria is a genus of tortoises in the family Testudinidae. The genus was erected by John Edward Gray in 1854.

Rhinoclemmys is a genus of turtles in the family Geoemydidae, the only genus in the subfamily Rhinoclemmydinae. Member species of the genus are commonly known as the Neotropical wood turtles and are the only geoemydids known from the Americas. As such, they have adapted to a wide range of habitats, which is reflected in the species' common names.
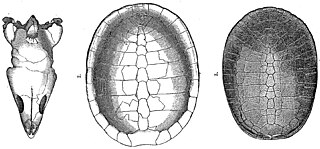
Glyptops is an extinct genus of pleurosternid freshwater turtle known from the Late Jurassic of North America.

Thalassemys is a genus of extinct thalassochelydian turtle from the Late Jurassic of western and central Europe. While the genus was originally named by Rütimeyer in 1859 for a large carapace and other associated fragments from the late Kimmeridgian of the Reuchenette Formation of Switzerland, although the taxon was not validly named until 1873 when Rütimeyer designated the type species T. hugii. Rütimeyer also named T. gresslyi from the Reunchenette Formation in the same paper as T. hugii, but it cannot be differentiated from the type material of T. hugii and is therefore a junior synonym. A large assemblage of shell and postcranial material from the Reunchenette was named as a species of Eurysternum, E. ignoratum, by Bräm in 1965. While originally distinguished based on the presence of fontanelles on the plastron, the feature was later identified on T. hugii and E. ignoratum was designated a junior synonym. Additional material from the Kimmeridge Clay of the United Kingdom has also been referred to T. hugii.

Dorsetochelys is an extinct genus of turtle from the Early Cretaceous of southern England and northwestern Germany.

The Myuchelys is a genus of turtles, the Australian saw-shelled turtles, in the family Chelidae and subfamily Chelodininae. They inhabit the headwaters and tributaries of rivers within their range and this led to the name Myuchelys, which is formed from the Aboriginal word myuna meaning clear water and the Greek chelys meaning turtle. They have a short neck and the intergular scute completely separates the gular scutes. They have no alveolar ridge separating them from the snapping turtles of the genus Elseya.

Eurysternum is an extinct genus of thalassochelydian turtle. Its type species is Eurysternum wagleri, the holotype of which has since been lost and only survives in illustrations.

Pleurosternon is an extinct genus of freshwater pleurosternid turtle from the late Jurassic period to the early Cretaceous period of Europe. Its type species, P. bullocki was described by the paleontologist Richard Owen in 1853. Since then, and throughout the late 19th century, many fossil turtles were incorrectly assigned to this genus, though only two are currently considered valid.
Mesorhinosuchus is an extinct genus of basal phytosaur possibly known from the Early Triassic of Saxony-Anhalt, central-eastern Germany. It was first named by Otto Jaekel in 1910 and the type species is Mesorhinus fraasi. The generic name Mesorhinus was preoccupied by Mesorhinus piramydatus Ameghino, 1885, a macraucheniid meridiungulatan mammal. Thus, an alternative generic name, Mesorhinosuchus, was proposed by Oskar Kuhn in 1961. The genus is occasionally misspelled as Mesorhinosaurus, while Stocker and Butler (2013) recently misspelled its original generic name as Mesosuchus.

Palaeoamyda is an extinct genus of softshell turtle belonging to the family Trionychidae. Remains have been found in the Eocene of Germany.
Achelonia is an extinct genus of marine thalassochelydian turtle. Its type species is Achelonia formosa. Fossils are known from the Upper Jurassic of Wattendorf, Germany, Cerin, France, and England. Material from England was originally considered to belong to the separate genus Enaliochelys and species Enaliochelys chelonia, named by Harry Govier Seeley in 1869 for a partial disarticulated skeleton from the early Kimmeridgian of the Kimmeridge Clay in Cambridgeshire. The synonymy was recognised in 2020.

Helochelydra is an extinct genus of extinct stem turtle known from the Early Cretaceous (Barremian) of the Isle of Wight, southern England.
Euryaspis is a dubious genus of extinct thalassochelydian turtle from the Late Jurassic of Germany. The type and only species is Euryaspis radians, originally proposed by Wagner in 1859 before being validly described and illustrated in 1861. The only specimen was a partial carapace probably from the Tithonian, although the original locality is unknown. The genus is referred to Thalassochelydia and has been considered a synonym of Eurysternum or Acichelys before, but casts that remain of the lost holotype show that it bears no features that can clarify its validity making it a nomen dubium.


















