
Siphonostomatoida is an order of copepods, containing around 75% of all the copepods that parasitise fishes. Their success has been linked to their possession of siphon-like mandibles and of a "frontal filament" to aid attachment to their hosts. Most are marine, but a few live in fresh water. There are 40 recognised families:

The Cyclopoida are an order of small crustaceans from the class Copepoda. Like many other copepods, members of Cyclopoida are small, planktonic animals living both in the sea and in freshwater habitats. They are capable of rapid movement. Their larval development is metamorphic, and the embryos are carried in paired or single sacs attached to first abdominal somite.
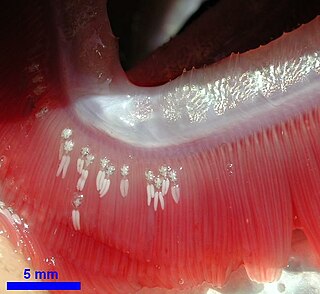
Ergasilidae is a widespread family of copepods and comprises many species. The type genus is Ergasilus. With a few doubtful exceptions all ergasilids are parasitic on fishes.

Trochoidea is a superfamily of small to very large vetigastropod sea snails with gills and an operculum. Species within this superfamily have nacre as the inner shell layer. The families within this superfamily include the Trochidae, the top snails. This superfamily is the largest vetigastropodan superfamily, containing more than 2,000 species.

The Cymothoidae are a family of isopods in the suborder Cymothoida found in both marine and freshwater environments. Cymoithoids are ectoparasites, usually of fish, and they include the bizarre "tongue-biter", which attaches to a fish's tongue, causing it to atrophy, and replaces the tongue with its own body. Ceratothoa oestroides is one of the most devastating ectoparasites in Mediterranean aquaculture. Around 40 genera and more than 380 species of cymothoid are recognised. Species of the Cymothoidae are generally found in warmer waters and rarely in the cool and cold climates.
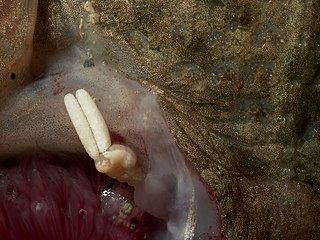
Chondracanthidae is a family of parasitic copepods, usually found infecting the branchial chamber of demersal fishes. It comprises the following genera:
Ceratomyxa is a genus of myxozoan.

Rhadinorhynchidae is a family of parasitic worms from the order Echinorhynchida.

Caligus is a genus of sea lice in the family Caligidae. The species are parasites of marine fishes and could be vectors of viruses. As of 2017, the World Register of Marine Species includes the following species:

Lernaeopodidae is a family of parasitic copepods. The females are typically large and fleshy, and attach to the host permanently using a plug made of chitin called the bulla. The males cling on to the females using their antennae. They parasitize both marine and freshwater fish. Some lernaeopodids, including Clavella and Salmincola, can have negative impacts on fish in aquaculture.

Eudactylina is a genus of copepods. They parasitise elasmobranch fishes.
Alexandr Vladimirovich Gussev, sometimes spelled Gusev in the literature, was a Russian helminthologist specialist of monogeneans.
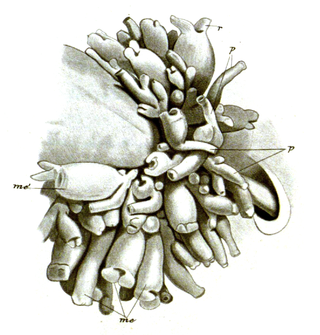
Cardiodectes is a genus of copepods in the family Pennellidae. Species are parasites of fish.

Ancyrocephalidae is a family of monogenean flatworms. The family is considered as a "temporary name" in WorMS but includes a large number of genera and species.

Chydoridae is a family of water fleas in the order Anomopoda. There are more than 50 genera and 520 described species in Chydoridae. A lot of Chydoridae species are non-native species, many of which pose a great threat to aquatic ecosystems.
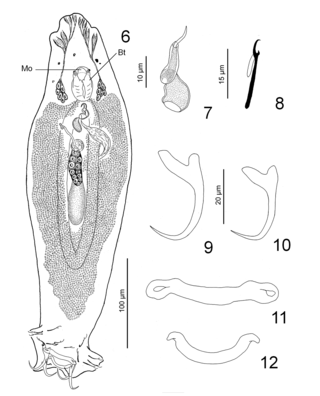
Ancyrocephalus is a genus of flatworms belonging to the family Ancyrocephalidae.













