
Dermochelyidae is a family of sea turtles which has seven extinct genera and one extant genus, containing one living species, the leatherback sea turtle. The oldest fossils of the group date to the Late Cretaceous.

Dolichosaurus is an extinct genus of marine squamate of the Upper Cretaceous Cenomanian chalk deposits of England. It is a member of the family Dolichosauridae. It was a small reptile measuring 0.5–1 m (1.6–3.3 ft) long. It had an elongate neck resulting from an increased number of cervical vertebrae.

Sinemys is an extinct genus of turtle from the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous of China. Three species have been named: S. lens, the type species, from the Kimmeridgian-Tithonian of Shandong; S. gamera, from the Valanginian-Albian of Nei Mongol, and S. brevispinus from Early Cretaceous of Nei Mongol. S. wuerhoensis, from the Aptian-Albian of Xinjiang, is not referrable to this genus. Specimen that may be belong to this genus were also known from Japan, although later abstract considered it as indeterminate sinemydid. The species S. gamera is noted for the presence of a pair of elongate spines projecting outwards and backwards from seventh costal of the carapace. These may have served a hydrodynamic function.
Corsochelys is an extinct genus of sea turtle that lived in the Late Cretaceous (Campanian). Zangerl (1960) named the type species, based upon remains found in Alabama within the Mooreville Chalk Formation.

Mesodermochelys is an extinct genus of sea turtle known from the Campanian to the Maastrichtian of what today is Japan and from the Maastrichtian of Chile. One species is known, the type species M. undulatus; it was given its binomial name by Ren Hirayama and Tsutomu Chitoku in 1996. Studies of its skull indicate that it was a primitive member of the Dermochelyidae that was closely related to the Protostegidae. It has been described as the best representative of Mesozoic dermochelyids.
Asiatoceratodus is an extinct genus of lungfish which lived during the Middle-Late Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous periods in what is now Asia (Kyrgyzstan), Africa and South America.

Cearachelys is an extinct genus of pleurodiran turtle which existed some 110 million years ago. The genus is monotypic, with only type species Cearachelys placidoi known.
Vallecillosaurus is an extinct genus of mosasauroid from the Late Cretaceous period, that lived in Mexico, in the state of Nuevo León. It was a relatively small reptile measuring less than 1 m (3.3 ft) long.

Aigialosaurus is an extinct genus of Late Cretaceous marine or semiaquatic lizard classified as part of the family Aigialosauridae within the Mosasauroidea. Exclusively found in deposits of Cenomanian age near Hvar, Croatia, the genus contains one valid species, A. dalmaticus. According to recent molecular and morphological data, Aigialosaurus is the oldest known member of the lineage leading to large Cretaceous marine reptiles called mosasaurs, a group most closely related to snakes among living squamates. It was a relatively small reptile with a complete specimen measuring 65 cm (2.13 ft) long.

Opetiosaurus is an extinct genus of Late Cretaceous marine or semiaquatic lizard classified as part of the family Aigialosauridae within the Mosasauroidea. Exclusively found in deposits of Cenomanian age near Hvar, Croatia, the genus contain one valid species, O. bucchichi. It was a small reptile measuring 1 metre (3.3 ft) long.

Pancheloniidae is a clade of sea turtles It is defined as all turtles more closely related to cheloniid sea turtles than to dermochelyid ("leatherback") sea turtles.

The Oulad Abdoun Basin is a phosphate sedimentary basin located in Morocco, near the city of Khouribga. It is the largest in Morocco, comprising 44% of Morocco's phosphate reserves, and at least 26.8 billion tons of phosphate. It is also known as an important site for vertebrate fossils, with deposits ranging from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian-Turonian) to the Eocene epoch (Ypresian), a period of about 25 million years.
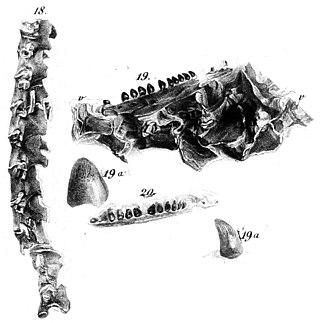
Coniasaurus is an extinct genus of Late Cretaceous marine squamates that range in age from Cenomanian to Santonian. It was first described by Richard Owen in 1850 from lower Cenomanian chalk deposits in South East England (Sussex). Two species have been described from this genus: C. crassidens, known from Cenomanian to Santonian deposits from South East England, Germany and North America, and C. gracilodens from the Cenomanian of southeast England.

Rhinochelys is an extinct genus of sea turtles belonging to the family Protostegidae.

Goulmimichthys is an extinct genus of ray-finned fishes in the family Pachyrhizodontidae. The genus, first described by Cavin in 1995, is known from various Turonian age formations. The type species G. arambourgi from the Akrabou Formation in the El Rachidia Province of Morocco, and other fossils described are G. gasparini of the La Frontera Formation, Colombia, and G. roberti from the Agua Nueva Formation of Mexico.

Glossochelys is an extinct genus of sea turtles from the Pancheloniidae that has been discovered in Eocene (Ypresian) deposits in Harwich, England that was first described as a species of Lytoloma in 1842. The type species, G. planimentum, was described as a separate species in 1871 by Harry Seeley. It was possibly the same animal as Euclastes or Erquelinnesia.
Araiochelys is an extinct genus of bothremydid pleurodiran turtle that was discovered in the Ouled Abdoun Basin, Morocco. The genus consists solely of type species A. hirayamai.
Phosphatochelys is an extinct genus of bothremydid pleurodiran turtle that was discovered near Oued Zem, Morocco. The genus consists solely of type species P. tedfordi.
Rhothonemys is an extinct genus of bothremydid pleurodiran turtle that was discovered in the Paleogene of Morocco. The genus consists solely of type species R. brinkmani.
Ummulisani is an extinct genus of bothremydid pleurodiran turtle that was discovered in the Eocene of Morocco. The genus consists solely of type species U. rutgersensis.














