
Metropolitan Manila, commonly shortened to Metro Manila and formally the National Capital Region, is the capital region and largest metropolitan area of the Philippines. Located on the eastern shore of Manila Bay, the region lies between the Central Luzon and Calabarzon regions. Encompassing an area of 636.00 km2 (245.56 sq mi) and with a population of 13,484,462 as of 2020, it is composed of sixteen highly urbanized cities: the capital city, Manila, Caloocan, Las Piñas, Makati, Malabon, Mandaluyong, Marikina, Muntinlupa, Navotas, Parañaque, Pasay, Pasig, Quezon City, San Juan, Taguig, and Valenzuela, along with one independent municipality, Pateros. As the second most populous and the most densely populated region in the Philippines, it ranks as the 9th most populous metropolitan area in Asia and the 6th most populous urban area in the world.

The Pasig River is a water body in the Philippines that connects Laguna de Bay to Manila Bay. Stretching for 25.2 kilometers (15.7 mi), it bisects the Philippine capital of Manila and its surrounding urban area into northern and southern halves. Its major tributaries are the Marikina River and San Juan River. The total drainage basin of the Pasig River, including the basin of Laguna de Bay, covers 4,678 square kilometers (1,806 sq mi).

Mandaluyong, officially the City of Mandaluyong, is a highly urbanized city in the National Capital Region of the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 425,758 people.

Epifanio de los Santos Avenue, commonly referred to by its acronym EDSA, is a limited-access circumferential highway around Manila, the capital city of the Philippines. It passes through 6 of Metro Manila's 17 local government units or cities, namely, from north to south, Caloocan, Quezon City, San Juan, Mandaluyong, Makati, and Pasay.

Rail transportation in the Philippines is currently used mostly to transport passengers within Metro Manila and provinces of Laguna and Quezon, as well as a commuter service in the Bicol Region. Freight transport services once operated in the country, but these services were halted. However, there are plans to restore old freight services and build new lines. From a peak of 1,100 kilometers (680 mi), the country currently has a railway footprint of 533.14 kilometers (331.28 mi), of which only 129.85 kilometers (80.69 mi) are operational as of 2024, including all the urban rail lines. World War II, natural calamities, underspending, and neglect have all contributed to the decline of the Philippine railway network. In the 2019 Global Competitiveness Report, the Philippines has the lowest efficiency score among other Asian countries in terms of efficiency of train services, receiving a score of 2.4, and ranking 86th out of 101 countries globally. The government is currently expanding the railway network up to 1,900 kilometers (1,200 mi) by 2022 through numerous projects.

The Metropolitan Manila Development Authority is a government agency of the Philippines responsible for constituting the regional government of Metro Manila, comprising the capital city of Manila, the cities of Quezon City, Caloocan, Pasay, Mandaluyong, Makati, Pasig, Marikina, Muntinlupa, Las Piñas, Parañaque, Valenzuela, Malabon, Taguig, Navotas and San Juan, and the municipality of Pateros.

Guadalupe station is an elevated Metro Rail Transit (MRT) station located on the MRT Line 3 (MRT-3) system in Makati. It is named because of its location between the barangays of Guadalupe Nuevo and Guadalupe Viejo, both are in turn named after Our Lady of Guadalupe.

The Pasig River Ferry Service (PRFS) is a public water bus service based in Metro Manila, the Philippines. It is currently the only water-based transportation service in Metro Manila that cruises the length of the Pasig River and Marikina River, passing through the cities of Manila, Makati, Mandaluyong, Pasig, Marikina, and Taguig.
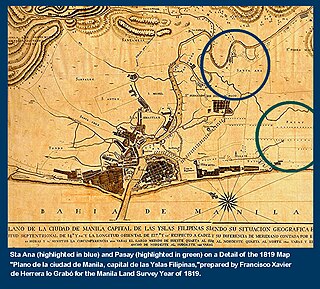
Namayan, also called Sapa, Maysapan, and sometimes Lamayan, was a Luzonian town that is now the Santa Ana district in Manila city proper along the Pasig River in the Philippines.

The transportation system in Metro Manila covers the road network, rail network, ferries, ports and airports located within the metropolitan Manila area. Road transportation in Metro Manila is diverse, composed of many types of private and public transport vehicles. These include taxis, buses, jeepneys, tricycles and pedicabs. In some areas, especially in Divisoria and large public markets, two-stroke motors are fitted in the pedicabs and are used for goods transport. Regardless of modernity, horse-drawn kalesas are still used in the streets of Binondo and Intramuros. Ridesharing services such as Grab also operate within Metro Manila.

The San Juan River is one of the main river systems in Metro Manila, Philippines, and is a major tributary of the Pasig River. It begins near La Mesa Dam as the San Francisco del Monte River, which officially takes the name San Juan River when it meets with Mariblo Creek in Quezon City. As the San Juan River, it passes through Quezon City, San Juan, the Manila district of Santa Mesa and Santa Ana, and Mandaluyong.

Shaw Boulevard is a 4-8 lane highway connecting the cities of Mandaluyong and Pasig in the Philippines. The boulevard is named after William James Shaw, the founder of the Wack Wack Golf and Country Club in Mandaluyong. The road is one of the major thoroughfares of the Ortigas Center in Mandaluyong and Pasig, housing many shopping malls like the Starmall shopping center and the posh Shangri-La Plaza at the EDSA-Shaw intersection and The Marketplace, which is visible from the Kalentong-Shaw intersection and Sevilla Bridge.

Pedro Gil Street is an east-west inner city street and a tertiary national road in south-central Manila, Philippines. It is 3.65 kilometers (2.27 mi) long and spans the entire length of Ermita, Malate, Paco, and Santa Ana. The street is served by the Pedro Gil LRT Station along Taft Avenue and the Paco railway station along Quirino Avenue. It also continues towards the central Metro Manila cities of Mandaluyong and San Juan across the Pasig River as New Panaderos and General Kalentong Streets.

J. P. Rizal Avenue, also known as J. P. Rizal Street, is a major local avenue in Makati and Taguig, Metro Manila, Philippines. It is a contour collector road on the south bank of the Pasig River that runs east–west from Pateros Bridge at the Taguig–Pateros boundary to its intersection with Zobel Roxas, Delpan, and Tejeron Streets at the Makati–Manila boundary. It is a component of Radial Road 4 (R-4). The avenue was named after the Philippines' national hero, Dr. José P. Rizal.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Metro Manila:

Radial Road 5, more commonly referred to as R-5, is a network of roads and bridges that all together form the fifth radial road of Manila in the Philippines. The road links the City of Manila with Mandaluyong and Pasig in the east, leading out of Metro Manila into the province of Rizal and south towards Laguna. It is the only arterial road traversing the east side of Laguna de Bay.

The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the Philippine capital region of Metro Manila.

The Estrella–Pantaleon Bridge, also known as the Rockwell Bridge, is a four-lane box girder bridge crossing the Pasig River in Metro Manila, Philippines. It connects Estrella Street in Makati on the south bank of the Pasig River, to Pantaleon Street via Barangka Drive in Mandaluyong on the north bank, near the site of the Acqua Private Residences.

The Guadalupe Bridge is a road bridge crossing the Pasig River in Metro Manila, Philippines, linking the cities of Makati and Mandaluyong. It serves as a conduit for EDSA and the MRT Line 3.

The Makati–Mandaluyong Bridge is a four-lane road bridge crossing the Pasig River between Makati and Mandaluyong in Metro Manila, Philippines. It connects P. Burgos Extension, a continuation of Makati Avenue in Poblacion, Makati at the south bank of the river to Coronado Street in Hulo, Mandaluyong at its north bank. The bridge was opened in 1986.












































