
Pelorosaurus is a genus of titanosauriform sauropod dinosaur. Remains referred to Pelorosaurus date from the Early Cretaceous period, about 140-125 million years ago, and have been found in England and Portugal. Thomas Holtz estimated its length at 24 meters.

Echinodon is a genus of heterodontosaurid dinosaur that lived during the earliest Cretaceous of southern England and possibly western France in the Berriasian epoch. The first specimens were jaw bones named Echinodon becklesii by Sir Richard Owen in 1861, and since their original description only additional teeth have been discovered. The specific name honours collector Samuel Beckles who discovered the material of Echinodon and many other taxa from across England, while the genus name translates as "prickly tooth" in reference to the dental anatomy of the taxon.

Cetiosaurus meaning 'whale lizard', from the Greek keteios/κήτειος meaning 'sea monster' and sauros/σαυρος meaning 'lizard', is a genus of herbivorous sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Period, living about 168 million years ago in what is now Britain.

Altispinax is a genus of large predatory theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous period of what is now the Wadhurst Clay Formation of East Sussex, England.

Aristosuchus is a genus of small coelurosaurian dinosaur whose name was derived from the Greek ἄριστος and σουχος. It shared many characteristics with birds.
Calamospondylus is a genus of theropod dinosaur. It lived during the Early Cretaceous and its fossils were found on the Isle of Wight in southern England. The type species is C. oweni.
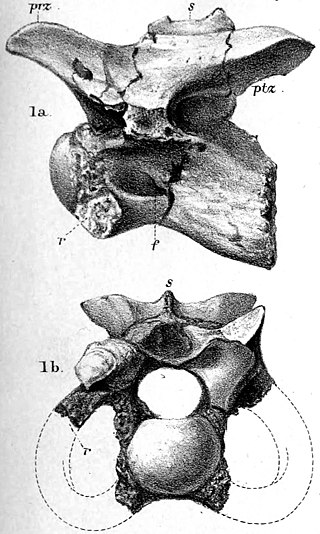
Calamosaurus was a genus of small theropod dinosaur from the Barremian-age Lower Cretaceous Wessex Formation of the Isle of Wight, England. It is based on two cervical vertebrae, collected by Reverend William Fox.

Valdoraptor is a genus of theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous. Its fossils were found in England. It is known only from bones of the feet. The holotype, BMNH R2559, was found near Cuckfield in layers of the Tunbridge Wells Sand Formation dating from the late Valanginian. The specimen is damaged lacking parts of the upper and lower ends. It has a conserved length of 215 millimetres (8.5 in) and an estimated length of 240 millimetres (9.4 in). This genus is paleontologically significant for being the first ornithomimosaur specimen known from England and represents the earliest record of ornithomimosaurs.

Chondrosteosaurus was a sauropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous Wessex Formation of England.

Ornithopsis is a genus of sauropod dinosaur, from the Early Cretaceous of England. The type species, which is the only species seen as valid today, is O. hulkei, which is only known from fragmentary remains, and has been regarded by many authors as dubious.

Nuthetes is the name given to a genus of theropod dinosaur, likely a dromaeosaurid, known only from fossil teeth and jaw fragments found in rocks of the middle Berriasian age in the Cherty Freshwater Member of the Lulworth Formation in England and also the Angeac-Charente bonebed in France. As a dromaeosaurid, Nuthetes would have been a small predator.

Pelochelys is a genus of very large softshell turtles in the family Trionychidae. They are found from peninsular India northeast to southern China, and south to Southeast Asia and New Guinea.

Mantellisaurus is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur that lived in the Barremian and early Aptian ages of the Early Cretaceous Period of Europe. Its remains are known from Belgium (Bernissart), England, Spain and Germany. The type and only species is M. atherfieldensis. Formerly known as Iguanodon atherfieldensis, the new genus Mantellisaurus was erected for the species by Gregory Paul in 2007. According to Paul, Mantellisaurus was more lightly built than Iguanodon and more closely related to Ouranosaurus, making Iguanodon in its traditional sense paraphyletic. It is known from many complete and almost complete skeletons. The genus name honours Gideon Mantell, the discoverer of Iguanodon.

Suchosaurus is a spinosaurid dinosaur from Cretaceous England and Portugal, originally believed to be a genus of crocodile. The type material, consisting of teeth, was used by British palaeontologist Richard Owen to name the species S. cultridens in 1841. Later in 1897, French palaeontologist Henri-Émile Sauvage named a second species, S. girardi, based on two fragments from the mandible and one tooth discovered in Portugal. Suchosaurus is possibly a senior synonym of the contemporary spinosaurid Baryonyx, but is usually considered a dubious name due to the paucity of its remains, and is considered an indeterminate baryonychine. In the Wadhurst Clay Formation of what is now southern England, Suchosaurus lived alongside other dinosaurs, as well as plesiosaurs, mammals, and crocodyliforms.

Manouria is a genus of tortoises in the family Testudinidae. The genus was erected by John Edward Gray in 1854.

Nannosuchus is an extinct genus of goniopholidid mesoeucrocodylian from the Berriasian Middle Purbeck Formation of England that was originally named as a species of Goniopholis. The type species, N. gracilidens, is based on the holotype BMNH 48217, scattered fragmentary remains that include parts of the skull and various other postcranial elements described in 1879.

Pholidosaurus is an extinct genus of neosuchian crocodylomorph. It is the type genus of the family Pholidosauridae. Fossils have been found in northwestern Germany. The genus is known to have existed during the Berriasian-Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous. Fossil material found from the Annero and Jydegård Formations in Skåne, Sweden and on the island of Bornholm, Denmark, have been referred to as a mesoeucrocodylian, and possibly represent the genus Pholidosaurus.

Pleurosternon is an extinct genus of freshwater pleurosternid turtle from the latest Jurassic to earliest Cretaceous of Europe. Its type species, P. bullockii was described by the paleontologist Richard Owen in 1853. Since then, and throughout the late 19th century, many fossil turtles were incorrectly assigned to this genus, though only two are currently considered valid.

Helochelydra is an extinct genus of extinct stem turtle known from the Early Cretaceous (Barremian) of the Isle of Wight, southern England.

















