Related Research Articles

Copper indium gallium (di)selenide (CIGS) is a I-III-VI2 semiconductor material composed of copper, indium, gallium, and selenium. The material is a solid solution of copper indium selenide (often abbreviated "CIS") and copper gallium selenide. It has a chemical formula of CuIn1−xGaxSe2, where the value of x can vary from 0 (pure copper indium selenide) to 1 (pure copper gallium selenide). CIGS is a tetrahedrally bonded semiconductor, with the chalcopyrite crystal structure, and a bandgap varying continuously with x from about 1.0 eV (for copper indium selenide) to about 1.7 eV (for copper gallium selenide).

A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity by using photovoltaic (PV) cells. PV cells are made of materials that produce excited electrons when exposed to light. The electrons flow through a circuit and produce direct current (DC) electricity, which can be used to power various devices or be stored in batteries. Solar panels are also known as solar cell panels, solar electric panels, or PV modules.
HelioVolt Corporation was a privately held solar energy company based in Austin, Texas that suspended operations in 2014. The company manufactured photovoltaic (PV) solar modules using a thin film semiconductor process based on copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) to produce CIGS solar cells. HelioVolt manufactured these thin film modules for commercial rooftop, utility-scale ground mount, residential, building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) and custom installations. The company raised over $230 million in investments, including over $80 million by SK Group.
MiaSolé is an American solar energy company selling copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) thin-film photovoltaic products. MiaSolé's manufacturing process lays CIGS on a flexible stainless steel substrate. MiaSolé produces all layers of photovoltaic material in a continuous sputtering process.
International Solar Electric Technology, or ISET, was a company invested in copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) photovoltaics. ISET's research over two decades had been largely funded by grants from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Members helped found or worked in many of the more well known CIGS companies, such as Nanosolar, Solopower, Showa, and Honda Soltec Despite a lack of venture capital, ISET planned to launch a thin film, produced in a new Chatsworth plant with hundreds of megawatts per year capacity after the pilot plant is proven. The company believed they will be able to at first achieve 10% efficient modules sold for $0.65 per watt, then 15% efficient for $0.50 per watt, and potentially ultimately as low as $0.40 per watt.
Global Solar Energy is a US-based manufacturer of CIGS solar cells, a thin-film based photovoltaic technology, with manufacturing operations in Tucson, Arizona, United States, and Berlin, Germany. In 2013, it was bought by Chinese renewable energy company Hanergy.

Ascent Solar Technologies, Inc. is a publicly traded photovoltaic (PV) company located in Thornton, Colorado. Its primary product is a flexible CIGS solar cell on a plastic substrate.
Odersun was a German photovoltaic (PV) company that developed and manufactured CIGS cells on a flexible copper backing, specifically designed for building-integrated photovoltaics. The insolvent company went into administration on 1 June 2012 and filed for bankruptcy.

Thin-film solar cells are made by depositing one or more thin layers of photovoltaic material onto a substrate, such as glass, plastic or metal. Thin-film solar cells are typically a few nanometers (nm) to a few microns (µm) thick–much thinner than the wafers used in conventional crystalline silicon (c-Si) based solar cells, which can be up to 200 µm thick. Thin-film solar cells are commercially used in several technologies, including cadmium telluride (CdTe), copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS), and amorphous thin-film silicon.

Between 1992 and 2023, the worldwide usage of photovoltaics (PV) increased exponentially. During this period, it evolved from a niche market of small-scale applications to a mainstream electricity source. From 2016-2022 it has seen an annual capacity and production growth rate of around 26%- doubling approximately every three years.

A copper indium gallium selenide solar cell is a thin-film solar cell used to convert sunlight into electric power. It is manufactured by depositing a thin layer of copper indium gallium selenide solid solution on glass or plastic backing, along with electrodes on the front and back to collect current. Because the material has a high absorption coefficient and strongly absorbs sunlight, a much thinner film is required than of other semiconductor materials.
SoloPower was a solar energy company developing and manufacturing Copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) thin-film flexible Photo-voltaic Solar Panels. The company used a special electroplating technology to utilize nearly 100% of its materials.
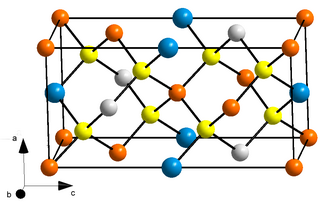
Copper zinc tin sulfide (CZTS) is a quaternary semiconducting compound which has received increasing interest since the late 2000s for applications in thin film solar cells. The class of related materials includes other I2-II-IV-VI4 such as copper zinc tin selenide (CZTSe) and the sulfur-selenium alloy CZTSSe. CZTS offers favorable optical and electronic properties similar to CIGS (copper indium gallium selenide), making it well suited for use as a thin-film solar cell absorber layer, but unlike CIGS (or other thin films such as CdTe), CZTS is composed of only abundant and non-toxic elements. Concerns with the price and availability of indium in CIGS and tellurium in CdTe, as well as toxicity of cadmium have been a large motivator to search for alternative thin film solar cell materials. The power conversion efficiency of CZTS is still considerably lower than CIGS and CdTe, with laboratory cell records of 11.0 % for CZTS and 12.6 % for CZTSSe as of 2019.
Solar Frontier Kabushiki Kaisha is a Japanese photovoltaic company that develops and manufactures thin film solar cells using CIGS technology. It is a fully owned subsidiary of Showa Shell Sekiyu and located in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The company was founded in 2006 as Showa Shell Solar, and renamed Solar Frontier in April 2010.
SoloPower Systems Inc. technology is used to create ultra-lightweight, thin-film, flexible Solar Panels, based on CIGS. Originally developed by San Jose, California-based Solopower Inc., the technology is now owned by Solopower Systems Inc., a solar panel development & manufacturing company based in Portland, Oregon. SoloPower technology features an electroplating process that utilizes nearly 100% of its materials to manufacture its CIGS cells.
Hanergy Holding Group Ltd. (Hanergy) is a Chinese multinational company headquartered in Beijing. The company is focusing on thin-film solar value chain, including manufacturing and solar parks development. It also owns the Jinanqiao Hydroelectric Power Station and two wind farms.
Siva Power, Inc. is an American solar power company that developed thin-film technology. The company designed and manufactured copper indium gallium deselenide (CIGS) photovoltaics. Siva Power is based in San Jose, California. Bruce Sohn is CEO and Mark Heising is Chairman.
Flisom was a developer and manufacturer of photovoltaic (PV) thin film solar cells, located near Zurich, Switzerland, founded in 2005. The company produced high-efficiency CIGS thin film solar modules on flexible plastic foil using proprietary roll-to-roll manufacturing techniques. It went into liquidation in 2023.
Hanwha Qcells is a major manufacturer of photovoltaic cells. The company is headquartered in Seoul, South Korea, after being founded in 1999 in Bitterfeld-Wolfen, Germany, where the company still has its engineering offices. Qcells was purchased out of bankruptcy in August 2012 by the Hanwha Group, a South Korean business conglomerate. Qcells now operates as a subsidiary of Hanwha Solutions, the group's energy and petrochemical company.
References
- ↑ "MiaSolé Thin Film Solar Panels: Complete Review | EnergySage". 3 June 2021.
- ↑ "About us", Midsummer. Retrieved 19 May 2022.
- ↑ Pickerel, Kelly (27 December 2018). "U.S. thin-film solar panel company Sunflare will expand its Chinese manufacturing facility with new equipment". Solar Power World. WTWH Media. Retrieved 21 January 2023.
- ↑ "Story". sunplugged. Retrieved 31 January 2024.
- ↑ "Die halbe Solarfabrik steht leer". 6 January 2022.
- ↑ "Another blow to thin film, as Solar Frontier quits manufacturing and switches sides". 3 November 2021.
- ↑ "Solarion wird abgewickelt". Stefan Schroeter. Retrieved 23 February 2024.
- ↑ "TSMC Solar—CIGS is Now a Reality". TSMC Solar. Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- ↑ "TSMC Pulls Plug on Solar Business". EE Times. Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- ↑ "Veeco drops CIGS solar systems biz", Renewable Energy World, 8.1.2011. Retrieved 19 May 2022.