
The Chelydridae is a family of turtles that has seven extinct and two extant genera. The extant genera are the snapping turtles, Chelydra and Macrochelys. Both are endemic to the Western Hemisphere. The extinct genera are Acherontemys, Chelydrops, Chelydropsis, Emarginachelys, Macrocephalochelys, Planiplastron, and Protochelydra.
The Wannagan Creek site is a fossil site found just west of the South Unit of Theodore Roosevelt National Park of North Dakota, USA. The site is Paleocene in age, approximately 60 million years old. Paleontologists of the Science Museum of Minnesota have studied the site for nearly thirty years. The site is thought to represent a paleoenviroment of subtropical swampy lowland and forests. Preservation is excellent for both the flora and fauna of the site. Trace fossils of crocodilians and other vertebrates have also been discovered.

Procolophonidae is an extinct family of parareptiles from the Permian and Triassic periods.

Ninjemys oweni is an extinct large meiolaniid stem-turtle from Pleistocene Queensland (Australia). It resembled its relative, Meiolania, save that the largest pair of horns on its head stuck out to the sides, rather than point backwards. It is only known from a mostly complete skull and the distal portion of a tail.
Corsochelys is an extinct genus of sea turtle that lived in the Late Cretaceous (Campanian). Zangerl (1960) named the type species, based upon remains found in Alabama within the Mooreville Chalk Formation.

Psephophorus is an extinct genus of sea turtle that lived from the Oligocene to the Pliocene. Its remains have been found in Europe, Africa, North America, and New Zealand. It was first named by Hermann von Meyer in 1847, and contains seven species, P. polygonus, P. calvertensis, P. eocaenus, P. oregonesis, P. californiensis, P. rupeliensis, P. scaldii, and a species discovered in 1995, P. terrypratchetti.

Toxochelys is an extinct genus of marine turtle from the Late Cretaceous period. It is the most commonly found fossilized turtle species in the Smoky Hill Chalk, in western Kansas.
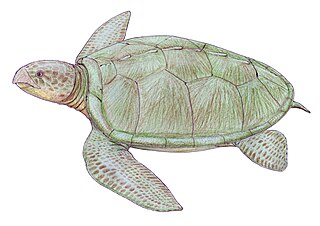
Notochelone is an extinct genus of sea turtle, which existed about 100 million years ago. The species was first described by Richard Lydekker in 1889. It was the most common marine reptile living in the inlands of the sea around Queensland, Australia. It was a small turtle, and was about the same size as the modern green turtle. Analytical studies have indicated that the creatures frequently ate benthic molluscs.

Mesodermochelys is an extinct genus of sea turtle known from the Campanian to the Maastrichtian of what today is Japan. One species is known, the type species M. undulatus; it was given its binomial name by Ren Hirayama and Tsutomu Chitoku in 1996. Studies of its skull indicate that it was a primitive member of the Dermochelyidae that was closely related to the Protostegidae. It has been described as the best representative of Mesozoic dermochelyids.

Akmonistion is an extinct genus of holocephalian that lived in the Early Carboniferous. The genus contains a single species, A. zangerli. It is distinguished by an unusual enlarged formation of the dorsal fin, called a "spine-brush complex", of unknown function. This is also found in the better known genus Stethacanthus. Remains have only been found near Bearsden in Scotland.
Cosmochelys is an extinct genus of sea turtle from the Eocene of Africa. It was first named by Andrews in 1920, and contains one species, C. dolloi.

Manchurochelys is an extinct genus of turtle in the order Paracryptodira. It existed during the early Cretaceous of what is now northeast China. It has been found in the Jianshangou Bed of West Liaoning's Yixian Formation. However, it is a rarely found fossil.
Terlinguachelys fischbecki is an extinct sea turtle that existed during the Late Cretaceous period some 80 million years ago. It is the sole species in the genus Terlinguachelys and is classified in the family Protostegidae along with other extinct marine turtles.
Caririemys is an extinct genus of side-necked turtles, belonging to the Pelomedusoides of the family Euraxemydidae. The type species is C. violetae. A single fossil of an individual was found in the Santana Formation in Brazil, an 80-million-year-old Late Cretaceous deposit that has so far preserved other fossil reptiles such as dinosaurs and crocodilians.
Chelydrops is an extinct genus of Chelydridae from Miocene of North America. Only one species is described, Chelydrops stricta.
Megapleuron is an extinct genus of prehistoric sarcopterygian or lobe-finned fish.

Dinochelys is an extinct genus of paracryptodiran turtle from the Late Jurassic Morrison Formation.
Mexichelys is an extinct monotypic genus of sea turtle which lived in Mexico during the Cretaceous. The only species is Mexichelys coahuilaensis. Mexichelys was erected in 2010 as a replacement name for Euclastes coahuilaensis, a species named in 2009.
Prochelidella is an extinct genus of Early to Late Cretaceous chelid turtles from the Bajo Barreal, Candeleros, Cerro Barcino and Portezuelo Formations of the Cañadón Asfalto, Golfo San Jorge and Neuquén Basins in Patagonia, Argentina. It includes the following species:
Berruchelus is an extinct genus of paracryptodiran turtle from the Cenozoic of western Europe.









