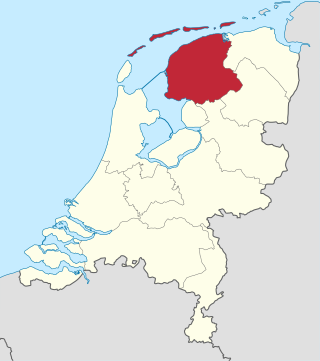
Friesland, historically and traditionally known as Frisia, named after the Frisians, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of Flevoland, northeast of North Holland, and south of the Wadden Sea. As of January 2020, the province had a population of 649,944 and a total area of 5,749 km2 (2,220 sq mi).

In the Low Countries, a stadtholder was a steward, first appointed as a medieval official and ultimately functioning as a national leader. The stadtholder was the replacement of the duke or count of a province during the Burgundian and Habsburg period.
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord and Pas-de-Calais (Artois). Also within this area were semi-independent fiefdoms, mainly ecclesiastical ones, such as Liège, Cambrai and Stavelot-Malmedy.

The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the Low Countries belonging to the Holy Roman Empire which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain and later by the Austrian Habsburgs until occupied and annexed by Revolutionary France (1794–1815).

The Duke of Brabant was the ruler of the Duchy of Brabant since 1183/1184. The title was created by the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick Barbarossa in favor of Henry I of the House of Reginar, son of Godfrey III of Leuven. The Duchy of Brabant was a feudal elevation of the existing title of landgrave of Brabant. This was an Imperial fief which was assigned to Count Henry III of Leuven shortly after the death of the preceding count of Brabant, Herman II of Lotharingia. Although the corresponding county was quite small its name was applied to the entire country under control of the dukes from the 13th century on. In 1190, after the death of Godfrey III, Henry I also became duke of Lotharingia. Formerly Lower Lotharingia, this title was now practically without territorial authority, but was borne by the later dukes of Brabant as an honorific title.

The counts of Holland ruled over the County of Holland in the Low Countries between the 10th and the 16th century.

Godfrey III was count of Louvain, landgrave of Brabant, margrave of Antwerp, and duke of Lower Lorraine from 1142 to his death.

The Burgundian Circle was an Imperial Circle of the Holy Roman Empire created in 1512 and significantly enlarged in 1548. In addition to the Free County of Burgundy, the Burgundian Circle roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., the areas now known as the Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg and adjacent parts in the French administrative region of Nord-Pas-de-Calais. For most of its history, its lands were coterminous with the holdings of the Spanish Habsburgs in the Empire.

The Duchy of Brabant, a state of the Holy Roman Empire, was established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant of 1085–1183, and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries. The Duchy comprised part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Netherlands from 1482, until it was partitioned after the Dutch revolt of 1566–1648.

The Frisii were an ancient Germanic tribe with Celtic cultural elements living in the low-lying region between the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and the River Ems.

The Duchy of Luxemburg was a state of the Holy Roman Empire, the ancestral homeland of the noble House of Luxembourg. The House of Luxembourg, now Duke of Limburg, became one of the most important political forces in the 14th century, competing against the House of Habsburg for supremacy in Central Europe. They would be the heirs to the Přemyslid dynasty in the Kingdom of Bohemia, succeeding the Kingdom of Hungary and contributing four Holy Roman Emperors until their own line of male heirs came to an end and the House of Habsburg got the pieces that the two Houses had originally agreed upon in the Treaty of Brünn in 1364.
These are lists of political office-holders in Germany.

The House of Limburg-Stirum, which adopted its name in the 12th century from the immediate county of Limburg an der Lenne in what is now Germany, is one of the oldest families in Europe. It is the eldest and only surviving branch of the House of Berg, which was among the most powerful dynasties in the region of the lower Rhine during the Middle Ages. Some historians link them to an even older dynasty, the Ezzonen, going back to the 9th century.

The Frisian Kingdom, also known as Magna Frisia, is a modern name for the post-Roman Frisian realm in Western Europe in the period when it was at its largest (650–734). This dominion was ruled by kings and emerged in the mid-7th century and probably ended with the Battle of the Boarn in 734 when the Frisians were defeated by the Frankish Empire. It lay mainly in what is now the Netherlands and – according to some 19th century authors – extended from the Zwin near Bruges in Belgium to the Weser in Germany. The center of power was the city of Utrecht.

The Dutch Republic Lion was the badge of the Union of Utrecht, the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands, and a precursor of the current coat of arms of the Kingdom the Netherlands.
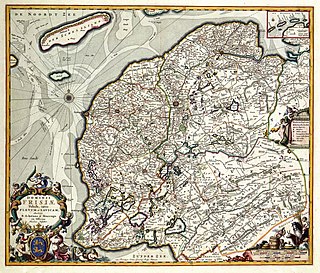
The Lordship of Frisia or Lordship of Friesland was a feudal dominion in the Netherlands. It was formed in 1498 by King Maximilian I and reformed in 1524 when Emperor Charles V conquered Frisia.
The Margraviate of Antwerp consisted since the eleventh century of the area around the cities of Antwerp and Breda.














