The World Intellectual Property Organization Copyright Treaty is an international treaty on copyright law adopted by the member states of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) in 1996. It provides additional protections for copyright to respond to advances in information technology since the formation of previous copyright treaties before it. As of August 2023, the treaty has 115 contracting parties. The WCT and WIPO Performances and Phonograms Treaty, are together termed WIPO "internet treaties".

The World Intellectual Property Organization is one of the 15 specialized agencies of the United Nations (UN). Pursuant to the 1967 Convention Establishing the World Intellectual Property Organization, WIPO was created to promote and protect intellectual property (IP) across the world by cooperating with countries as well as international organizations. It began operations on 26 April 1970 when the convention entered into force. The current Director General is Singaporean Daren Tang, former head of the Intellectual Property Office of Singapore, who began his term on 1 October 2020.

The European Union Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO) is a decentralised agency of the EU responsible for the registration of EU-wide unitary trade marks and industrial design rights. These exist alongside the intellectual property rights of individual EU member states, so the agency also works to harmonise EU-wide and national registration processes. Other responsibilities include the administration of the rights of certain products in the EU to carry geographical indications.

Three European Union schemes of geographical indications and traditional specialties, known as protected designation of origin (PDO), protected geographical indication (PGI), and traditional speciality guaranteed (TSG), promote and protect names of agricultural products and foodstuffs, wines and spirits. Products registered under one of the three schemes may be marked with the logo for that scheme to help identify those products. The schemes are based on the legal framework provided by the EU Regulation No 1151/2012 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 November 2012 on quality schemes for agricultural products and foodstuffs. This regulation applies within the EU as well as in Northern Ireland. Protection of the registered products is gradually expanded internationally via bilateral agreements between the EU and non-EU countries. It ensures that only products genuinely originating in that region are allowed to be identified as such in commerce. The legislation first came into force in 1992. The purpose of the law is to protect the reputation of the regional foods, promote rural and agricultural activity, help producers obtain a premium price for their authentic products, and eliminate the unfair competition and misleading of consumers by non-genuine products, which may be of inferior quality or of different flavour. Critics argue that many of the names, sought for protection by the EU, have become commonplace in trade and should not be protected.
The Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property, signed in Paris, France, on 20 March 1883, was one of the first intellectual property treaties. It established a Union for the protection of industrial property. The convention is still in force in 2024. The substantive provisions of the Convention fall into three main categories: national treatment, priority right and common rules.

Industrial property is one of two subsets of intellectual property, it takes a range of forms, including patents for inventions, industrial designs, trademarks, service marks, layout-designs of integrated circuits, commercial names and designations, geographical indications and protection against unfair competition. In some cases, aspects of intellectual creation, although present, are less clearly defined. The object of industrial property consists of signs conveying information, in particular to consumers, regarding products and services offered on the market. Protection is directed against unauthorized use of such signs that could mislead consumers, and against misleading practices in general.
Intellectual property rights (IPRs) have been acknowledged and protected in China since 1980. China has acceded to the major international conventions on protection of rights to intellectual property. Domestically, protection of intellectual property law has also been established by government legislation, administrative regulations, and decrees in the areas of trademark, copyright, and patent.

A geographical indication (GI) is a name or sign used on products which corresponds to a specific geographical location or origin. The use of a geographical indication, as an indication of the product's source, is intended as a certification that the product possesses certain qualities, is made according to traditional methods, or enjoys a good reputation due to its geographical origin.

Chacha is a Georgian pomace brandy, clear and strong, which is sometimes called "wine vodka", "grape vodka", or "Georgian vodka/grappa". It is made of grape pomace. The term chacha is used in Georgia to refer to grape distillate. It may be also produced from unripe or wild grapes. Other common fruits or herbs used are figs, tangerines, oranges, mulberries or tarragon.

The Organisation Africaine de la Propriété Intellectuelle or OAPI is an intellectual property organization, headquartered in Yaoundé, Cameroon. The organisation was created by Bangui Agreement of March 2, 1977. The Bangui Agreement was subsequently amended in 1999.

The Berne Convention for the Protection of Literary and Artistic Works, usually known as the Berne Convention, was an international assembly held in 1886 in the Swiss city of Berne by ten European countries with the goal of agreeing on a set of legal principles for the protection of original work. They drafted and adopted a multi-party contract containing agreements for a uniform, border-crossing system that became known under the same name. Its rules have been updated many times since then. The treaty provides authors, musicians, poets, painters, and other creators with the means to control how their works are used, by whom, and on what terms. In some jurisdictions these type of rights are referred to as copyright; on the European continent they are generally referred to as authors' rights or makerright.

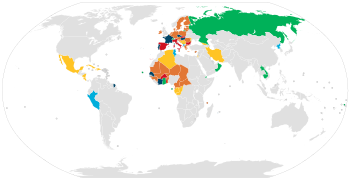
The Hague Agreement Concerning the International Deposit of Industrial Designs, also known as the Hague system provides a mechanism for registering an industrial design in several countries by means of a single application, filed in one language, with one set of fees. The system is administered by WIPO.

Iran is a member of the WIPO since 2001 and has acceded to several WIPO intellectual property treaties. Iran joined the Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property in 1959. In December 2003 Iran became a party to the Madrid Agreement and the Madrid Protocol for the International Registration of Marks. In 2005 Iran joined the Lisbon Agreement for the Protection of Appellations of Origin and their International Registration, which ensures the protection of geographical names associated with products. As at February 2008 Iran had yet to accede to The Hague Agreement for the Protection of Industrial Designs.
The Madrid System, also known as the Madrid Protocol or simply Madrid, is the primary international system for facilitating the registration of trademarks in multiple jurisdictions around the world. It was established pursuant to the multilateral treaties Madrid Agreement Concerning the International Registration of Marks of 1891 and the Protocol Relating to the Madrid Agreement (1989), which has been the sole governing treaty since 2016.
The country of Georgia is the first among the EU neighbourhood countries to take an important step towards protecting its local food and beverages from being copied in other countries. The country has a rich history of local and specialist agricultural production and has long been famed for its wines. Names of as many as 18 premium quality local wines have been protected by the use of appellation system, the appellations usually being the geographical name of the area in which the wine is produced.
Geographical Indications in Cambodia are a form of intellectual property consisting of an "which is a name or represents a geographical origin and identifies the goods as originating in such geographical area where a given quality, reputation or other characteristic of the goods is essentially attributable to its geographical origin;". Geographical indications can be registered based on the Law on Geographical Indications Registration is open for agricultural goods and foodstuffs, but also for handicraft goods
Geographical Indications in Tunisia are a form of intellectual property available for "natural or processed agricultural and food products". Geographical indications can be registered based on the Law No. 99-57 of June 28, 1999, on Controlled Appellations of Origin and Indications of Source of Agricultural Products Registrations is possible as a Appellation of Origin or as an Indication of Source.
The WIPO Hague System provides an international mechanism for securing and managing design rights simultaneously, in multiple countries and regions, through one application filed directly with WIPO. The resulting international registration provides design owners with the equivalent of a bundle of national or regional registrations. The subsequent management of that international registration – including modifications, updates and renewals – is a single step procedure through WIPO.
The Intergovernmental Committee on Intellectual Property and Genetic Resources, Traditional Knowledge and Folklore is in charge of negotiating one or several international legal instruments (treaty) to protect traditional knowledge, traditional cultural expressions, and genetic resources in relation with intellectual property, thus bridging existing gaps in international law. The IGC is convened in Geneva by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), and has been meeting regularly since 2001.