
North Macedonia is a country situated in southeastern Europe with geographic coordinates 41°50′N22°00′E, bordering Kosovo and Serbia to the north, Bulgaria to the east, Greece to the south and Albania to the west. The country is part of the wider region of Macedonia and makes up most of Vardar Macedonia. The country is a major transportation corridor from Western and Central Europe to Southern Europe and the Aegean Sea. North Macedonia is a landlocked country but has three major natural lakes: Lake Ohrid, Lake Prespa and Lake Dojran. It has a water area of 857 km2, while its land area is 24,856 km2.

The Šarplaninac or Sharr dog is a breed of dog of livestock guardian type. It is named for the Šar Mountains or Šar Planina range in the Balkans, where it is principally found. It was recognised by the Fédération Cynologique Internationale as the Illyrian Shepherd Dog or Ilirski Ovčar from 1939 until 1957, when the name was changed to Yugoslavian Shepherd Dog – Sharplanina or Jugoslovenski Ovčarski Pas – Šarplaninac.

The Šar Mountains or Sharr Mountains is a mountain range extending from southern Kosovo, to northwestern North Macedonia, to northeastern Albania. The sections in Kosovo, and in North Macedonia are national parks. Rugged and barren, the mountains are among the highest in the Balkans, with 30 peaks higher than 2,500 m (8,202 ft).

Europe is traditionally defined as one of seven continents. Physiographically, it is the northwestern peninsula of the larger landmass known as Eurasia ; Asia occupies the centre and east of this continuous landmass. Europe's eastern frontier is usually delineated by the Ural Mountains in Russia, which is the largest country by land area in the continent. The southeast boundary with Asia is not universally defined, but the modern definition is generally the Ural River or, less commonly, the Emba River. The boundary continues to the Caspian Sea, the crest of the Caucasus Mountains, and on to the Black Sea. The Bosporus, the Sea of Marmara, and the Dardanelles conclude the Asian boundary. The Mediterranean Sea to the south separates Europe from Africa. The western boundary is the Atlantic Ocean. Iceland is usually included in Europe because it is over twice as close to mainland Europe as mainland North America. There is ongoing debate on where the geographical centre of Europe falls.

Baba, also known by the name of its highest peak, Pelister, is a mountain in North Macedonia. The Pelister peak overlooks the city of Bitola. Baba is the third highest mountain in North Macedonia. Other peaks besides Pelister are Dva Groba, Veternica, Musa, Ržana, Široka, Kozji Kamen, Griva and Golema Čuka in North Macedonia, and Belavoda, Kirko. The Baba massif splits up the rivers in the region, so that they either flow towards the Adriatic.

Jakupica or Mokra is a mountain range in the central part of North Macedonia. The headwaters of the Axios river, mentioned by Homer as the home of the Paeonians allies of Troy, spring from its flanks.

Osogovo, or Osogovska Planina or Osogovski Planini, is a mountain range and ski resort between the south-western part of Bulgaria and the north-eastern part of North Macedonia. Osogovo Monastery is situated on the mountain.

Radika is a river in southern Kosovo and western North Macedonia, a 70 km (43 mi)-long right tributary to the Black Drin river.

Golyam Perelik is the highest peak in the Rhodope Mountains, situated 19 km to the west of Smolyan. It makes the Rhodopes the seventh highest Bulgarian mountain range after Rila, Pirin, Stara Planina, Vitosha, Osogovo and Slavyanka. The peak is easily accessible, but currently cannot be climbed because a unit of the Bulgarian Army is stationed in its vicinity.

Tourism in North Macedonia is a large factor of the nation's economy. The country's large abundance of natural and cultural attractions make it suitable for tourism.

The Pindus Mountains mixed forests constitute a terrestrial ecoregion of Europe according to both the WWF and Digital Map of European Ecological Regions by the European Environment Agency. It belongs to the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome, and is in the Palearctic realm.

Korab is a mountain range in eastern Albania and western North Macedonia, running along the border between the two countries. It forms also the European Green Belt. In Albania, it is also called Vargu lindor, but this term encompasses mountains further north, such as the Koritnik and Gjallica. The highest peak is Mount Korab at 2,764 m (9,068 ft) above sea level. With a prominence of 2,169 m (7,116 ft), Korab is the 18th most prominent mountain peak in the European continent. The mountains are composed of sedimentary rock, including shale, sandstone, dolomite and limestone. The name refers to a pre-Christian sea god.
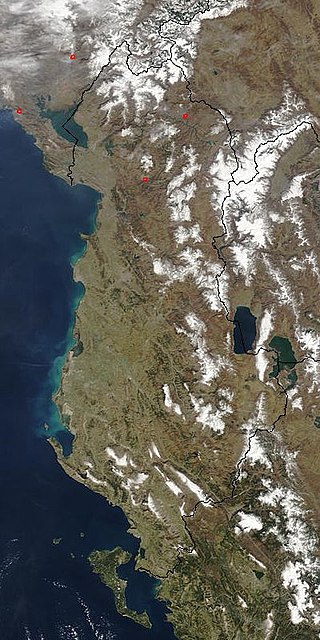
The Central Mountain Region is a physiogeographical region encompassing the central and eastern edge of Albania. It comprises the mountainous inland extending all the way from the valley of Drin and the mountains of Sharr, Skanderbeg, Korab, and Shebenik-Jabllanicë, through the lakes of Ohrid and Prespa, until it reaches the village of Ersekë and the mountains of Pindus close to the border between the country and Greece.

Mavrovo National Park is the largest of the four national parks of North Macedonia. Located in the west of the country, it spreads over an area of about 780 km2 and is characterized by deep canyons, lakes, and dense forests that abound with diverse wildlife. It was established in 1949 by a law passed by the National Assembly of Macedonia; later the legislation was changed to enforce a much stricter protection system, dividing the park into three zones: strict nature reserves, managed reserves, and a tourist zone.

Geum montanum, the Alpine avens, is a species of flowering plant of the genus Geum in the Rosaceae family, native to the mountains of central and southern Europe.

Pelister National Park is a national park in the Municipality of Bitola, North Macedonia. The park is located in the Baba Mountain massif and covers an area of 171.5 square kilometres (66.2 sq mi). The altitude of the park varies between 927 and 2,601 m above sea level and is filled with exquisite flora and fauna. Among flora elements, the presence is especially significant of the five-needle pine molica, Pinus peuce - a unique species of Cenozoic age being present on only a few mountains in the Balkan Peninsula. The beauty of the landscape is enhanced by the diverse wildlife: bears, roe deer, wolves, chamois, deer, wild boars, rabbits, several species of eagles, partridges, red-billed choughs, and the endemic Macedonian Pelagonia trout.

The geology of North Macedonia includes the study of rocks dating to the Precambrian and a wide array of volcanic, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks formed in the last 539 million years.
Geum molle is a species of flowering plant of the genus Geum (avens) in the family Rosaceae. A perennial herbaceous plant found on meadows, it is native to the mountains of the Balkan Peninsula and Italy. It blooms with yellow flowers between June and August.





















