Related Research Articles

The Deutsche Bahn AG is the national railway company of Germany, and a state-owned enterprise under the control of the German government. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company (AG).

The Deutsche Reichsbahn, also known as the German National Railway, the German State Railway, German Reich Railway, and the German Imperial Railway, was the German national railway system created after the end of World War I from the regional railways of the individual states of the German Empire. The Deutsche Reichsbahn has been described as "the largest enterprise in the capitalist world in the years between 1920 and 1932"; nevertheless its importance "arises primarily from the fact that the Reichsbahn was at the center of events in a period of great turmoil in German history".

The Deutsche Reichsbahn or DR(German Reich Railways) was the operating name of state owned railways in the German Democratic Republic, and after German reunification until 1 January 1994.
The railways in Germany use several abbreviations to differentiate between various types of stations, stops, railway facilities and other places of rail service.

Kassel-Wilhelmshöhe is a railway station in the city of Kassel, in the German state of Hesse. It is the city's most important railway station, as it is connected to the Hanover-Würzburg high-speed rail line, with InterCityExpress services calling at the station.

Hamburg Hauptbahnhof, or Hamburg Central Station in English, is the main railway station of the city of Hamburg, Germany. Opened in 1906 to replace four separate terminal stations, today Hamburg Hauptbahnhof is operated by DB Station&Service AG. With an average of 550,000 passengers a day, it is Germany's busiest railway station and the second-busiest in Europe after the Gare du Nord in Paris. It is classed by Deutsche Bahn as a category 1 railway station.

Mannheim Hauptbahnhof is a railway station in Mannheim in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is the second largest traffic hub in southwestern Germany after Stuttgart Hauptbahnhof, with 658 trains a day, including 238 long-distance trains. It is also a key station in the Rhine-Neckar S-Bahn. 100,000 passengers embark, disembark or transfer between trains at the station each day. The station was modernised in 2001. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 2 station.
In Germany and Austria, the running of railway services for a railway administration or the regional network of a large railway company was devolved to railway divisions, variously known as Eisenbahndirektionen (ED), Bundesbahndirektionen (BD) or Reichsbahndirektionen (RBD/Rbd). Their organisation was determined by the railway company concerned or by the state railway and, in the German-speaking lands at least, they formed the intermediate authorities and regional management organisations within the state railway administration's hierarchy. On the formation of the Deutsche Bahn AG in 1994 the system of railway divisions (Eisenbahndirektionen) in Germany was discontinued and their tasks were transferred to new "business areas".

A Kleinlokomotive or Kleinlok is a German locomotive of small size and low power for light shunting duties at railway stations and on industrial railways. Most are powered by diesel engines, but Kleinloks with steam, petrol, or electric engines were also produced.
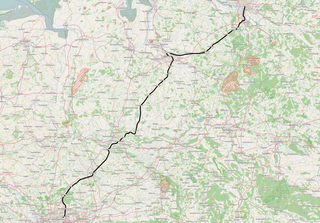
The Wanne-Eickel–Hamburg railway is the shortest railway link between the Metropole Ruhr and the Hamburg Metropolitan Region and hence one of the most important railway lines in northwest Germany. The Route runs over the cities Münster (Westfalen), Osnabrück and Bremen.

This article shows a list of railway stations in Germany. The list is subdivided per federal state. Due to the number of railway stations it shows a selection of the principal stations and links to related state articles. Where there are 2 or more passenger stations in a large town or city, the most important is often designated by the Deutsche Bahn as the Hauptbahnhof, of which there are 122 in total.

Hanau Hauptbahnhof is a railway station in Hanau in the German state of Hesse, and is a major railway junction east of Frankfurt am Main. It was opened in 1867, but the current building was built in the late 1960s. It is located about 1.5 kilometres (0.93 mi) south-east of central Hanau. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn (DB) as a category 2 station and has many train services, including Intercity Express, regional and S-Bahn services.

Plochingen station is the only station in the town of Plochingen in the German state of Baden-Württemberg and the most important railway junction of the Esslingen district. It is located 22.8 kilometres from Stuttgart Hauptbahnhof on the Fils Valley Railway and at the beginning of the Plochingen–Immendingen railway.

A station code is a brief, standardised abbreviation, or alphanumeric code, used by railways to identify a railway station uniquely. Codes are mostly used internally but can be seen on railway traffic signs and on some timetables.

Malmsheim station is in the town of Malmsheim in the municipality of Renningen in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located at kilometer 22.4 of the Black Forest Railway and it is served by line S 6 of the Stuttgart S-Bahn.

Leinfelden station is located in Leinfelden-Echterdingen at the 20.6 kilometre point of the Stuttgart-Rohr–Filderstadt railway in the German state of Baden-Württemberg and is a station on the Stuttgart S-Bahn network.
The Nuremberg–Feucht railway is a 12.5-kilometre (7.8 mi)-long main-line railway in the German state of Bavaria, running from Nuremberg Hauptbahnhof to Feucht. It was built parallel with the Nuremberg–Regensburg railway during the first construction phase of the Nuremberg S-Bahn and opened on 21 November 1992.

Mühlheim (Main) station is a railway station serving the town of Mühlheim am Main, approximately 11.5 kilometres (7.1 mi) to the east of the city of Frankfurt am Main in Hesse, Germany. It has two tracks on a single island platform, and both are served by S-Bahn lines S8 and S9, which run from Wiesbaden in the west to Hanau in the east via Frankfurt Airport, Frankfurt Hauptbahnhof and the city tunnel, and Offenbach Ost. Trains call approximately every 30 minutes during the day, with more frequent quarter-hourly services during the rush hour. Late in the evenings, early in the mornings, and on Sundays, services are restricted to once per hour in either direction, as other S8 and S9 services terminate at Offenbach Ost instead of Hanau Hbf.
References
- ↑ Deutsche Bahn AG: Richtlinie 100.0001A01 Abkürzungen für Örtlichkeiten (status: 2016)