| Plesiochelyidae Temporal range: Late Jurassic, | |
|---|---|
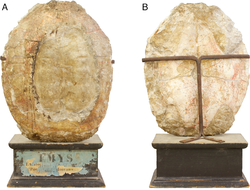 | |
| Holotype carapace and plastron of Plesiochelys etalloni (previously Emy etalloni). Mount is situated upside-down. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Pantestudines |
| Clade: | Testudinata |
| Clade: | † Thalassochelydia |
| Family: | † Plesiochelyidae Baur, 1888 |
| Genera [1] | |
The Plesiochelyidae are an extinct family of turtles in the clade Thalassochelydia originally classified within the Cryptodira suborder, mostly belonging from the Jurassic period. [1] An alternate study placed the clade Thalassochelydia in the Angolachelonia and outside the Testudines. [3]


