
Camptosaurus is a genus of plant-eating, beaked ornithischian dinosaurs of the Late Jurassic period of western North America. The name means 'flexible lizard'.
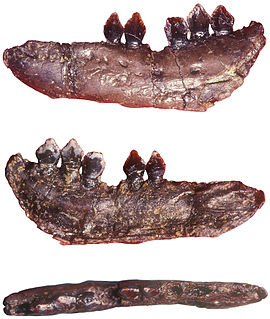
Echinodon is a genus of heterodontosaurid dinosaur that lived during the earliest Cretaceous of southern England and possibly western France in the Berriasian epoch. The first specimens were jaw bones named Echinodon becklesii by Sir Richard Owen in 1861, and since their original description only additional teeth have been discovered. The specific name honours collector Samuel Beckles who discovered the material of Echinodon and many other taxa from across England, while the genus name translates as "prickly tooth" in reference to the dental anatomy of the taxon.

Goniopholis is an extinct genus of goniopholidid crocodyliform that lived in Europe and Africa during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. Being semi-aquatic it is very similar to modern crocodiles. It ranged from 2–4 metres in length, and would have had a very similar lifestyle to the American alligator or Nile crocodile.

Nuthetes is the name given to a dubious dromaeosaurid, genus of theropod dinosaur, known only from fossil teeth and jaw fragments found in rocks of the middle Berriasian age in the Cherty Freshwater Member of the Lulworth Formation in England. As a dromaeosaurid, Nuthetes would have been a small predator.

Plataleorhynchus is a genus of ctenochasmatid pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous periods of what is now the Purbeck Limestone of Dorset, England.
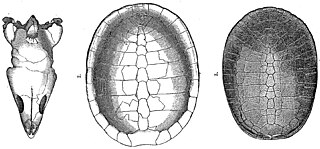
Glyptops is an extinct genus of pleurosternid freshwater turtle known from the Late Jurassic of North America.
Paramacellodus is an extinct genus of scincomorph lizards from the Early Cretaceous of England and France, and the Late Jurassic of Portugal and the western United States. The type species, Paramacellodus oweni, was named in 1967 from the earliest Cretaceous (Berriasian) Purbeck Group in Dorset, England. Additional material referable to a species of Paramacellodus, possibly P. oweni, has been described from the Morrison Formation, specifically in Como Bluff, Wyoming, and Dinosaur National Monument, Utah. An indeterminate species is known from the Berriasian aged Angeac-Charente bonebed in France. Paramacellodus belongs to an extinct family of scincomorphs called Paramacellodidae, which spanned most of Laurasia during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous and represented one of the earliest evolutionary radiations of lizards.

Oweniasuchus is an extinct genus of goniopholidid mesoeucrocodylian. Remains have been found from England and Portugal that are Cretaceous in age.
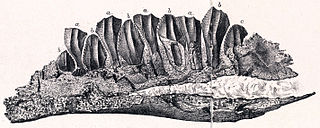
Owenodon is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur known from a partial lower jaw discovered in Early Cretaceous-age rocks of Durlston Bay, Dorset, United Kingdom. The specimen, NHM R2998, comes from the Purbeck Limestone, dating to the middle Berriasian stage. It was first described by Richard Owen, who in 1874 assigned it to Iguanodon as the type specimen of the new species I. hoggii, the specific name honouring naturalist A.J. Hogg who had originally collected the fossil in 1860. The bone was damaged during initial preparation but was freed from the surrounding rock matrix by an acid bath between 1975 and 1977. David Norman and Paul Barrett subsequently transferred the species to Camptosaurus in 2002, but this was challenged, and in 2009 Peter Galton assigned the species to the new genus Owenodon, meaning "Owen's tooth", named after Sir Richard Owen. Galton interpreted the genus as an iguanodontoid more derived than Camptosaurus but less derived than Lurdusaurus.

Pholidosaurus is an extinct genus of neosuchian crocodylomorph. It is the type genus of the family Pholidosauridae. Fossils have been found in northwestern Germany. The genus is known to have existed during the Berriasian-Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous. Fossil material found from the Annero and Jydegård Formations in Skåne, Sweden and on the island of Bornholm, Denmark, have been referred to as a mesoeucrocodylian, and possibly represent the genus Pholidosaurus.
Compsemys is an extinct genus of prehistoric turtles from the Late Cretaceous and Paleocene of North America and possibly Europe. The type species C. victa, first described by Joseph Leidy from the Hell Creek Formation in Montana in 1856., and another probable species C. Russelli, described in 2012, from Paleocene deposits in France. Its affinites have long been uncertain, but it has recently been considered to be the most basal member of Paracryptodira, despite the clade first appearing in the Late Jurassic, and is sometimes included in its own family, Compsemydidae. A revision in 2020 found Compsemydidae to be more expansive, also containing Riodevemys and Selenemys from the Late Jurassic of Europe, and Peltochelys from the Early Cretaceous of Europe.

Pleurosternon is an extinct genus of freshwater pleurosternid turtle from the late Jurassic period to the early Cretaceous period of Europe. Its type species, P. bullocki was described by the paleontologist Richard Owen in 1853. Since then, and throughout the late 19th century, many fossil turtles were incorrectly assigned to this genus, though only two are currently considered valid.

The Lulworth Formation is a geologic formation in England. It dates from the late Tithonian to the mid Berriasian. It is a subunit of the Purbeck Group. In Dorset, it consists of three members, which are in ascending order, the Mupe Member, the Ridgway Member, and the Warbarrow Tout Member. The Mupe Member is typically 11 to 16 m thick and largely consists of marls and micrites with interbeds of calcareous mudstone. The Ridgeway Member is about 3 to 7 m thick and consists of in its western portion carbonaceous muds, marls and micrites, in the east the muds are replaced by micritic limestone. The Warbarrow Tout Member is 17 to 39 m thick and consists of limestone at the base and micrite and mudstone for the rest of the sequence, this member is the primary source of the vertebrate fossils within the formation. Elsewhere the unit is undifferentiated.

Pleurosternidae is an extinct family of freshwater turtles belonging to Paracryptodira. They are definitively known from the Late Jurassic to Early Cretacous (Albian) of Western Europe and North America.

The Helochelydridae are an extinct family of stem-turtles known from fossils found in North America and Europe that have been dated from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous. Although referred to as Solemydidae in recent literature on extinct turtles, Helochelydridae has priority over Solemydidae. The skull, shell and osteoderms of helochelydrids are covered in small, cylindrical protuberances, which are a distinctive characteristic of the group. They are thought to be terrestrial, based on the presence of limb osteoderms and bone histology. Their skull morphology is dissimilar to that of extant tortoises, suggesting an omnivorous habit similar to that of box turtles. Their phylogenetic placement has been unclear, a 2021 analysis placed them within the family Pleurosternidae.

Helochelydra is an extinct genus of extinct stem turtle known from the Early Cretaceous (Barremian) of the Isle of Wight, southern England.
Sunnybatrachus is a genus of extinct frog that lived during the Berriasian epoch of the Early Cretaceous of England. The only known material, including the holotype ilium as well as bones of the skull, vertebral column, forelimb, pelvis, and hindlimb was named Sunnybatrachus purbeckensis by Susan E. Evans and Gerard J. McGowan in 2002. The species name describes the Purbeck Limestone Group, while the genus name is for the Sunnydown Farm locality of the Lulworth Formation, where the fossils were found.
Hylaeochelys is an extinct genus of plesiochelyid turtle that lived during the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous in Portugal, Spain, France, and southern England. The type species was originally named by Richard Owen as Pleurosternon latiscutatum in 1853, before being moved to the new genus Hylaeochelys by Richard Lydekker in 1889. Other species included in the genus are H. belli, H. kappa and H. lata, originally named under different genera by Gideon Mantell and Owen, respectively. All species are represented by carapaces, primarily from the Lulworth Formation of the Purbeck Limestone Group that was deposited during the Berriasian.
Purbicella is a genus of extinct squamate from the Early Cretaceous of southern England. The type and only species is Purbicella ragei, which was described by Susan E. Evans and colleagues in 2012 for a mostly complete and articulated skull from the Berriasian Lulworth Formation of Dorset. The generic name described the region of Purbeck where the fossil was found, while the species name honours paleoherpetologist Jean-Claude Rage. Purbicella has the most complete skull of any British fossil lizard, British Geological Survey (BGS) specimen GSb581, which was originally collected prior to 1911, but then remained in BGS storage until it was rediscovered and described by Evans and colleagues. The skull is unique among coexisting taxa for having fused frontal bones, and Purbicella is likely closer to modern lacertoids than any of the other British forms.

Thalassochelydia is a clade of extinct marine turtles from the Late Jurassic and earliest Cretaceous of Europe and South America. The group is defined as including Eurysternum, Plesiochelys and Thalassemys to the exclusion of Pelomedusa, Testudo and Protostega. While a clade uniting the families Eurysternidae, Plesiochelyidae and Thalassemydidae had been supported by phylogenetic evidence, a name was not given for the clade until 2017, when Jérémy Anquetin and colleagues coined Thalassochelydia.
















