
A chatbot is a software application or web interface that is designed to mimic human conversation through text or voice interactions. Modern chatbots are typically online and use generative artificial intelligence systems that are capable of maintaining a conversation with a user in natural language and simulating the way a human would behave as a conversational partner. Such chatbots often use deep learning and natural language processing, but simpler chatbots have existed for decades.
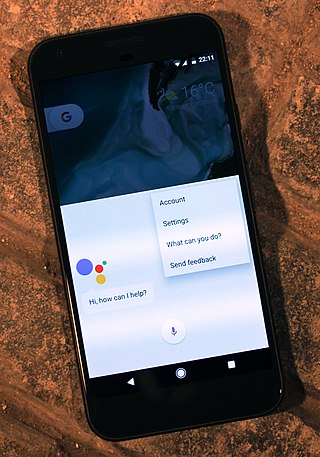
A virtual assistant (VA) is a software agent that can perform a range of tasks or services for a user based on user input such as commands or questions, including verbal ones. Such technologies often incorporate chatbot capabilities to simulate human conversation, such as via online chat, to facilitate interaction with their users. The interaction may be via text, graphical interface, or voice - as some virtual assistants are able to interpret human speech and respond via synthesized voices.

Siri is the digital assistant that is part of Apple Inc.'s iOS, iPadOS, watchOS, macOS, tvOS, audioOS, and visionOS operating systems. It uses voice queries, gesture based control, focus-tracking and a natural-language user interface to answer questions, make recommendations, and perform actions by delegating requests to a set of Internet services. With continued use, it adapts to users' individual language usages, searches, and preferences, returning individualized results.

Cleverbot is a chatterbot web application. It was created by British AI scientist Rollo Carpenter and launched in October 2008. It was preceded by Jabberwacky, a chatbot project that began in 1988 and went online in 1997. In its first decade, Cleverbot held several thousand conversations with Carpenter and his associates. Since launching on the web, the number of conversations held has exceeded 150 million. Besides the web application, Cleverbot is also available as an iOS, Android, and Windows Phone app.

Messenger, also known as Facebook Messenger, is an American proprietary instant messaging app and platform developed by Meta Platforms. Originally developed as Facebook Chat in 2008, the company revamped its messaging service in 2010, released standalone iOS and Android apps in 2011, and released standalone Facebook Portal hardware for Messenger calling in 2018. In April 2015, Facebook launched a dedicated website interface, Messenger.com, and separated the messaging functionality from the main Facebook app, allowing users to use the web interface or download one of the standalone apps. In April 2020, Facebook released a Messenger desktop app for Windows and macOS.

Google Now was a feature of Google Search of the Google app for Android and iOS. Google Now proactively delivered information to users to predict information they might need in the form of informational cards. Google Now branding is no longer used, but the functionality continues in the Google app and its discover tab.

Maluuba is a Canadian technology company conducting research in artificial intelligence and language understanding. Founded in 2011, the company was acquired by Microsoft in 2017.
Kuki is an embodied AI bot designed to befriend humans in the metaverse. Formerly known as Mitsuku, Kuki is a chatbot created from Pandorabots AIML technology by Steve Worswick. It is a five-time winner of a Turing Test competition called the Loebner Prize, for which it holds a world record. Kuki is available to chat via an online portal, and on Facebook Messenger, Twitch group chat, Telegram, Kik Messenger, Discord, and was available on Skype, but was removed by its developer. The AI also has accounts on Instagram, TikTok, YouTube, and Twitter, as well as a game on Roblox.

Cortana is a discontinued virtual assistant developed by Microsoft, that used the Bing search engine to perform tasks such as setting reminders and answering questions for users.
Viv is a discontinued intelligent personal assistant created by the developers of Siri.

The Google Assistant is a virtual assistant software application developed by Google that is primarily available on mobile and home automation devices. Based on artificial intelligence, The Google Assistant can engage in two-way conversations, unlike the company's previous virtual assistant, Google Now.

Google Allo was an instant messaging mobile app by Google for the Android and iOS mobile operating systems, with a web client available in some web browsers. It closed on March 12, 2019.
Amazon Alexa or Alexa is a virtual assistant technology largely based on a Polish speech synthesizer named Ivona, bought by Amazon in 2013. It was first used in the Amazon Echo smart speaker and the Echo Dot, Echo Studio and Amazon Tap speakers developed by Amazon Lab126. It is capable of natural language processing (NLP) for tasks such as voice interaction, music playback, creating to-do lists, setting alarms, streaming podcasts, playing audiobooks, providing weather, traffic, sports, other real-time information and news. Alexa can also control several smart devices as a home automation system. Alexa capabilities may be extended by installing "skills" such as weather programs and audio features. It performs these tasks using automatic speech recognition, NLP, and other forms of weak AI.

Witlingo is a B2B Software as a Service (SaaS) company that enables businesses and organization of all sizes to use the latest innovations in Human Language Technology and Conversational AI, such Speech recognition, Natural Language Processing, IVR, Virtual Assistant apps on Smartphone platforms(iOS and Android), Chatbots, and Digital audio, to deeply engage with their communities.
Alice is a Russian intelligent personal assistant for Android, iOS and Windows operating systems and Yandex's own devices developed by Yandex. Alice was officially introduced on 10 October 2017. Aside from common tasks, such as internet search or weather forecasts, it can also run applications and chit-chat. Alice is also the virtual assistant used for the Yandex Station smart speaker.

Haptik is an Indian enterprise conversational AI platform founded in August 2013, and acquired by Reliance Industries Limited in 2019. The company develops technology to enable enterprises to build conversational AI systems that allow users to converse with applications and electronic devices in free-format, natural language, using speech or text. The company has been accorded numerous accolades including the Frost & Sullivan Award, NASSCOM's Al Game Changer Award, and serves Fortune 500 brands globally in industries such as financial, insurance, healthcare, technology and communications.

Artificial intelligence (AI) has a range of uses in government. It can be used to further public policy objectives, as well as assist the public to interact with the government. According to the Harvard Business Review, "Applications of artificial intelligence to the public sector are broad and growing, with early experiments taking place around the world." Hila Mehr from the Ash Center for Democratic Governance and Innovation at Harvard University notes that AI in government is not new, with postal services using machine methods in the late 1990s to recognise handwriting on envelopes to automatically route letters. The use of AI in government comes with significant benefits, including efficiencies resulting in cost savings, and reducing the opportunities for corruption. However, it also carries risks.

Microsoft Copilot is a chatbot developed by Microsoft. Based on a large language model, it was launched as Bing Chat on February 7, 2023, as a built-in feature for Microsoft Bing and Microsoft Edge, and is Microsoft’s primary replacement for the discontinued Cortana.
Comparison of user features of chatbots refers to a comparison of the general user features of major chatbot applications or web interfaces, in a narrative format. It is a comparison of basic roles and the most prominent features. It does not encompass a full exhaustive comparison or description of all technical details of all chatbots. It also includes the most important features of the chatbots origins, historical development, and role.













