
The Cryptodira are a suborder of Testudines that includes most living tortoises and turtles. Cryptodira differ from Pleurodira in that they lower their necks and pull the heads straight back into the shells, instead of folding their necks sideways along the body under the shells' marginals. They include among their species freshwater turtles, snapping turtles, tortoises, softshell turtles, and sea turtles.

Trionychia is a superfamily of turtles which encompasses the species that are commonly referred to as softshelled turtles as well as some others. The group contains two families, Carettochelyidae, which has only one living species, the pig-nosed turtle native to New Guinea and Northern Australia, and Trionychidae, the softshelled turtles, containing numerous species native to Asia, North America and Africa. These families likely diverged during the late Jurassic. The oldest known stem-trionychian is Sinaspideretes from the Late Jurassic of China.

Protostegidae is a family of extinct marine turtles that lived during the Cretaceous period. The family includes some of the largest sea turtles that ever existed. The largest, Archelon, had a head one metre (39 in) long. Like most sea turtles, they had flattened bodies and flippers for front appendages; protostegids had minimal shells like leatherback turtles of modern times.

Paracryptodira is an extinct group of reptiles in the clade Testudinata, known from the Jurassic to Paleogene of North America and Europe. Initially treated as a suborder sister to Cryptodira, they were then thought to be a very primitive lineage inside the Cryptodira according to the most common use of the latter taxon. They are now often regarded as late-diverging stem-turtles, lying outside the clade formed by Cryptodira and Pleurodira. Paracryptodires are divided into three main groups, Compsemydidae, known from the Late Jurassic to Paleocene of North America and Europe, Pleurosternidae, known from the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous of North America and Europe, and Baenidae, known from the Early Cretaceous to Eocene of North America. The latter two groups are more closely related to each other than to Compsemys, forming the clade Baenoidea.

Sinaspideretes is an extinct genus of turtle from the Late Jurassic of China, probably from the Shaximiao Formation. It is considered the earliest and most basal representative of the Trionychia, and is possibly the oldest known member of Cryptodira. In 2013, it was proposed that this animal and the genus Yehguia are in fact one and the same.

Bouliachelys is an extinct genus of sea turtle from Cretaceous Australia. It was originally described as a member of Protostegidae. In 2013 study it was considered to be a member of Dermochelyoidae, although later studies consider it as a protostegid again.

Thalassemys is a genus of extinct thalassochelydian turtle from the Late Jurassic of western and central Europe. While the genus was originally named by Rütimeyer in 1859 for a large carapace and other associated fragments from the late Kimmeridgian of the Reuchenette Formation of Switzerland, although the taxon was not validly named until 1873 when Rütimeyer designated the type species T. hugii. Rütimeyer also named T. gresslyi from the Reunchenette Formation in the same paper as T. hugii, but it cannot be differentiated from the type material of T. hugii and is therefore a junior synonym. A large assemblage of shell and postcranial material from the Reunchenette was named as a species of Eurysternum, E. ignoratum, by Bräm in 1965. While originally distinguished based on the presence of fontanelles on the plastron, the feature was later identified on T. hugii and E. ignoratum was designated a junior synonym. Additional material from the Kimmeridge Clay of the United Kingdom has also been referred to T. hugii.
The Reuchenette Formation is a Jurassic geologic formation in Switzerland. It is Kimmeridgian in age and predominantly consists of well stratified limestone, with lithology variable both laterally and stratigraphically including wackestones, packstones and grainstones, as well as mudstone. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, including the Turiasaurian sauropod Amanzia greppini, alongside a theropod tooth belonging to Ceratosauria indet, originally assigned to Megalosaurus meriani. teleosaurid crocodyliformes are also known, including Sericodon, Proexochokefalos and Machimosaurus. The metriorhynchid thalatosuchians Torvoneustes and Dakosaurus. The hybodontid shark Asteracanthus. The thalassochelydian turtle Thalassemys and Solnhofia is known from the formation, as is the platychelyid turtles Platychelys, and the plesiochelyid turtle Plesiochelys.

Pleurosternon is an extinct genus of freshwater pleurosternid turtle from the latest Jurassic to earliest Cretaceous of Europe. Its type species, P. bullockii was described by the paleontologist Richard Owen in 1853. Since then, and throughout the late 19th century, many fossil turtles were incorrectly assigned to this genus, though only two are currently considered valid.

Ocepechelon is an extinct genus of giant protostegid sea turtle known from the Late Cretaceous of Morocco. The feeding apparatus of Ocepechelon, a bony pipette-like snout, is unique among tetrapods and shares unique convergences with both syngnathid fishes and beaked whales.

The Plesiochelyidae are an extinct family of turtles in the clade Thalassochelydia originally classified within the Cryptodira suborder, mostly belonging from the Jurassic period. An alternate study placed the clade Thalassochelydia in the Angolachelonia and outside the Testudines.

Macrobaenidae is an extinct family of turtles, known from the Early Cretaceous to Paleogene of Laurasia. Their relationships to other turtles and whether they form a monophlyletic group are controversial. They are typically interpreted as stem or crown group cryptodires, but some more recent analyses have found them to lie outside crown group Testudines. Macrobaenids can be distinguished from other testudinatans by the presence of a carotid fenestra, cruciform plastron with strap-like epiplastra, and a lack of extragulars.

The Helochelydridae are an extinct family of stem-turtles known from fossils found in North America and Europe spanning the Early to Late Cretaceous.

Perichelydia is a clade within Pantestudines known from the Middle Jurassic to Holocene. Alongside crown group Testudines, it also contains Helochelydridae, which is known from the Cretaceous of Europe and North America, Sichuanchelyidae from the Middle Jurassic to Paleocene of Asia and Europe, Meiolaniformes, which is known from the Cretaceous to Holocene of South America, Australia and Oceania, and Spoochelys, known from the Mid-Cretaceous Griman Creek Formation of Australia. Kallokibotion from the Late Cretaceous of Europe is also considered part of this group. Several other groups, including the proposed clade Angolachelonia, Paracryptodira, Macrobaenidae, Sinemydidae and Xinjiangchelyidae, which are sometimes considered members of Cryptodira, have also been found outside crown Testudines in several analyses. These groups are usually considered to be closer to the crown group than the other members of Perichelydia.
Euryaspis is a dubious genus of extinct thalassochelydian turtle from the Late Jurassic of Germany. The type and only species is Euryaspis radians, originally proposed by Wagner in 1859 before being validly described and illustrated in 1861. The only specimen was a partial carapace probably from the Tithonian, although the original locality is unknown. The genus is referred to Thalassochelydia and has been considered a synonym of Eurysternum or Acichelys before, but casts that remain of the lost holotype show that it bears no features that can clarify its validity making it a nomen dubium.

Owadowia is a genus of extinct thalassochelydian turtle from the Late Jurassic of Poland. The type and only species is Owadowia borsukbialynickae, named by Szczygielski and colleagues in 2017 for a partial lower jaw, coracoid, ilium and femur from the early Tithonian Kcynia Formation. The limited material means that it is difficult to compare Owadowia to its relatives, and it may not be a unique taxon. The genus lacks the features diagnostic to its parent clade Thalassochelydia, has similarities to Solnhofia and Portlandemys as well as being a Late Jurassic marine turtle like the remainder of the group.
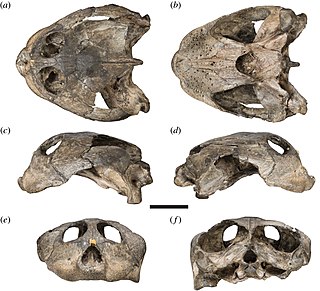
Sandownidae is a family of extinct marine turtles from the Cretaceous and Paleogene distributed around the Atlantic Ocean and adjacent areas. The family is defined as all taxa closer to the type genus Sandownia than to Pelomedusa, Testudo, Solnhofia, Eurysternum, Plesiochelys, Thalassemys or Protostega, a definition that encompasses the previous concept of the clade while also excluding it from being synonymous with other clades of modern or extinct marine turtles. Sandownidae may be within the larger clade Angolachelonia, defined as inclusive of Angolachelys and Solnhofia, sister to the entirely Late Jurassic marine group Thalassochelydia, although the concepts of the clades may shift with further phylogenetic analysis.

Angolachelonia is a clade of extinct turtles from the Late Jurassic to Paleogene of Eurasia. The group is defined as all taxa derived from the ancestor of the type genus Angolachelys and Solnhofia, a definition that could potentially encompass a clade of entirely marine turtles. Angolachelonia was originally inclusive of only Solnhofia, Angolachelys and Sandownia when originally conceived by Octavio Mateus and colleagues in 2009, but later phylogenetic analyses by Serjocha Evers and Roger Benson in 2018 unites the family Sandownidae, including Angolachelys and Sandownia among other taxa, with the entirely Late Jurassic clade Thalassochelydia, where Solnhofia may be a basal member. While the placement of Solnhofia is weak and the clade that Angolachelonia represents may change with further analysis, the clade of Sandownidae and Thalassochelydia is well-supported, and does not collapse despite the uncertain evolutionary history of the group. Three alternative potential origins of Angolachelonia sensu Evers and Benson are shown below.

Compsemydidae is an extinct family of turtles, likely belonging to the clade Paracryptodira. The earliest undisputed member is Tongemys from the Berriasian age of the Early Cretaceous; two Late Jurassic genera have also sometimes been included in the group, but may alternatively be members of the family Pleurosternidae. The genus Compsemys survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event and lasted until the Thanetian age of the Paleocene.
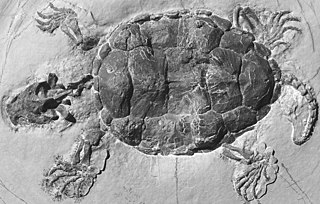
Platychelyidae is an extinct family of pan-pleurodiran turtles, known from the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous of Europe, South America, North America, and the Caribbean. It represents the oldest known clade of stem-pleurodires. All known members have been found in marine or coastal deposits. Despite this, their limb morphology suggests that they were not adapted for open marine conditions, but were likely inhabitants of shallow water environments, including brackish and saline waters, and they likely never inhabited environments more marine than lagoons. Their tolerance for saline environments likely aided their dispersal during the breakup of Pangea. Unlike modern pleurodires, which retract their necks to the sides, Platychelys retracted its neck inwards, similar to modern cryptodire turtles. Platychelys is strongly morphologically similar to mata mata and snapping turtles, suggesting that it had a similar ecology as a ram or suction feeder.





















