
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera, in the superorder Holometabola. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 described species, is the largest of all orders, constituting almost 40% of described insects and 25% of all known animal species; new species are discovered frequently, with estimates suggesting that there are between 0.9 and 2.1 million total species. Found in almost every habitat except the sea and the polar regions, they interact with their ecosystems in several ways: beetles often feed on plants and fungi, break down animal and plant debris, and eat other invertebrates. Some species are serious agricultural pests, such as the Colorado potato beetle, while others such as Coccinellidae eat aphids, scale insects, thrips, and other plant-sucking insects that damage crops. Some others also have unusual characteristics, such as fireflies, which use a light-emitting organ for mating and communication purposes.

Bookworm is a general name for any insect that is said to bore through books.

A woodworm is the wood-eating larva of many species of beetle. It is also a generic description given to the infestation of a wooden item by these larvae.

Histeridae is a family of beetles commonly known as clown beetles or hister beetles. This very diverse group of beetles contains 3,900 species found worldwide. They can be easily identified by their shortened elytra that leaves two of the seven tergites exposed, and their geniculate (elbowed) antennae with clubbed ends. These predatory feeders are most active at night and will fake death if they feel threatened. This family of beetles will occupy almost any kind of niche throughout the world. Hister beetles have proved useful during forensic investigations to help in time of death estimation. Also, certain species are used in the control of livestock pests that infest dung and to control houseflies. Because they are predacious and will even eat other hister beetles, they must be isolated when collected.

Trogidae, sometimes called hide beetles, is a family of beetles with a distinctive warty or bumpy appearance. Found worldwide, the family includes about 300 species contained in four or five genera.

Dermestidae are a family of Coleoptera that are commonly referred to as skin beetles. Other common names include larder beetle, hide or leather beetles, carpet beetles, and khapra beetles. There are over 1,800 species described.

Frass refers loosely to the more or less solid excreta of insects, and to certain other related matter.

Powderpost beetles are a group of seventy species of woodboring beetles classified in the insect subfamily Lyctinae. These beetles, along with spider beetles, death watch beetles, common furniture beetles, skin beetles, and others, make up the superfamily Bostrichoidea. While most woodborers have a large prothorax, powderpost beetles do not, making their heads more visible. In addition to this, their antennae have two-jointed clubs. They are considered pests and attack deciduous trees, over time reducing the wood to a powdery dust. The damage caused by longhorn beetles is often confused with that of powderpost beetles, but the two groups are unrelated. The larvae of the Cerambycidae are white, straight and generally flat-headed, whereas those of the Bostrichidae are white and C-shaped.

Lyctus linearis is a species of beetle in the family Bostrichidae. It is a member of the subfamily Lyctinae, the powderpost beetles. It was originally native to tropical regions, but it can now be found worldwide. It is a common pest of wood and wood products and it is transported around the world with them. It is most common in deciduous tree woods.

The term woodboring beetle encompasses many species and families of beetles whose larval or adult forms eat and destroy wood. In the woodworking industry, larval stages of some are sometimes referred to as woodworms. The three most species-rich families of woodboring beetles are longhorn beetles, bark beetles and weevils, and metallic flat-headed borers. Woodboring is thought to be the ancestral ecology of beetles, and bores made by beetles in fossil wood extend back to the earliest fossil record of beetles in the Early Permian (Asselian), around 295-300 million years ago.

Dermestes lardarius, commonly known as the larder beetle or moisture bug, is a species of beetle in the family Dermestidae, the skin beetles. It is found worldwide. It is a common pest of households and storage facilities ("larders") in much of the world. It eats animal products, such as dried meats and fish, pet food, skins and hides, feathers, cheese, and museum specimens such as dried insects. It may also eat plant material that is high in protein, such as grain.
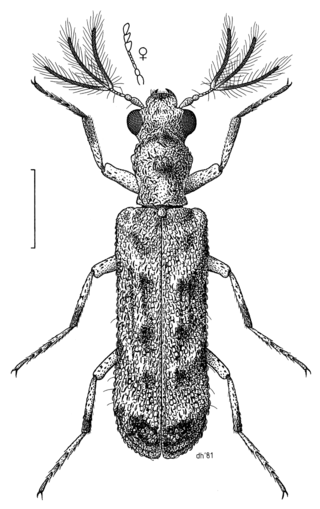
The Bostrichidae are a family of beetles with more than 700 described species. They are commonly called auger beetles, false powderpost beetles, or horned powderpost beetles. The head of most auger beetles cannot be seen from above, as it is downwardly directed and hidden by the thorax. Exceptions are the powderpost beetles, and members of the subfamily Psoinae.

Coccinellidae is a widespread family of small beetles. They are commonly known as ladybugs in North America and ladybirds in the United Kingdom; "lady" refers to mother Mary. Entomologists use the names ladybird beetles or lady beetles to avoid confusion with true bugs. The more than 6,000 described species have a global distribution and are found in a variety of habitats. They are oval beetles with a domed back and flat underside. Many of the species have conspicuous aposematic (warning) colours and patterns, such as red with black spots, that warn potential predators that they taste bad.

Tenebroides mauritanicus, commonly known as the cadelle, is a species of beetle in the family Trogossitidae. It is a common cosmopolitan pest in storehouses and granaries.

Mezium americanum, the American spider beetle or black spider beetle, is a species of beetle in the subfamily Ptininae, the spider beetles. These are sometimes mistaken for spiders or mites because of their rounded abdomens and long legs. It has a cosmopolitan distribution, but it is an exotic species in Australia.

Lyctus is a genus of powder-post beetles in the family Bostrichidae, being present on all continents except Antarctica.

Acanthinodera is a genus of longhorned beetles in the family Cerambycidae. It is monotypic, being represented by the single species Acanthinodera cumingii. It is the largest species of beetle in Chile. The beetle is endemic to central Chile and can be found from IV Coquimbo Region to IX La Araucanía Region.

Lyctus cavicollis, known generally as the shiny powderpost beetle or western lyctus beetle, is a species of powder-post beetle in the family Bostrichidae. It is found in Australia, Europe and Northern Asia, and North America.

Lyctus africanus, the African powderpost beetle, is a species of powder-post beetle in the family Bostrichidae. It is found in Africa, Europe and Northern Asia, North America, and Southern Asia.


















