
Carettochelyidae is a family of cryptodiran turtles belonging to the Trionychia. It contains only a single living species, the pig-nosed turtle native to New Guinea and Northern Australia. Stem-group carettochelyids are known from the Cretaceous of Asia, with the family being widely distributed across North America, Europe, Asia and Africa during much of the Cenozoic.

Chelidae is one of three living families of the turtle suborder Pleurodira, and are commonly called Austro-South American side-neck turtles. The family is distributed in Australia, New Guinea, parts of Indonesia, and throughout most of South America. It is a large family of turtles with a significant fossil history dating back to the Cretaceous. The family is entirely Gondwanan in origin, with no members found outside Gondwana, either in the present day or as a fossil.

Podocnemididae is a family of pleurodire (side-necked) turtles, once widely distributed. Most of its 41 genera and 57 species are now extinct. Seven of its eight surviving species are native to South America: the genus Peltocephalus, with two species, only one of which is extant ; and the genus Podocnemis, with six living species of South American side-necked river turtles and four extinct. There is also one genus native to Madagascar: Erymnochelys, the Madagascan big-headed turtle, whose single species E. madagascariensis.

Megalosaurus is an extinct genus of large carnivorous theropod dinosaurs of the Middle Jurassic Epoch of southern England. Although fossils from other areas have been assigned to the genus, the only certain remains of Megalosaurus come from Oxfordshire and date to the late Middle Jurassic.

Podocnemis is a genus of aquatic turtles, commonly known as South American river turtles, in the family Podocnemididae. The genus consists of six extant species occurring in tropical South America. Four additional species are known only from fossils. These turtles have pig-like noses but are not closely related to the pig-nosed turtle.

Chelodina, collectively known as snake-necked turtles, is a large and diverse genus of long-necked chelid turtles with a complicated nomenclatural history. Although in the past, Macrochelodina and Macrodiremys have been considered separate genera and prior to that all the same, they are now considered subgenera of the Chelodina, further Macrochelodina and Macrodiremys are now known to apply to the same species, hence Chelydera is used for the northern snake-necked turtles.

Bothremydidae is an extinct family of side-necked turtles (Pleurodira) known from the Cretaceous and Cenozoic. They are closely related to Podocnemididae, and are amongst the most widely distributed pleurodire groups, with their fossils having been found in Africa, India, the Middle East, Europe, North America and South America. Bothremydids were aquatic turtles with a high morphological diversity, indicative of generalist, molluscivorous, piscivorous and possibly herbivorous grazing diets, with some probably capable of suction feeding. Unlike modern pleurodires, which are exclusively freshwater, bothremydids inhabited freshwater, marine and coastal environments. Their marine habits allowed bothremydids to disperse across oceanic barriers into Europe and North America during the early Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian). The youngest records of the group are indeterminate remains from Saudi Arabia and Oman, dating to the Miocene.

Hesperotestudo is an extinct genus of tortoise native to North and Central America from the Early Miocene to the Late Pleistocene. Species of Hesperotestudo varied widely in size, with a large undescribed specimen from the Late Pleistocene of El Salvador reaching

Psephophorus is an extinct genus of sea turtle that lived from the Oligocene to the Pliocene. Its remains have been found in Europe, Africa, North America, and New Zealand. It was first named by Hermann von Meyer in 1847, and contains seven species, P. polygonus, P. calvertensis, P. eocaenus, P. oregonesis, P. californiensis, P. rupeliensis, P. scaldii, and a species discovered in 1995, P. terrypratchetti.

Toxochelys is an extinct genus of marine turtle from the Late Cretaceous period. It is the most commonly found fossilized turtle species in the Smoky Hill Chalk, in western Kansas.
Prochelidella is an extinct genus of Early to Late Cretaceous chelid turtles from the Bajo Barreal, Candeleros, Cerro Barcino and Portezuelo Formations of the Cañadón Asfalto, Golfo San Jorge and Neuquén Basins in Patagonia, Argentina. It includes the following species:

Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2013.
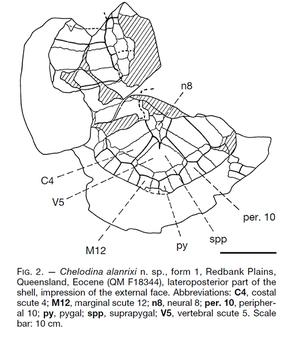
Chelodina alanrixi is a species of snake-necked fossil turtle which was described in 2001 using material gathered in Redbank Plains, Queensland, Australia. It is a member of the Chelidae Pleurodira. The fossil has been dated to the Eocene Epoch.

Megalochelys is an extinct genus of tortoises that lived from the Miocene to Pleistocene. They are noted for their giant size, the largest known for any tortoise, with a maximum carapace length of over 2 m (6.5 ft) in M. atlas. The genus ranged from western India and Pakistan to as far east as Sulawesi and Timor in Indonesia, though the island specimens likely represent distinct species.

The Ash Hollow Formation of the Ogallala Group is a geological formation found in Nebraska and South Dakota. It preserves fossils dating back to the Neogene period. It was named after Ash Hollow, Nebraska and can be seen in Ash Hollow State Historical Park. Ashfall Fossil Beds State Historical Park is within this formation.
Hydropelta is a genus of Late Jurassic turtle from marine deposits in the Jura Mountains of eastern France.

Helochelydra is an extinct genus of extinct stem turtle known from the Early Cretaceous (Barremian) of the Isle of Wight, southern England.
Arenila is an extinct genus of bothremydid pleurodiran turtle that was discovered in the Western Desert of Egypt. The genus consists solely of type species A. krebsi.
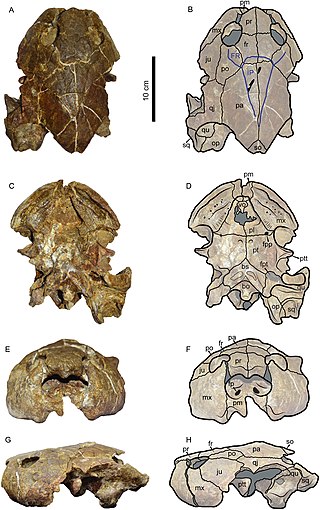
Caninemys is an extinct genus of large freshwater side-necked turtle, belonging to the family Podocnemididae. Its fossils have been found in Brazil and Colombia, in rocks dating back from the middle to late Miocene.
This list of fossil reptiles described in 2014 is a list of new taxa of fossil reptiles that were described during the year 2014, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to reptile paleontology that occurred in 2014.
















