Related Research Articles
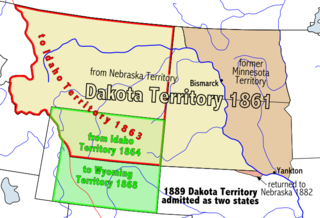
The Territory of Dakota was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 2, 1861, until November 2, 1889, when the final extent of the reduced territory was split and admitted to the Union as the states of North and South Dakota.
The Territory of Oregon was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from August 14, 1848, until February 14, 1859, when the southwestern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Oregon. Originally claimed by several countries, Spanish "El Orejón" was part of the Territorio de Nutca (1789–1795), later in the 19th century, the region was divided between the British Empire and the US in 1846. When established, the territory encompassed an area that included the current states of Oregon, Washington, and Idaho, as well as parts of Wyoming and Montana. The capital of the territory was first Oregon City, then Salem, followed briefly by Corvallis, then back to Salem, which became the state capital upon Oregon's admission to the Union.
The Territory of Washington was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 2, 1853, until November 11, 1889, when the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Washington. It was created from the portion of the Oregon Territory north of the lower Columbia River and north of the 46th parallel east of the Columbia. At its largest extent, it also included the entirety of modern Idaho and parts of Montana and Wyoming, before attaining its final boundaries in 1863.

The Territory of Wyoming was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 25, 1868, until July 10, 1890, when it was admitted to the Union as the State of Wyoming. Cheyenne was the territorial capital. The boundaries of the Wyoming Territory were identical to those of the modern State of Wyoming.

The Washington State Legislature is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Washington. It is a bicameral body, composed of the lower Washington House of Representatives, composed of 98 Representatives, and the upper Washington State Senate, with 49 Senators plus the Lieutenant Governor acting as president. The state is divided into 49 legislative districts, each of which elect one senator and two representatives.

The 51st United States Congress, referred to by some critics as the Billion Dollar Congress, was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from March 4, 1889, to March 4, 1891, during the first two years of Benjamin Harrison's presidency.

Melbourne Haddock Ford was an American politician from Michigan.

Jabez Gridley Sutherland was a politician and judge from the U.S. state of Michigan.

William Henry Calkins was an American lawyer and Civil War veteran who served four terms as a U.S. Representative from Indiana from 1877 to 1884.

The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the U.S. state of Washington.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and a topical guide to the history of the United States.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the U.S. state of Montana:

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the U.S. state of Washington:

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the U.S. state of Wyoming:
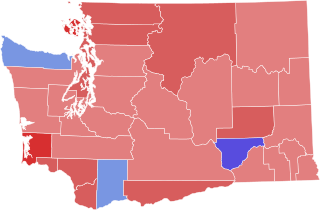
The 1889 Washington gubernatorial election took place on October 1, 1889, to elect the first Governor of Washington shortly before it was admitted as a U.S. state. Both candidates, Republican Elisha P. Ferry and Democrat Eugene Semple, previously served as Territorial Governor, a position appointed by the President of the United States.

The 1892 United States presidential election in Washington took place on November 8, 1892, as part of the 1892 United States presidential election. Voters chose four representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
References
- ↑ Lange, Greg (February 15, 2003). "Washington is admitted as the 42nd state to the United States of America on November 11, 1889". Historylink.org. Archived from the original on June 22, 2011. Retrieved November 10, 2010.