Related Research Articles

South Dakota is a landlocked state in the North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Dakota Sioux tribe, which comprises a large portion of the population with nine reservations currently in the state and has historically dominated the territory. South Dakota is the 17th-largest by area, but the fifth-least populous, and the fifth-least densely populated of the 50 United States. Pierre is the state capital, and Sioux Falls, with a population of about 213,900, is South Dakota's most populous city. The state is bisected by the Missouri River, dividing South Dakota into two geographically and socially distinct halves, known to residents as "East River" and "West River". South Dakota is bordered by North Dakota to the north, Minnesota to the east, Iowa to the southeast, Nebraska to the south, Wyoming to the west, and Montana to the northwest.

Alonzo Jay Edgerton was a United States senator from Minnesota and a United States district judge of the United States District Court for the District of South Dakota.
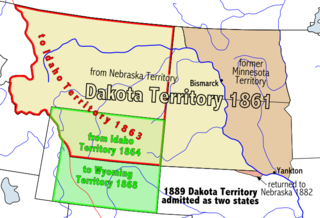
The Territory of Dakota was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 2, 1861, until November 2, 1889, when the final extent of the reduced territory was split and admitted to the Union as the states of North and South Dakota.

The Dakotas, also known as simply Dakota, is a collective term for the U.S. states of North Dakota and South Dakota. It has been used historically to describe the Dakota Territory, and is still used for the collective heritage, culture, geography, fauna, sociology, economy, and cuisine of the two states.

The United States District Court for the District of South Dakota is the United States District Court or the Federal district court, whose jurisdiction for issues pertaining to federal law or diversity for the state of South Dakota. The court is based in Sioux Falls with other courthouses in Rapid City, Pierre, and Aberdeen. The district was created in 1889, when the Dakota Territory was divided into North and South Dakota.

The South Dakota Supreme Court is the highest court in the state of South Dakota. It is composed of a chief justice and four associate justices appointed by the governor. One justice is selected from each of five geographic appointment districts. Justices face a nonpolitical retention election three years after appointment and every eight years after that. The justices also select their own chief justice.

The Great Sioux Reservation is an Indian reservation created by the United States through treaty with the Sioux, principally the Lakota, who dominated the territory before its establishment. In the Fort Laramie Treaty of 1868, the reservation included lands west of the Missouri River in South Dakota and Nebraska, including all of present-day western South Dakota. The treaty also provided rights to roam and hunt in contiguous areas of North Dakota, Montana Wyoming, and northwest Colorado.

South Dakota's at-large congressional district is the sole congressional district for the state of South Dakota. Based on area, it is the fourth largest congressional district in the nation.

Dakota Territory's at-large congressional district is an obsolete congressional district that encompassed the entire Dakota Territory prior to admission to the Union. The district elected a delegate to the United States Congress.
The history of South Dakota describes the history of the U.S. state of South Dakota over the course of several millennia, from its first inhabitants to the recent issues facing the state.
The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the U.S. state of North Dakota.
The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the U.S. state of South Dakota.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the U.S. state of North Dakota:

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to South Dakota:

The following outline traces the territorial evolution of the U.S. State of South Dakota.

The 1888–89 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, coinciding with Benjamin Harrison's victory over incumbent President Grover Cleveland. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1888 and 1889, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.
The Dakota Territorial Supreme Court was the highest court of the Dakota Territory, then an organized incorporated territory of the United States. It was the first Territorial Supreme Court in American history, and was established under Article One of the United States Constitution, with justices were appointed directly by the President of the United States. The court sat in Yankton, South Dakota, and existed from March 2, 1861, to November 2, 1889. The first court consisted of three justices: Philemon Bliss, Lorenzo P. Williston, and Joseph Lanier Williams, appointed by President Abraham Lincoln. The court heard no cases until December 3, 1867. In 1879 the court enlarged to four justices, then six in 1884, and eight in 1888.
References
- ↑ "Today in History: November 2". loc.gov. Library of Congress.