| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||

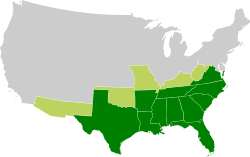
Events from the year 1861 in the United States. This year marked the beginning of the American Civil War.
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||

Events from the year 1861 in the United States. This year marked the beginning of the American Civil War.