
Psilogramma menephron, the privet hawk moth or large brown hawkmoth, is a member of the family Sphingidae. It was described by Pieter Cramer in 1780. It is usually found in Sri Lanka, India, Nepal, central and southern China, Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia and the Philippines. Psilogramma casuarinae from eastern Australia was long treated as a synonym but is now thought to be a distinct species. The introduced population on Hawaii was first thought to be P. menephron, but is Psilogramma increta.

Acherontia styx, the lesser death's head hawkmoth or bee robber, is a sphingid moth found in Asia, one of the three species of death's-head hawkmoth. It is very fond of honey, and bee keepers have reported finding dead moths in their hives as a result of bee stings. They can mimic the scent of bees so that they can enter a hive unharmed to get honey. Their tongue, which is stout and very strong, enables them to pierce the wax cells of the beehive and suck the honey out. They are also known to be a pest of yuzu in South Korea, using their tongue to pierce and damage the fruit.

Theretra oldenlandiae, the impatiens hawkmoth, taro hornworm or white-banded hunter hawkmoth, is a member of the family Sphingidae.

Nephele hespera, the crepuscular hawkmoth, is a sphingid moth described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1775.

Hippotion celerio, the vine hawk-moth or silver-striped hawk-moth, is a moth of the family Sphingidae. It was described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae.

Theretra nessus, the yam hawk moth, is a moth of the family Sphingidae. It was described by Dru Drury in 1773.

Hippotion velox, the dark striated hawkmoth, is a species of sphingid moth or the family Sphingidae. The species was described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1793.

Macroglossum belis, the common hummingbird hawkmoth, is a moth of the family Sphingidae. It was described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae. It is known from Sri Lanka, India, Nepal, Thailand, southern China, Taiwan, Japan, Vietnam and Indonesia (Java).

Macroglossum glaucoptera, the dark hummingbird hawkmoth, is a moth of the family Sphingidae. It was described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1875. It is known from Sri Lanka, Thailand, southern China, Vietnam, Malaysia (Peninsular), Indonesia and the Philippines (Mindanao). Single specimen recorded from Papua New Guinea.

Macroglossum gyrans is a moth of the family Sphingidae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1856 and is known from South-east Asia and Madagascar.

Macroglossum insipida, the hermit hummingbird hawkmoth, is a moth of the family Sphingidae. It was described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1875.

Macroglossum mitchellii, the grey-striped hummingbird hawkmoth, is a moth of the family Sphingidae described by Jean Baptiste Boisduval in 1875. It is known from Sri Lanka, southern and eastern India, Thailand, southern China, Taiwan, Vietnam, Malaysia and Indonesia.
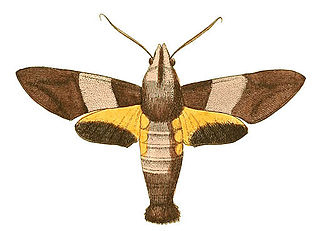
Macroglossum passalus, the black-based hummingbird hawkmoth, is a moth of the family Sphingidae described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is known from Sri Lanka, India, Thailand, south-eastern China, Taiwan, southern Japan, Indonesia and the Philippines.

Macroglossum sitiene, the crisp-banded hummingbird hawkmoth, is a moth of the family Sphingidae described by Francis Walker in 1856.

Pergesa is a monotypic moth genus in the family Sphingidae first described by Francis Walker in 1856. Its only species, Pergesa acteus, the green pergesa hawkmoth, was described by Pieter Cramer in 1779.

Acosmeryx shervillii, the dull forest hawkmoth, is a moth of the family Sphingidae. The species was first described by Jean Baptiste Boisduval in 1875. It is found from the Indian subregion, Sri Lanka, to Sundaland, the Philippines and Sulawesi. Acosmeryx pseudonaga is sometimes treated as a valid species.

Amplypterus panopus, the mango hawkmoth, is a moth of the family Sphingidae. The species was first described by Pieter Cramer in 1779. It is found in Sri Lanka, southern and northern India, Nepal, Myanmar, southern China, Thailand, Vietnam, Laos, Indonesia and the Philippines.

Theretra gnoma is a moth of the family Sphingidae described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1775. It is known from India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Nepal, Thailand, China.

Theretra lycetus, the white-edged hunter hawkmoth, is a moth of the family Sphingidae. It was described by Pieter Cramer in 1775.

Ambulyx substrigilis, the dark-based gliding hawkmoth, is a species of moth of the family Sphingidae. It was described by John O. Westwood in 1847.





















