Contents
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
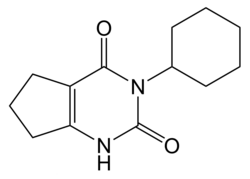
| Preferred IUPAC name 3-cyclohexyl-1,5,6,7-tetrahydrocyclopenta[d]pyrimidine-2,4-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.818 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H18N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 234.299 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.32 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 315.6 to 316.8 °C (600.1 to 602.2 °F; 588.8 to 590.0 K) |
| 6 mg/L (25 °C) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Warning | |
| H351, H410 | |
| P203, P273, P280, P318, P391, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Lenacil is a uracil-derived chemical herbicide used to control broadleaf weeds.
