
The Brazil nut is a South American tree in the family Lecythidaceae, and it is also the name of the tree's commercially harvested edible seeds. It is one of the largest and longest-lived trees in the Amazon rainforest. The fruit and its nutshell – containing the edible Brazil nut – are relatively large and weigh as much as 2 kg (4.4 lb) in total. As food, Brazil nuts are notable for diverse content of micronutrients, especially a high amount of selenium. The wood of the Brazil nut tree is prized for its quality in carpentry, flooring, and heavy construction.

Liquidambar, commonly called sweetgum, gum, redgum, satin-walnut, styrax or American storax, is the only genus in the flowering plant family Altingiaceae and has 15 species. They were formerly often treated as a part of the Hamamelidaceae. They are native to southeast and east Asia, the eastern Mediterranean and North America. They are decorative deciduous trees that are used in the wood industry and for ornamental purposes.

Picea abies, the Norway spruce or European spruce, is a species of spruce native to Northern, Central and Eastern Europe.

American sweetgum, also known as American storax, hazel pine, bilsted, redgum, satin-walnut, star-leaved gum, alligatorwood, gumball tree, or simply sweetgum, is a deciduous tree in the genus Liquidambar native to warm temperate areas of eastern North America and tropical montane regions of Mexico and Central America. Sweetgum is one of the main valuable forest trees in the southeastern United States, and is a popular ornamental tree in temperate climates. It is recognizable by the combination of its five-pointed star-shaped leaves and its hard, spiked fruits. It is currently classified in the plant family Altingiaceae, but was formerly considered a member of the Hamamelidaceae.

Eleocharis dulcis, the Chinese water chestnut or water chestnut, is a grass-like sedge native to Asia, tropical Africa, and Oceania. It is grown in many countries for its edible corms, but if eaten uncooked, the surface of the plants may transmit fasciolopsiasis.

Comptonia peregrina is a species of flowering plant in the family Myricaceae native to eastern North America. It is the only extant (living) species in the genus Comptonia, although a number of extinct species are placed in the genus.

Juniperus excelsa, commonly called the Greek juniper, is a juniper found throughout the eastern Mediterranean, from northeastern Greece and southern Bulgaria across Turkey to Syria and Lebanon, Jordan, the Caucasus mountains, and southern coast of Crimea.

Doryanthes excelsa, commonly known as the gymea lily, is a flowering plant in the family Doryanthaceae that is endemic to coastal areas of New South Wales near Sydney. It has sword-like leaves more than 1 metre (3 ft) long and it grows a flower spike up to 6 metres (20 ft) high. The apex of the spike bears a large cluster of bright red flowers, each 10 centimetres (4 in) across. Its common name is derived from kai'mia in the indigenous Dharawal language. The Sydney suburbs of Gymea and Gymea Bay are named after the lily.

Juniperus foetidissima, with common names foetid juniper or stinking juniper, is a juniper tree species in the family Cupressaceae.

Aralia excelsa is a species of flowering plant in the family Araliaceae. It is native to Mexico, Central America, northern South America and parts of the Caribbean.
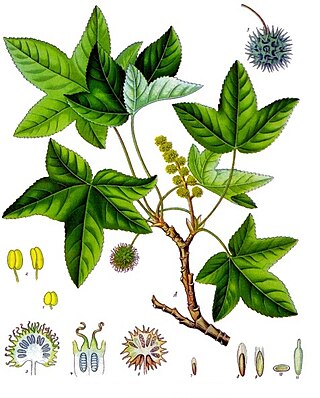
Liquidambar orientalis, commonly known as oriental sweetgum or Turkish sweetgum, is a deciduous tree in the genus Liquidambar, native to the eastern Mediterranean region, that occurs as pure stands mainly in the floodplains of southwestern Turkey and on the Greek island of Rhodes.

Milicia excelsa is a tree species from the genus Milicia of the family Moraceae. Distributed across tropical Central Africa, it is one of two species yielding timber commonly known as ọjị, African teak, iroko, intule, kambala, moreira, mvule, odum and tule.

Picconia excelsa, commonly known as palo blanco, pau blanco, or branqueiro, is a species of tree in the family Oleaceae. It is endemic to Macaronesia, occurring only on Madeira and the Canary Islands.
Liquidambar chingii is a species of plant in the Altingiaceae family. It is native to Vietnam and China. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Iroko is a large hardwood tree from the west coast of tropical Africa that can live up to 500 years. This is the common name for the genus Milicia, in which there are two recognized species, which are closely related: Milicia excelsa and Milicia regia.

Liquidambar formosana, commonly known as the Formosan gum, Chinese sweet gum and Formosa sweet gum, is a species of tree in the family Altingiaceae native to East and Southeast Asia.

Parinari excelsa, the Guinea plum, is a species of large, evergreen tree in the family Chrysobalanaceae. It has a very wide distribution in tropical Africa and the Americas. This species grows to 50 m (160 ft) tall while the trunk is up to 1.5 m (5 ft) in diameter.
Azadirachta excelsa, commonly known as sentang, is a tree in the mahogany family Meliaceae. The specific epithet excelsa is from the Latin meaning 'lofty'.

Liquidambar acalycina, Chang's sweetgum, is a species of flowering plant in the family Altingiaceae native to southern China. Growing to 30–50 ft (9.1–15.2 m) tall and 20–30 ft (6.1–9.1 m) broad. It is a medium-sized deciduous tree with three-lobed maple-like leaves that turn red in autumn before falling. It is monoecious, meaning both male and female flowers appear on the same plant. The flowers are insignificant, yellow/green in colour, and are followed by small gum-balls that persist on the tree until winter. The wood exudes a sweet-smelling resin when pierced, giving the tree its common name.

Salix excelsa is a species of flowering plant in the willow family Salicaceae. It is native to the Caucasus, Central Asia, Iran, Afghanistan, and Pakistan, and has been introduced to the Levant, Yemen, the Himalayas, and India. It is closely related to Salix acmophylla. It is used as a street tree in Georgia and Iran.




















