This article needs additional citations for verification .(September 2014) |
Prince-Bishopric of Utrecht | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1024–1528 | |||||||||||
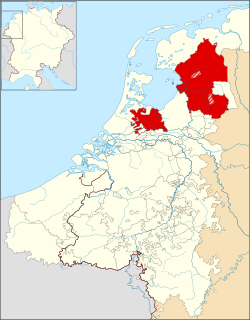 Bishopric of Utrecht c. 1350. Nedersticht is the smaller territory while Oversticht is the larger territory. | |||||||||||
| Status | State of the Holy Roman Empire | ||||||||||
| Capital | Utrecht | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Middle Dutch, Medieval Latin, Middle Low German | ||||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism (State religion) | ||||||||||
| Government | Ecclesiastical principality | ||||||||||
| Prince-bishop | |||||||||||
• (1024–1026) [a] | Adalbold II of Utrecht | ||||||||||
• (1524–1528) [b] | Henry of the Palatinate | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||||
| 959 | |||||||||||
• Established | 1024 | ||||||||||
| 1075–1122 | |||||||||||
| 1122 | |||||||||||
• Joined the Burgundian Circle | 1512 | ||||||||||
| 1502–1543 | |||||||||||
• Disestablished | 1528 | ||||||||||
• Union of Utrecht signed | 1579 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Netherlands | ||||||||||
The Bishopric of Utrecht (Dutch : Sticht Utrecht; Latin : Episcopatus Ultraiectensis) was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire in the Low Countries, in the present-day Netherlands. From 1024 to 1528, as one of the prince-bishoprics of the Holy Roman Empire, it was ruled by the bishops of Utrecht.
Contents
- History
- Background
- Foundation
- Dissolution
- Prince-bishops
- Notes
- References
- Further reading
- External links
The Prince-Bishopric of Utrecht is not to be confused with the Diocese of Utrecht, which covered a larger area. Over the areas outside the Prince-Bishopric, the bishop exercised only spiritual, not temporal, authority.
In 1528, Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor secularized the Prince-Bishopric, depriving the bishop of its secular authority.