
Bearberries are three species of dwarf shrubs in the genus Arctostaphylos. Unlike the other species of Arctostaphylos, they are adapted to Arctic and subarctic climates, and have a circumpolar distribution in northern North America, Asia and Europe.

Myrtus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Myrtaceae. It was first described by Swedish botanist Linnaeus in 1753.

Goji, goji berry, or wolfberry is the sweet fruit of either Lycium barbarum or Lycium chinense, two closely related species of boxthorn in the nightshade family, Solanaceae. L. barbarum and L. chinense fruits are similar but can be distinguished by differences in taste and sugar content.

Lycium is a genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family, Solanaceae. The genus has a disjunct distribution around the globe, with species occurring on most continents in temperate and subtropical regions. South America has the most species, followed by North America and southern Africa. There are several scattered across Europe and Asia, and one is native to Australia. Common English names for plants of this genus include box-thorn, wolfberry, and desert-thorn. Plants of the World Online currently accepts 101 species. Other estimates are of 70 to 80 species.

Lycium barbarum is a shrub native to China, with present-day range across Asia and southeast Europe. It is one of two species of boxthorn in the family Solanaceae from which the goji berry or wolfberry is harvested, the other being Lycium chinense.

Lycium chinense is one of two species of boxthorn shrub in the family Solanaceae. Along with Lycium barbarum, it produces the goji berry ("wolfberry"). Two varieties are recognized, L. chinense var. chinense and L. chinense var. potaninii. It is also known as Chinese boxthorn, Chinese matrimony-vine, Chinese teaplant, Chinese wolfberry, wolfberry, and Chinese desert-thorn.
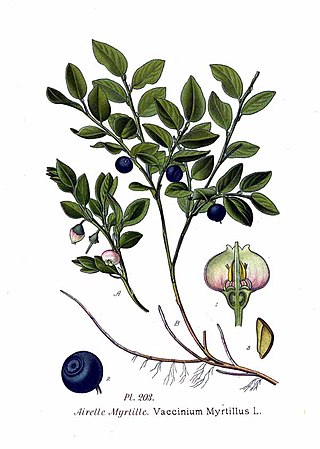
Vaccinium myrtillus or European blueberry is a holarctic species of shrub with edible fruit of blue color, known by the common names bilberry, blaeberry, wimberry, and whortleberry. It is more precisely called common bilberry or blue whortleberry to distinguish it from other Vaccinium relatives.

Commiphora gileadensis, the Arabian balsam tree, is a shrub species in the genus Commiphora growing in Saudi Arabia, Yemen, southern Oman, Sudan and in southeast Egypt where it may have been introduced. Other common names for the plant include balm of Gilead and Mecca myrrh, but this is due to historical confusion between several plants and the historically important expensive perfumes and drugs obtained from them.
Gymnosporia dhofarensis is a species of plant in the family Celastraceae and is found in Oman and Yemen. It is an intricately branched spiny shrub or small tree with its leaves arranged alternately or clustered on short shoots. The flowers have white or cream petals and the fruit are purple or red. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Lycium californicum is a spreading shrub in the nightshade family known by the common names California boxthorn and California desert-thorn.

Lycium andersonii is a species of flowering plant in the nightshade family, Solanaceae. Its common names include water-jacket, redberry desert-thorn, Anderson thornbush, Anderson's desert thorn, Anderson boxthorn, Anderson lycium, Anderson wolfberry, and squawberry.

The Arabian Peninsula coastal fog desert, also known as the Southwestern Arabian coastal xeric scrub, is desert ecoregion on the southern coasts of the Arabian Peninsula, which experiences thick fogs where visibility may be reduced to 10 metres (33 ft). It is classed as an Afrotropical fog desert

Lycium brevipes is a species of flowering plant in the nightshade family known by the common name Baja desert-thorn. It is native to northwestern Mexico and it occurs in California as far as the Sonoran Desert as well as some of the Channel Islands. It grows in the scrub of desert and coastline. It is also used as a southwestern landscaping plant. This is a bushy, spreading shrub approaching a maximum height of 4 metres (13 ft) with many long, thorny, tangled branches. The branches are lined with small, fleshy green leaves up to 1.5 centimetres (0.59 in) long and coated with glandular hairs. The inflorescence is a small cluster of tubular flowers roughly 1–2 centimetres (0.39–0.79 in) long including the calyx of sepals at the base. The lavender to nearly white corolla is funnel-shaped and has 2 to 6 lobes at the mouth. The five stamens and one style protrude from the flower. The fruit is a bright red spherical berry about a centimeter wide containing many seeds. The berries attract birds.

Lycium fremontii is a species of flowering plant in the nightshade family, Solanaceae, that is native to northwestern Mexico and the southernmost mountains and deserts of California and Arizona in the United States. It often grows in areas with alkaline soils, such as alkali flats.

Rhamnus lycioides, the black hawthorn, European buckthorn, or Mediterranean buckthorn, is a shrub up to about 1 metre tall in the buckthorn family, Rhamnaceae. It is found in the Mediterranean region, in southern Europe and northern Africa. Its scientific name lycioides refers to its resemblance to the botanical genus Lycium.

Lycium berlandieri is a species of flowering plant in the nightshade family known by the common name Berlandier's wolfberry. It is native to Mexico and the south-western United States from Arizona to Texas.

Lycium pallidum is a species of flowering plant in the nightshade family known by the common names pale wolfberry and pale desert-thorn. It is native to northern Mexico and the southwestern United States. In Mexico it can be found in Sonora, Chihuahua, Zacatecas, and San Luis Potosi. In the United States it occurs from California to Texas and as far north as Utah and Colorado.

A nabkha, nebkha or nebka is a type of sand dune. Other terms used include coppice dune and dune hummock or hummocky dune, but these more accurately refer to similar, but different, sand dune types. Authors have also used the terms phytogenic hillock, bush-mound, shrub-coppice dune, knob dune, dune tumulus, rebdou, nebbe, and takouit.
Jabal Aja Protected Area is a protected area in northern Saudi Arabia. It consists of a red granite mountain range projecting from a flatter area and is of importance for both plant and animal life. It lies at 27°30'N and 41°30'E close to the town of Ha'il and has a total area of around 200,000 hectares. Jabal Aja has been designated an Important Plant Area and an Important Bird and Biodiversity Area.
Cyphostemma ternatum is a perennial climbing herb that grows up to 2m. It is edible and distributed throughout Northeast Africa to South Arabia. ternatum in Latin means "arranged in threes" and alludes to the arrangement of the leaves.
















