
Developmental psychology is the scientific study of how and why human beings change over the course of their life. Originally concerned with infants and children, the field has expanded to include adolescence, adult development, aging, and the entire lifespan. Developmental psychologists aim to explain how thinking, feeling, and behaviors change throughout life. This field examines change across three major dimensions: physical development, cognitive development, and socioemotional development. Within these three dimensions are a broad range of topics including motor skills, executive functions, moral understanding, language acquisition, social change, personality, emotional development, self-concept, and identity formation.

Infant baptism is the practice of baptising infants or young children. In theological discussions, the practice is sometimes referred to as paedobaptism, or pedobaptism, from the Greek pais meaning "child". This can be contrasted with what is called "believer's baptism", or credobaptism, from the Latin word credo meaning "I believe", which is the religious practice of baptising only individuals who personally confess faith in Jesus, therefore excluding underage children. Opposition to infant baptism is termed catabaptism. Infant baptism is also called "christening" by some faith traditions.

Botulism is a rare and potentially fatal illness caused by a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. The disease begins with weakness, blurred vision, feeling tired, and trouble speaking. This may then be followed by weakness of the arms, chest muscles, and legs. Vomiting, swelling of the abdomen, and diarrhea may also occur. The disease does not usually affect consciousness or cause a fever.

Infant formula, baby formula or just formula or baby milk, infant milk or first milk, is a manufactured food designed and marketed for feeding to babies and infants under 12 months of age, usually prepared for bottle-feeding or cup-feeding from powder or liquid. The U.S. Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA) defines infant formula as "a food which purports to be or is represented for special dietary use solely as a food for infants by reason of its simulation of human milk or its suitability as a complete or partial substitute for human milk".

Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), also known as cot death or crib death, is the sudden unexplained death of a child of less than one year of age. Diagnosis requires that the death remain unexplained even after a thorough autopsy and detailed death scene investigation. SIDS usually occurs during sleep. Typically death occurs between the hours of 00:00 and 09:00. There is usually no noise or evidence of struggle.
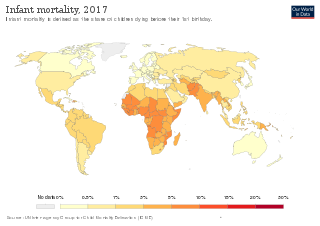
Infant mortality is the death of young children under the age of 1. This death toll is measured by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the number of deaths of children under one year of age per 1000 live births. The under-five mortality rate, which is referred to as the child mortality rate, is also an important statistic, considering the infant mortality rate focuses only on children under one year of age.
An infant is the more formal or specialised synonym for "baby", the very young offspring of a human. The term may also be used to refer to juveniles of other organisms.

A lullaby, or cradle song, is a soothing song or piece of music that is usually played for children. The purposes of lullabies vary. In some societies they are used to pass down cultural knowledge or tradition. In addition, lullabies are often used for the developing of communication skills, indication of emotional intent, maintenance of infants' undivided attention, modulation of infants' arousal, and regulation of behavior. Perhaps one of the most important uses of lullabies is as a sleep aid for infants. As a result, the music is often simple and repetitive. Lullabies can be found in many countries, and have existed since ancient times.
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen to the body that arises from abnormal breathing. An example of asphyxia is choking. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which affects primarily the tissues and organs. There are many circumstances that can induce asphyxia, all of which are characterized by an inability of an individual to acquire sufficient oxygen through breathing for an extended period of time. Asphyxia can cause coma or death.
An infant school is a term used primarily in England and Wales. This for the education of children between the ages of four and seven years. It is usually a small school serving a particular area.

Breast milk or mother milk refers to milk produced by mammary glands located in the breast of a human female to feed a child. Milk is the primary source of nutrition for newborns before they are able to eat and digest other foods; older infants and toddlers may continue to be breastfed, in combination with other foods from six months of age when solid foods should be introduced.

Attachment theory is a psychological model attempting to describe the dynamics of long-term and short-term interpersonal relationships between humans. "Attachment theory is not formulated as a general theory of relationships; it addresses only a specific facet": how human beings respond in relationships when hurt, separated from loved ones, or perceiving a threat.

Cuteness is a subjective term describing a type of attractiveness commonly associated with youth and appearance, as well as a scientific concept and analytical model in ethology, first introduced by Konrad Lorenz. Lorenz proposed the concept of baby schema (Kindchenschema), a set of facial and body features, that make a creature appear "cute" and activate ("release") in others the motivation to care for it. Cuteness may be ascribed to people as well as things that are regarded as attractive or charming.
Infante, also anglicised as Infant or translated as Prince, is the title and rank given in the Iberian kingdoms of Spain and Portugal to the sons and daughters (infantas) of the king, regardless of age, sometimes with the exception of the [male] heir apparent to the throne, who usually bears a unique princely or ducal title. The wife of a male infante was accorded the title of infanta if the marriage was dynastically approved, although since 1987 this is no longer automatically the case in Spain. Husbands of born infantas did not obtain the title of infante through marriage, although occasionally elevated to that title de gracia at the sovereign's command.
Neonatology is a subspecialty of pediatrics that consists of the medical care of newborn infants, especially the ill or premature newborn. It is a hospital-based specialty, and is usually practiced in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs). The principal patients of neonatologists are newborn infants who are ill or require special medical care due to prematurity, low birth weight, intrauterine growth restriction, congenital malformations, sepsis, pulmonary hypoplasia or birth asphyxia.

A neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), also known as an intensive care nursery (ICN), is an intensive care unit (ICU) specializing in the care of ill or premature newborn infants. Neonatal refers to the first 28 days of life. Neonatal care, as known as specialized nurseries or intensive care, has been around since the 1960s.

An infant bodysuit or onesie is a garment designed to be worn by infants much like a T-shirt; they are distinguished from T-shirts by an extension below the waist, with snaps that allow it to be closed over the crotch.The purpose of the opening at the crotch is to facilitate access to the infant's diaper as well as preventing the garment from riding up the infant's body and exposing skin. Like T-shirts, infant bodysuits come in a wide variety of designs and may be worn as undergarments or as outer shirts.

Breastfeeding, also known as nursing, is the feeding of babies and young children with milk from a woman's breast. Health professionals recommend that breastfeeding begin within the first hour of a baby's life and continue as often and as much as the baby wants. During the first few weeks of life babies may nurse roughly every two to three hours, and the duration of a feeding is usually ten to fifteen minutes on each breast. Older children feed less often. Mothers may pump milk so that it can be used later when breastfeeding is not possible. Breastfeeding has a number of benefits to both mother and baby, which infant formula lacks.













